Gravity in Space: A Different Universal Experience
Understanding Downward and Upward Directions
The concepts of downward and upward directions play a fundamental role in our perception of the physical world and are key elements in various scientific, navigational, and everyday contexts. Let's delve into what these directions mean and their significance in different aspects of life.
Defining Downward Direction
The downward direction is commonly associated with the force of gravity, which pulls objects toward the center of the Earth or another massive body. This direction is typically perceived as the opposite of "up" or the direction in which objects fall naturally when released. Gravity's influence is profound and affects everything from how we walk on the ground to the behavior of celestial bodies in space.
In physics and engineering, the downward direction often serves as a reference point for analyzing forces, pressures, and motions. For instance, when considering the dynamics of a falling object, its velocity, acceleration, and impact are all influenced by the force pulling it downward.
Exploring Upward Direction
Conversely, the upward direction is the opposite of downward and is often associated with forces that counteract gravity or movements against gravity. When objects move upward, they go against the natural gravitational pull, requiring energy input to overcome this force.
In various fields, the upward direction symbolizes growth, progress, and aspiration. For instance, in aviation, spacecraft launch, or skyscraper construction, moving upward represents achieving new heights and overcoming challenges.
Significance in Navigation and Orientation
Understanding these directional concepts is crucial for navigation and orientation. In geographical terms, maps and compasses use cardinal directions like north, south, east, and west, which are based on the Earth's magnetic poles. These directions help travelers and explorers find their way and determine positions relative to landmarks or coordinates.
In everyday life, we encounter the significance of these directions in simple tasks such as climbing stairs (moving upward) or objects falling to the ground (moving downward). These actions highlight the constant interaction between gravitational forces and our physical movements.
Symbolism and Metaphorical Meanings
Beyond their physical implications, downward and upward directions often carry metaphorical or symbolic meanings. Downward might symbolize descent, introspection, or decline, while upward can signify progress, enlightenment, or achievement. These symbolic interpretations are prevalent in literature, art, and cultural expressions worldwide.
Conclusion
In essence, the concepts of downward and upward directions are fundamental to our understanding of the world around us. From the laws of physics to our everyday experiences, these directions shape how we perceive motion, forces, and spatial relationships. Embracing the meanings and significance of these directions enriches our knowledge and appreciation of the intricate workings of the universe.
Exploring the Concept of Gravitation: Understanding the Force That Shapes the Universe
Gravitation, often simply referred to as gravity, is one of the fundamental forces governing the behavior of objects in the universe. This force, first described by Sir Isaac Newton and later refined by Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, plays a pivotal role in shaping celestial bodies, planetary orbits, and even the structure of galaxies. Let's delve deeper into what gravitation means and its significance in the grand scheme of physics and cosmology.
Understanding Gravitation
Gravitation is the force of attraction that exists between all objects with mass or energy. This force is universal, meaning it affects every particle, planet, star, and galaxy in the cosmos. The magnitude of gravitational attraction depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. The larger the masses and the closer the objects, the stronger the gravitational force.
According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the force of gravity between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This mathematical relationship elegantly explains how gravity operates on a macroscopic scale, influencing the motion of celestial bodies like planets orbiting stars or moons orbiting planets.
Significance in Planetary Motion
Gravitation is the driving force behind planetary motion within our solar system and beyond. Planets orbit stars like the Sun due to the gravitational pull between them. This orbital motion follows elliptical paths, with the star at one of the foci of the ellipse. The laws of gravitation and motion formulated by Newton provided the framework to accurately predict and describe these planetary orbits, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos.
Einstein's Theory of General Relativity
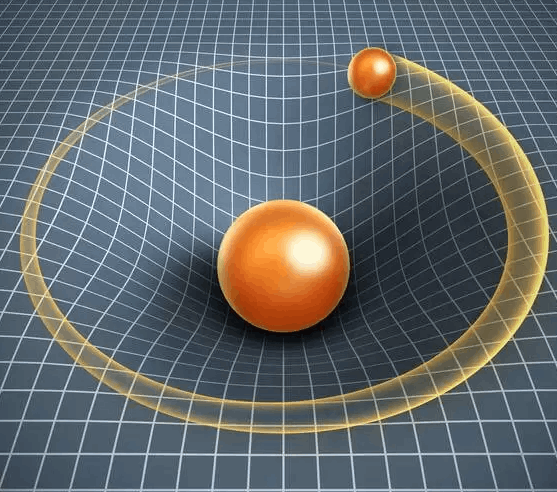
While Newtonian gravity sufficed for most practical purposes, it was Albert Einstein's revolutionary theory of general relativity that provided a deeper understanding of gravity's nature. According to general relativity, gravity is not merely a force but rather a curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. Massive objects like stars and planets create a "gravity well" in the fabric of spacetime, and other objects, including light, follow curved paths around these wells.
General relativity also predicted phenomena like gravitational time dilation, gravitational lensing, and the bending of starlight near massive objects. These predictions have been experimentally verified and have led to groundbreaking discoveries in astrophysics and cosmology.
Implications for Cosmology
Gravitation plays a central role in cosmology, the study of the origin and evolution of the universe. The gravitational attraction between galaxies influences their clustering and distribution in the vast cosmic web. Dark matter, a mysterious substance that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, is believed to interact primarily through gravity, contributing significantly to the gravitational pull in galaxies and galactic clusters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gravitation is a fundamental force that governs the dynamics of celestial bodies, shapes the structure of the universe, and underpins our understanding of cosmology. From Newton's elegant laws to Einstein's profound insights into spacetime curvature, the concept of gravitation has been pivotal in advancing human knowledge of the cosmos. Its exploration continues to fuel scientific inquiry and inspire new discoveries about the nature of our vast and wondrous universe.
Understanding Gravity in Space: The Invisible Force That Shapes the Cosmos
Gravity is a fundamental force of nature that influences the behavior of objects in space, shaping the structure and dynamics of the cosmos. In the vacuum of space, where there is no air or atmosphere, gravity plays a crucial role in governing the motion of celestial bodies and the formation of galaxies, stars, planets, and other cosmic structures. Let's delve into what gravity is in space and how it affects the universe on a grand scale.
The Nature of Gravity
Gravity is the force of attraction that exists between all objects with mass. It is a fundamental interaction that acts over long distances and is responsible for phenomena like the Earth's gravitational pull on objects near its surface. In space, gravity continues to exert its influence, albeit in a different environment devoid of air resistance or atmospheric effects.
Effects of Gravity in Space
- Orbital Motion: One of the most noticeable effects of gravity in space is orbital motion. Celestial bodies such as planets, moons, and satellites orbit larger objects like stars or planets due to gravitational attraction. This motion follows elliptical paths governed by Newton's laws of gravitation and motion, ensuring stable and predictable orbits.
- Formation of Cosmic Structures: Gravity plays a vital role in the formation and evolution of cosmic structures. Gravity acts as the sculptor of the universe, causing matter to clump together under its influence. Over time, these gravitational interactions lead to the formation of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and superclusters, where billions of stars and planetary systems reside.
- Black Holes: In regions of extremely concentrated mass, such as the remnants of massive stars after a supernova explosion, gravity becomes incredibly intense. These objects, known as black holes, exhibit such strong gravitational pull that not even light can escape from their vicinity. Black holes represent extreme examples of how gravity shapes space and time itself, as described by Einstein's general theory of relativity.
Challenges and Mysteries
While our understanding of gravity in space has advanced significantly through scientific observations and theories like general relativity, there are still mysteries and challenges to explore. Dark matter, an invisible and mysterious substance that does not emit or interact with light, exerts gravitational effects on visible matter and plays a crucial role in galactic dynamics. Understanding the nature of dark matter and its gravitational influence remains a forefront area of research in astrophysics.
Conclusion
Gravity in space is a fundamental force that governs the dynamics and structure of the cosmos. From planetary orbits to the formation of galaxies and the enigmatic realms of black holes, gravity's influence is pervasive and profound. Continued scientific exploration and observation, coupled with theoretical advancements, deepen our understanding of this invisible force and its role in shaping the vast and wondrous universe we inhabit.
cover photo source: https://seyfullahdemir.com/kutlecekim-uzay-iliskisi/
1.photo source: https://www.chip.com.tr/guncel/ok-isareti-nasil-yapilir-klavyede-ok-isareti-yapilisi_283.html
2.photo source: https://eksiseyler.com/kutlecekim-kuvvetinin-bildigimiz-gibi-bir-sey-olmadiginin-saglam-bir-aciklamasi
3.photo source : https://www.muhendisbeyinler.net/newtonun-kutle-cekim-kuvveti-dogru-mu/
4.photo source : https://www.frmtr.com/sinavlar-ve-hazirlik-osym/7710134-yercekimi-nedir.html