Abstract
Abstract:
Butterflies, with their vibrant colors and graceful flight, have long captured the imagination of humans. This comprehensive article delves into every aspect of these fascinating creatures, exploring their biology, ecology, behavior, cultural significance, conservation status, and more. From their miraculous metamorphosis to their role as pollinators and indicators of environmental health, butterflies hold a unique place in the natural world. Through this in-depth examination, we aim to deepen our understanding and appreciation of these enchanting insects.
1. Introduction:
Butterflies, members of the order Lepidoptera, are among the most captivating creatures in the insect world. With their intricate wing patterns and delicate flight, they have intrigued humans for centuries. This article provides a comprehensive overview of butterflies, covering their taxonomy, anatomy, and evolutionary history.
2. Taxonomy and Classification:
Butterflies belong to the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Within this order, they are further classified into various families, genera, and species. This section explores the taxonomy of butterflies and highlights the diversity within this insect group.
3. Anatomy and Morphology:
The anatomy of butterflies is finely adapted to their aerial lifestyle. From their wing structure to their specialized mouthparts for feeding, this section examines the physical characteristics that distinguish butterflies from other insects.
4. Life Cycle:
One of the most remarkable aspects of butterflies is their life cycle, which includes four distinct stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (chrysalis), and adult. This section details each stage of the life cycle and explores the biological processes that drive metamorphosis.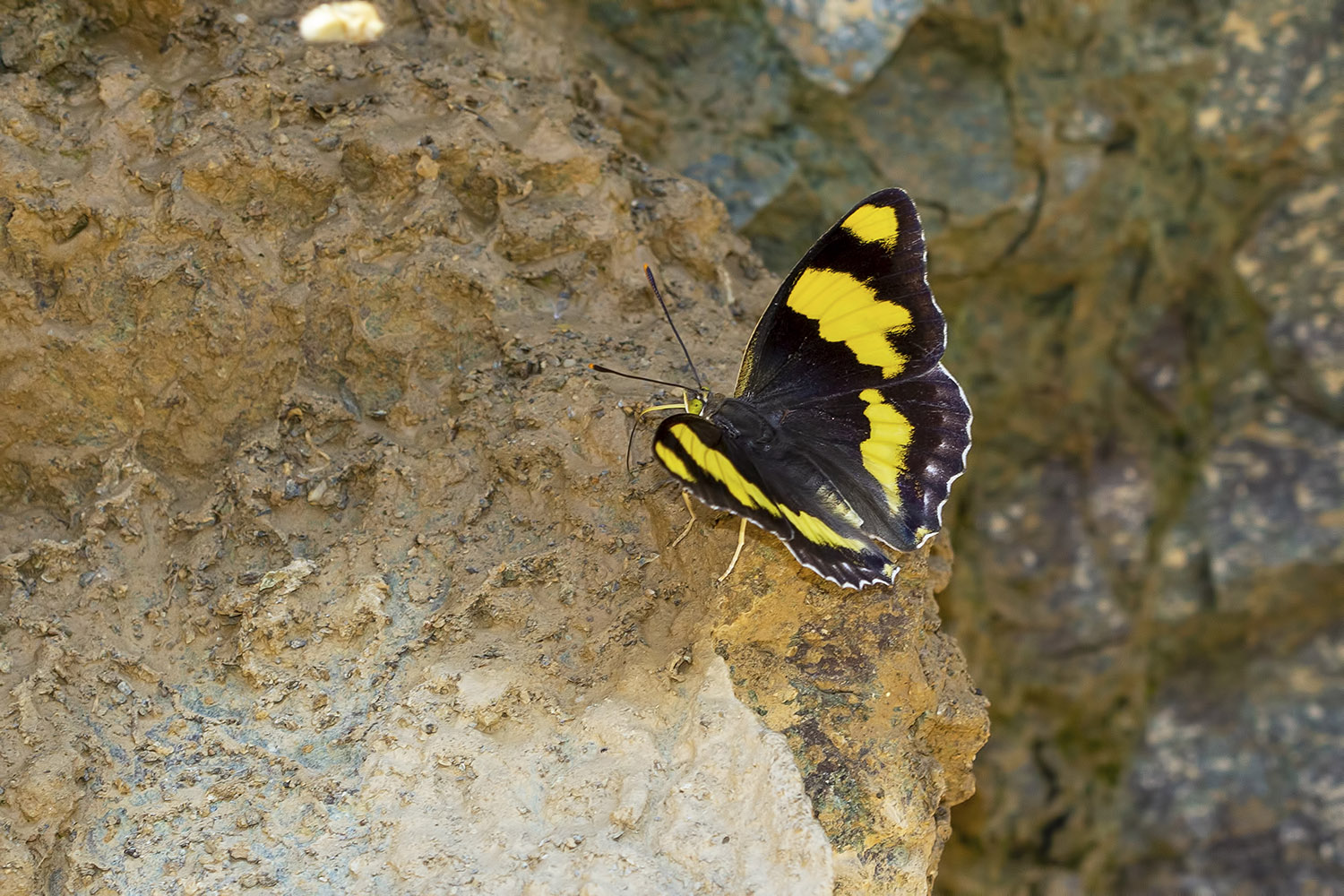
5. Behavior and Ecology:
Butterflies exhibit a wide range of behaviors, from mating rituals to migration patterns. This section explores the behavioral ecology of butterflies, including their feeding habits, territoriality, and interactions with other organisms.
6. Reproduction and Mating Strategies:
Reproduction is a crucial aspect of butterfly biology, and different species employ various mating strategies to ensure reproductive success. This section discusses the reproductive behaviors of butterflies, including courtship displays and mate selection.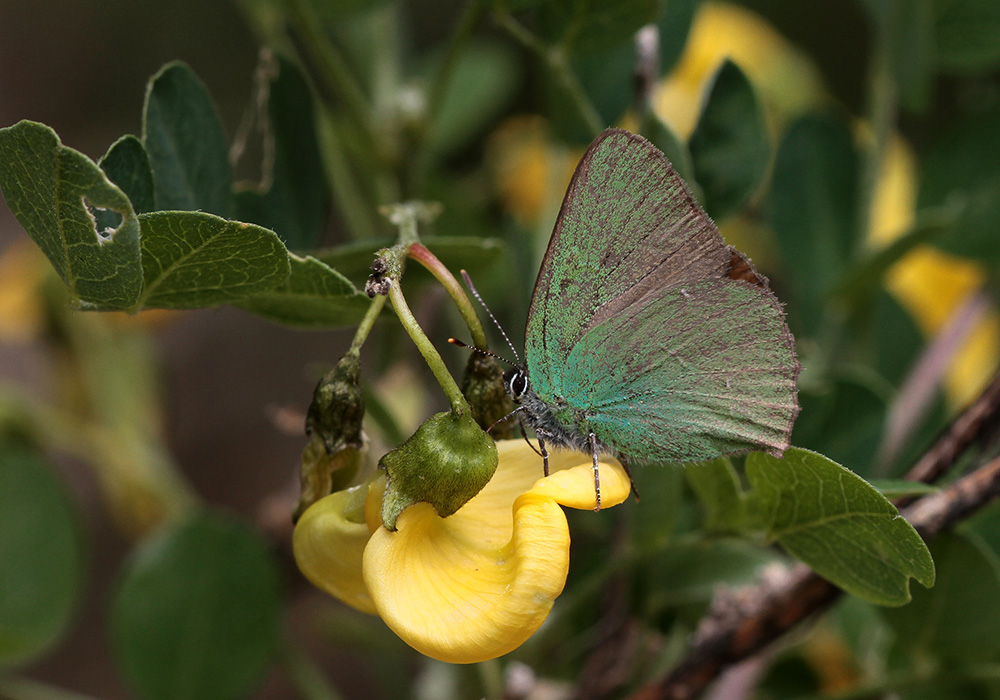
7. Butterfly Conservation:
Despite their beauty, butterflies face numerous threats, including habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use. This section examines the conservation challenges facing butterflies and highlights efforts to protect and restore their habitats.
8. Cultural Significance:
Butterflies have held symbolic significance in cultures around the world for centuries. This section explores the cultural and spiritual significance of butterflies in art, literature, and folklore.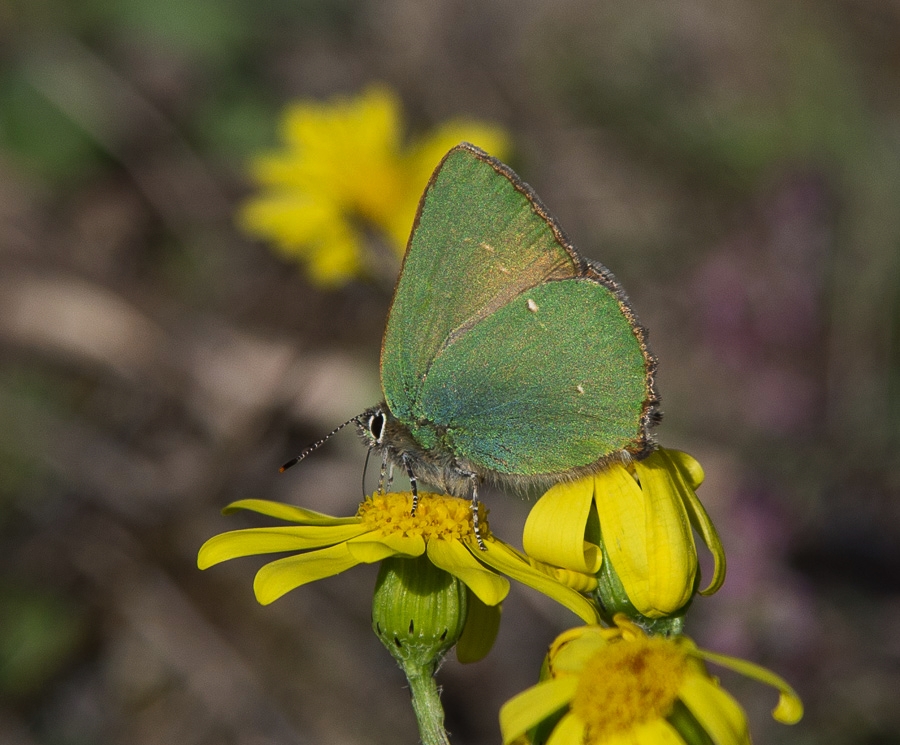
9. Butterfly Gardening:
Creating butterfly-friendly gardens is a popular pastime for nature enthusiasts and conservationists alike. This section provides practical tips for designing gardens that attract and support butterflies.
10. Conclusion:
Butterflies are more than just beautiful insects; they are vital components of ecosystems and important indicators of environmental health. By understanding and appreciating the complexities of butterfly biology and ecology, we can work together to ensure the conservation of these enchanting creatures for future generations.
Kaynakça
- ^ Mason, C. W. (1927). "Structural Colors in Insects. II". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 31 (3): 321-354. doi:10.1021/j150273a001.
- ^ Vukusic, P.; J. R. Sambles; H. Ghiradella (2000). "Optical Classification of Microstructure in Butterfly Wing-scales". Photonics Science News. 6: 61-66.
- ^ Prum, R.; Quinn, T.; Torres, R. (February 2006). "Anatomically Diverse Butterfly Scales all Produce Structural Colours by Coherent Scattering". The Journal of Experimental Biology. 209 (Pt 4): 748-65. doi:10.1242/jeb.02051
 . ISSN 0022-0949. PMID 16449568.
. ISSN 0022-0949. PMID 16449568. - ^ a b c d e Gullan, P. J.; Cranston, P. S. (2014). The Insects: An Outline of Entomology (5 bas.). Wiley. ss. 523-524. ISBN 978-1-118-84616-2. 10 Haziran 2016 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 8 Ocak 2016.
- ^ Herrera, Carlos M. (1992). "Activity Pattern and Thermal Biology of a Day-Flying Hawkmoth (Macroglossum stellatarum) under Mediterranean summer conditions". Ecological Entomology. 17: 52-56. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2311.1992.tb01038.x. hdl:10261/44693
- ^ "Butterflies and Moths (Order Lepidoptera)". Amateur Entomologists' Society. 28 Eylül 2015 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 13 Eylül 2015.
- ^ Traut, W.; Marec, F. (August 1997). "Sex Chromosome Differentiation in Some Species of Lepidoptera (Insecta)". Chromosome Research. 5 (5): 283-91. doi:10.1023/B:CHRO.0000038758.08263.c3. ISSN 0967-3849. PMID 9292232.
- ^ a b Williams, Ernest; Adams, James; Snyder, John. "Frequently Asked Questions". The Lepidopterists' Society. 13 Mayıs 2015 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 9 Eylül 2015.
- ^ "Global Distribution". Monarch Lab. 6 Ekim 2015 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 9 Eylül 2015.
- ^ "Chill Turns Monarchs North; Cold Weather Flips Butterflies' Migratory Path". Science News. 183 (6). 23 Mart 2013. 2 Ekim 2013 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 5 Ağustos 2014.
- ^ Pyle, Robert Michael (1981). National Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Butterflies. Alfred A. Knopf. ss. 712-713. ISBN 978-0-394-51914-2.