Plastic Recycling Technology: Advancements and Challenges
Plastic recycling technology plays a vital role in addressing the growing concern of plastic waste and its impact on the environment. This paper delves into the various aspects of plastic recycling technology, exploring its advancements, challenges, and potential solutions. It examines the different methods employed in plastic recycling, including mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and pyrolysis. Furthermore, the paper discusses the benefits of plastic recycling, such as resource conservation and waste reduction, while also addressing the limitations and obstacles faced by the industry. By understanding the current state of plastic recycling technology, we can identify opportunities for improvement and promote sustainable practices for a cleaner future.
Introduction
Plastic waste has become a global environmental issue due to its non-biodegradable nature and its adverse effects on ecosystems. Plastic recycling technology has emerged as a crucial approach to mitigate this problem. This section provides an overview of the significance of plastic recycling and outlines the objectives of the paper.
Plastic Recycling Methods
1.Mechanical Recycling
Mechanical recycling is one of the most commonly used methods in plastic recycling. It involves the collection, sorting, cleaning, and processing of plastic waste into reusable plastic pellets. This section explores the different steps involved in mechanical recycling and discusses the challenges associated with contamination and quality control.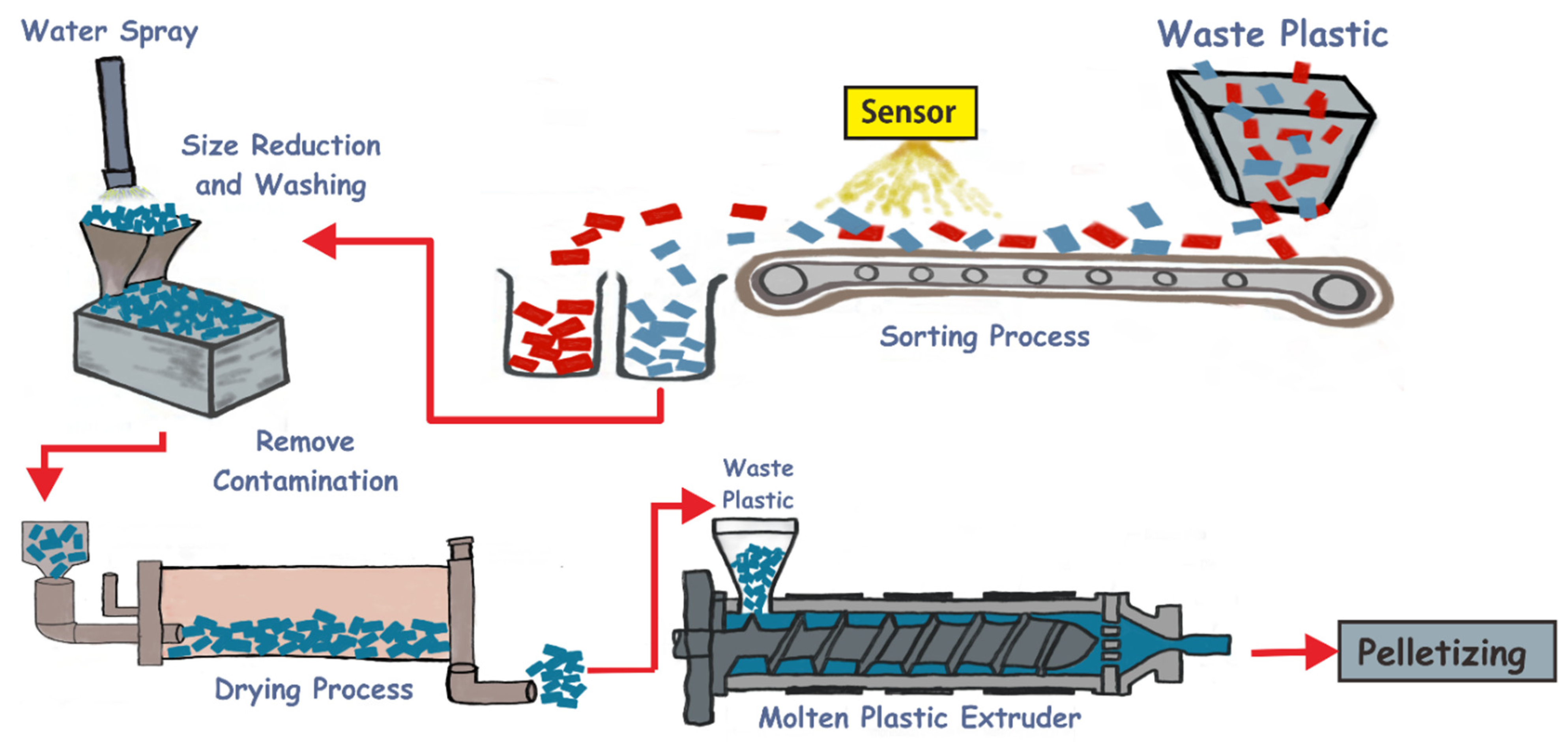
2. Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling offers an alternative approach by converting plastic waste into its original monomers or other valuable chemicals. This section delves into the various chemical recycling techniques, such as depolymerization, dissolution, and gasification, highlighting their potential benefits and limitations. It also examines the progress made in industrial-scale chemical recycling and the role of catalysts in enhancing the efficiency of these processes.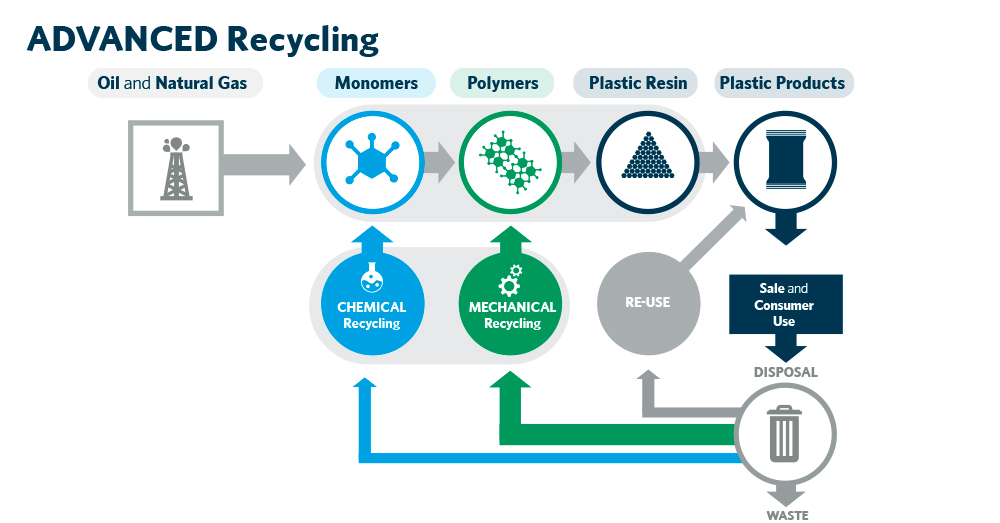
3. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermal degradation process that breaks down plastic waste into its constituent components, including oil, gas, and char. This section explores the different types of pyrolysis, such as slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis, and microwave pyrolysis, highlighting their advantages and challenges. It also discusses the potential applications of pyrolysis products, such as biofuels and chemical feedstocks.
4.Benefits of Plastic Recycling
Plastic recycling technology offers numerous benefits to the environment, economy, and society as a whole. This section examines the advantages of plastic recycling, including resource conservation, energy savings, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and job creation. It also discusses the potential for a circular economy approach in which recycled plastics are used as feedstock for new products, minimizing the demand for virgin plastics.
5.Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, plastic recycling technology faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. This section identifies and discusses the key obstacles, such as the complexity of plastic waste streams, lack of infrastructure, technological limitations, and the economic viability of recycling processes. It also explores potential solutions to these challenges, such as improved collection systems, advancements in sorting and recycling technologies, and policy interventions.
Conclusion
Plastic recycling technology is a critical tool in addressing the mounting issue of plastic waste. By adopting advanced recycling methods and overcoming the associated challenges, we can create a more sustainable and circular plastic economy. This paper has provided an overview of the different plastic recycling methods, highlighting their benefits and limitations. It has also discussed the obstacles faced by the industry and explored potential solutions. As technology continues to advance, further research and collaboration are essential to optimize plastic recycling processes and promote a cleaner and greener future.










