The Evolving Landscape of Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies, and Institutional Adoption
The Evolving Landscape of Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies, and Institutional Adoption
Introduction
The blockchain industry has undergone remarkable evolution, catalyzing the emergence of new cryptocurrencies and capturing the attention of traditional financial institutions like Wall Street and global entities such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF). This article explores the dynamics driving these changes, examining the intersection of technology, finance, and regulation in shaping the future of digital assets.
Blockchain Technology: A Foundation for Innovation
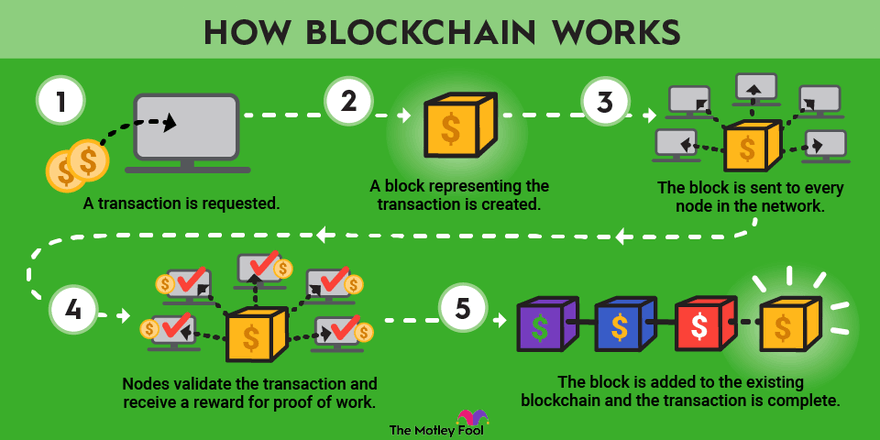
Blockchain technology, originally conceived as the underlying infrastructure for Bitcoin, has transcended its roots to offer a decentralized and secure framework for various applications.
Smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent just a few of the innovative use cases enabled by blockchain technology.
The transparency, immutability, and efficiency of blockchain systems have garnered interest across industries, from supply chain management to voting systems.
The Rise of New Cryptocurrencies: Beyond Bitcoin
While Bitcoin remains the flagship cryptocurrency, the market has witnessed the proliferation of alternative digital assets, known as altcoins. Ethereum, with its programmable smart contract functionality, has become a prominent platform for decentralized applications (dApps) and token issuance.
Other notable cryptocurrencies include Ripple (XRP), Litecoin (LTC), and Cardano (ADA), each offering unique features and use cases within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
The emergence of stablecoins, pegged to fiat currencies or commodities, has provided a bridge between traditional finance and the digital asset space, offering stability and liquidity for users and investors.
Wall Street's Engagement with Cryptocurrencies
Initially met with skepticism, Wall Street has increasingly embraced cryptocurrencies as a legitimate asset class, driven by growing investor demand and the potential for lucrative returns. Major financial institutions, including Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and Morgan Stanley, have established dedicated cryptocurrency trading desks or invested in blockchain-related ventures.
The introduction of Bitcoin futures contracts on regulated exchanges has facilitated institutional participation in cryptocurrency markets, providing avenues for hedging and speculation. However, regulatory uncertainty, security concerns, and volatility remain significant barriers to broader institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies.
The International Monetary Fund's Perspective
The IMF, tasked with promoting global monetary cooperation and stability, has recognized the transformative potential of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. In a 2022 report, the IMF highlighted the role of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) in fostering financial inclusion, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing cross-border payments.
While acknowledging the benefits of innovation, the IMF has also emphasized the importance of regulatory frameworks to mitigate risks associated with money laundering, terrorism financing, and consumer protection. Collaborative efforts between central banks, international organizations, and private sector stakeholders are essential to harnessing the benefits of digital currencies while addressing regulatory and governance challenges.
Conclusion
The convergence of blockchain technology, new cryptocurrencies, Wall Street involvement, and IMF oversight underscores the dynamic evolution of the digital asset ecosystem.
As innovation continues to drive progress, stakeholders must navigate regulatory complexities and foster collaboration to realize the full potential of blockchain and cryptocurrencies in shaping the future of finance.
References
1. Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
2. Buterin, V. (2013). Ethereum: A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform.
https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/
3. World Economic Forum. (2021). Central Bank Digital Currencies: Policy Implications, Considerations, and Practical Guidance. https://www.weforum.org/reports/central-bank-digital-currencies-policy-implications-considerations-and-practical-guidance
4. International Monetary Fund. (2022). The Rise of Digital Money. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/Departmental-Papers-Policy-Papers/Issues/2022/11/09/The-Rise-of-Digital-Money-50237