The Vietnam War: A Complex Conflict and Its Detractors
The Vietnam War, a protracted conflict that spanned the 1950s to the 1970s, remains a deeply divisive chapter in global history. Its roots are complex, intertwined with the broader Cold War dynamics, and its legacy continues to shape political and social discourse. This article explores the underlying causes of the war and the perspectives of those who opposed U.S. involvement.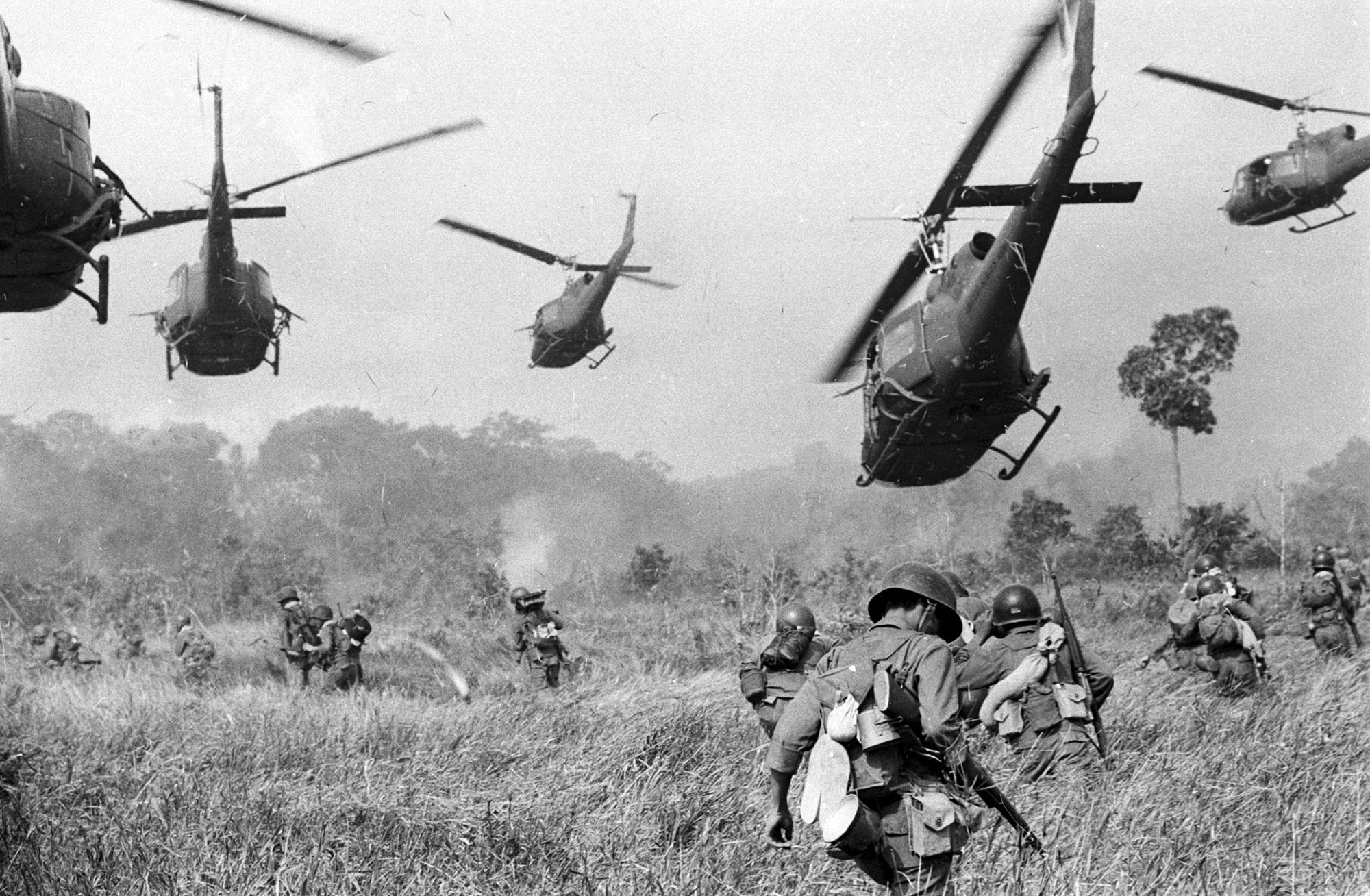 
The Roots of the Conflict
To understand the Vietnam War, it is essential to examine its historical context. The conflict emerged from the broader struggle for independence from French colonial rule. Ho Chi Minh, a charismatic leader, led the Vietnamese in their fight for liberation. The defeat of the French at Dien Bien Phu in 1954 marked a turning point, resulting in the division of Vietnam into North and South along the 17th parallel.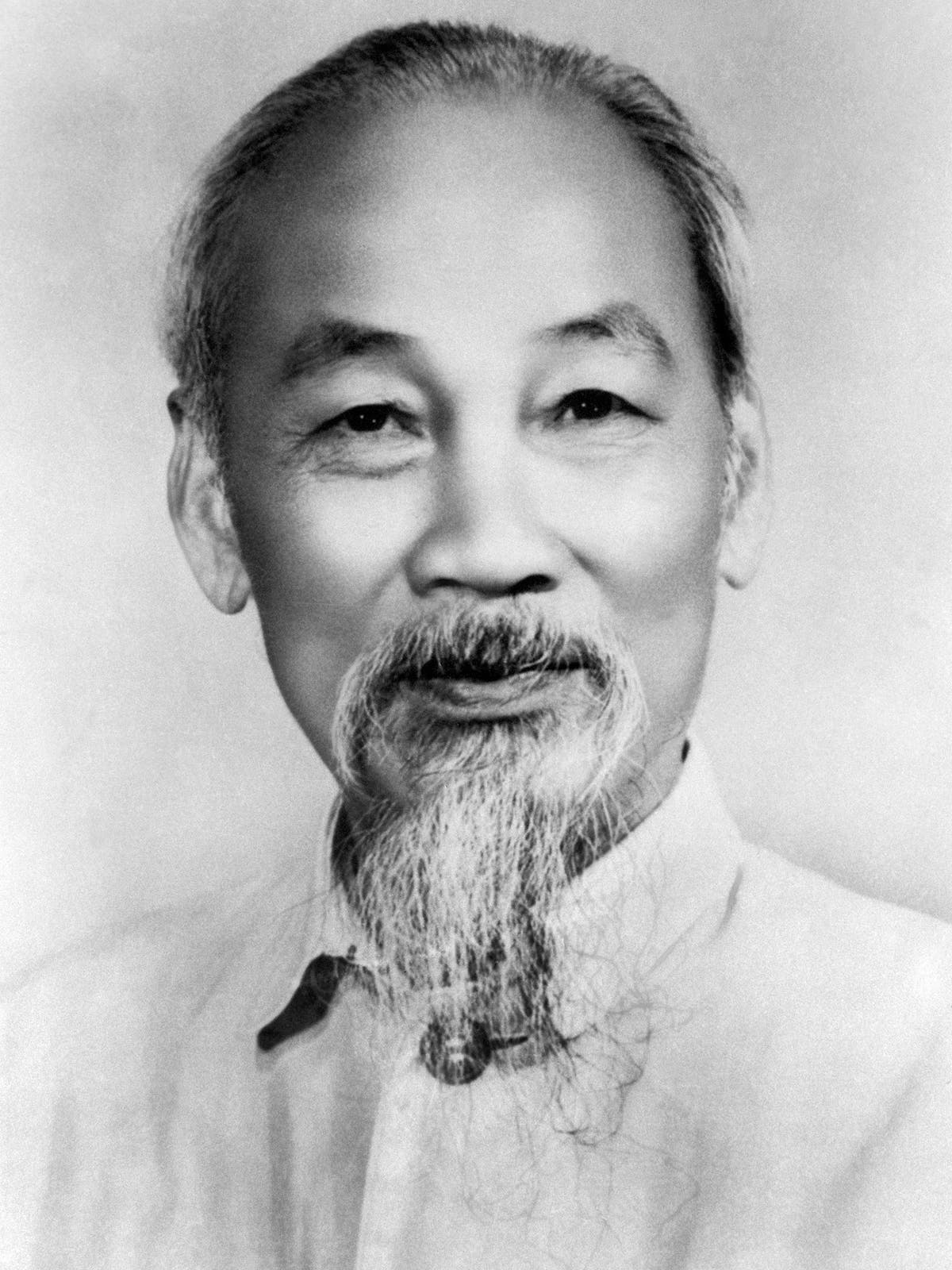  The Cold War provided the ideological backdrop for the escalation of the conflict. The United States, fearing the spread of communism, supported South Vietnam, while the Soviet Union and China backed North Vietnam. This proxy war became a battleground for competing ideologies and geopolitical interests.
The Cold War provided the ideological backdrop for the escalation of the conflict. The United States, fearing the spread of communism, supported South Vietnam, while the Soviet Union and China backed North Vietnam. This proxy war became a battleground for competing ideologies and geopolitical interests.
Several factors contributed to the deepening U.S. involvement. The Domino Theory, a belief that if one country fell to communism, neighboring countries would follow, influenced U.S. policy. Additionally, the Gulf of Tonkin incident in 1964, where alleged attacks on U.S. naval vessels were reported, provided a pretext for increased military intervention.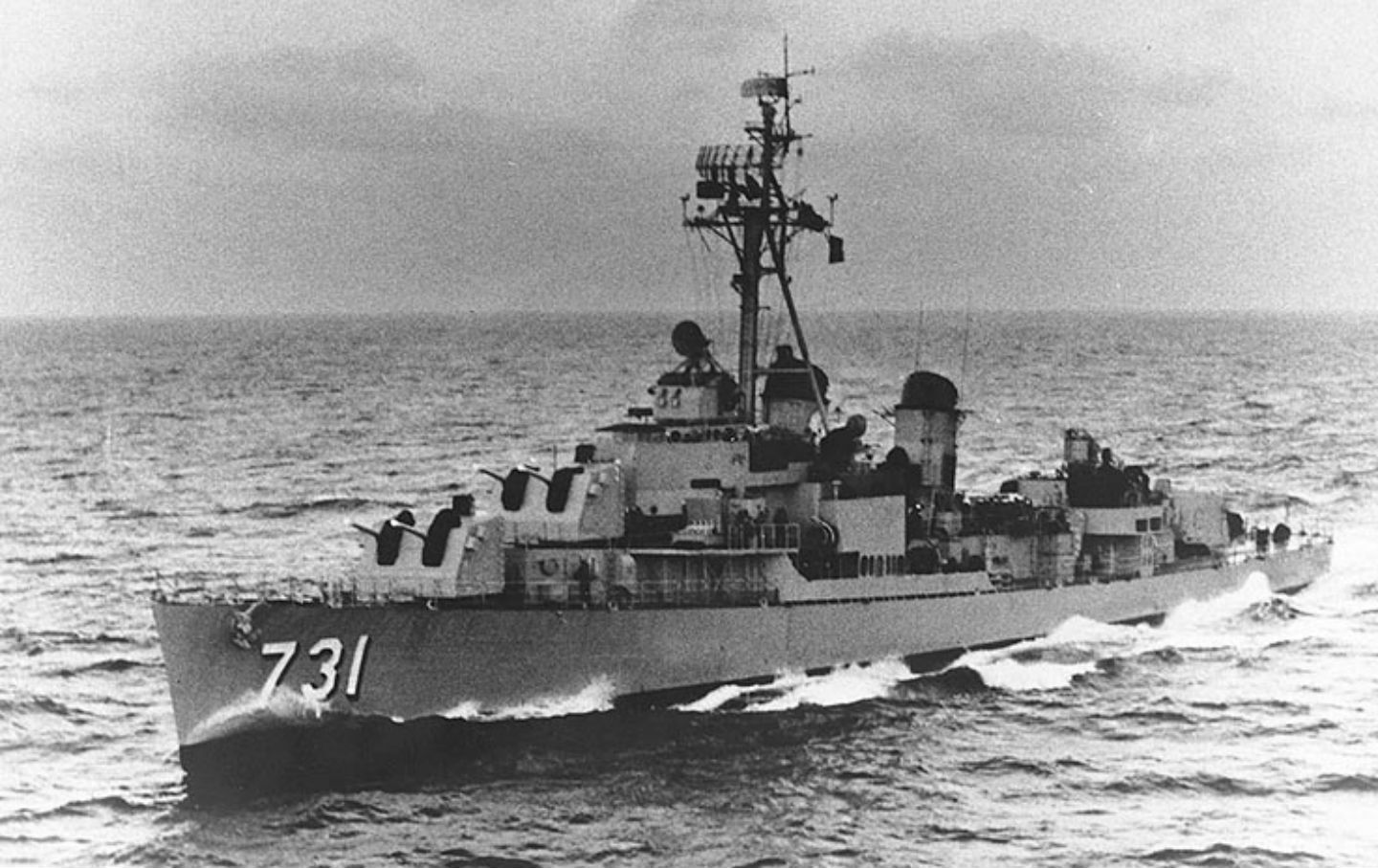 
The Anti-War Movement
The growing U.S. involvement in Vietnam coincided with a burgeoning anti-war movement. This movement was a diverse coalition of individuals and groups united by their opposition to the war. Their reasons for dissent were multifaceted.
- Moral and Ethical Concerns: Many individuals were deeply troubled by the human cost of the war, including the loss of innocent lives and the widespread destruction. They questioned the morality of using overwhelming military force against a small, agrarian nation.
- Civil Liberties Violations: The war era was marked by infringements on civil liberties, such as the surveillance of anti-war activists and the erosion of free speech rights. These actions alienated many who believed in democratic principles.
- Economic and Social Costs: The war drained significant resources from domestic programs, leading to criticisms that social needs were being neglected. Rising inflation and economic inequality exacerbated public discontent.
- Doubt About the War's Goals: As the conflict dragged on without a clear victory, skepticism grew about the legitimacy of U.S. objectives. Many questioned whether the goal of containing communism justified the immense human and material costs.
- Distrust of Government: The credibility of the government was undermined by the revelation of classified documents, such as the Pentagon Papers, which exposed deception and mismanagement of the war. This eroded public trust and fueled anti-war sentiment.
The anti-war movement employed a variety of tactics, from peaceful protests and civil disobedience to more radical actions. College campuses became hotbeds of activism, with students organizing demonstrations and sit-ins. The media played a crucial role in shaping public opinion, with television bringing the horrors of war into living rooms. Iconic images of the war, such as the burning of a Buddhist monk and the My Lai massacre, galvanized opposition.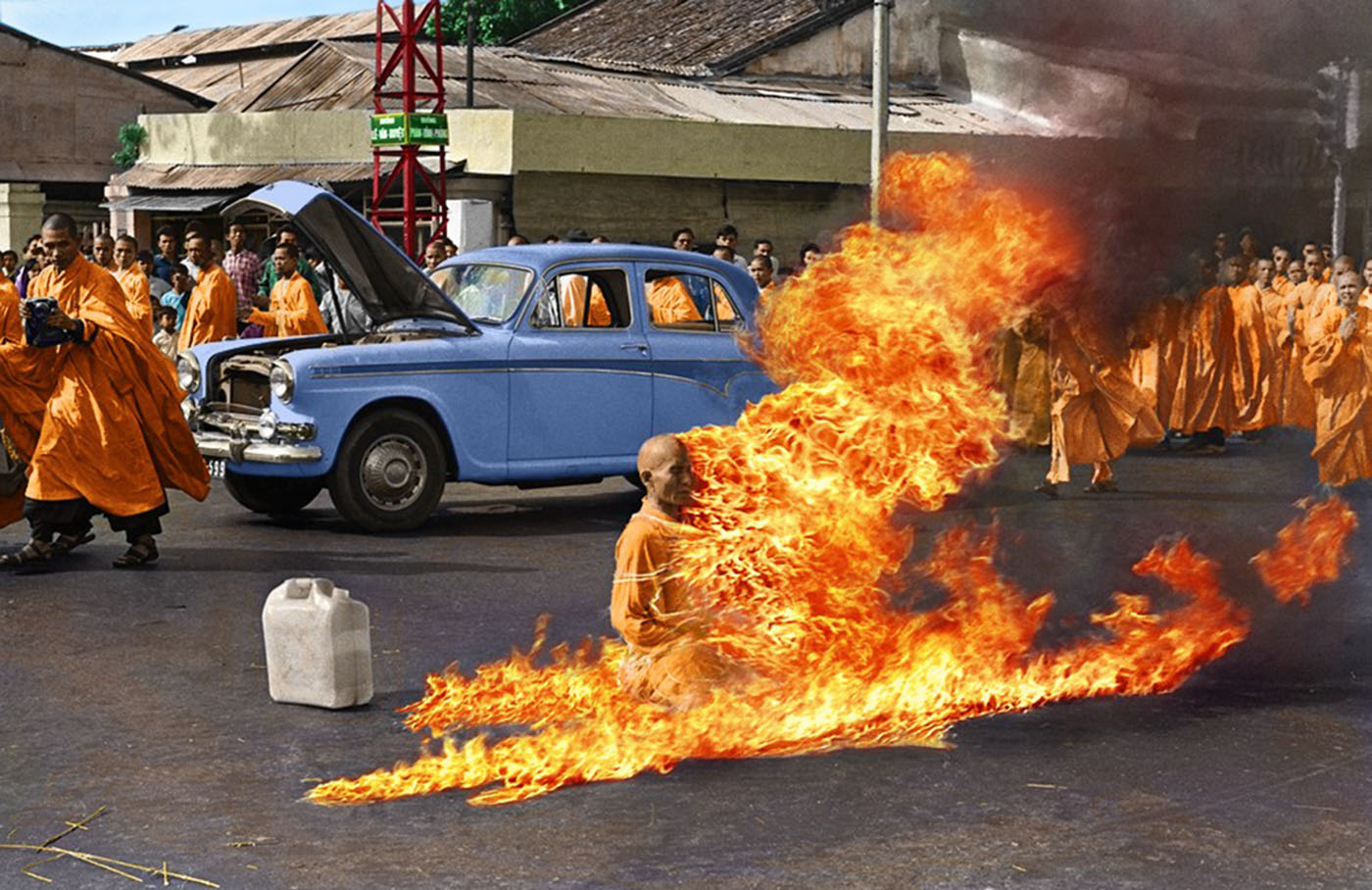 
The Legacy of the War
The Vietnam War left a profound and enduring impact on the United States and Vietnam. The conflict resulted in the deaths of millions, both military and civilian, and caused widespread devastation. The war also fractured American society, leaving a legacy of distrust and division that persists to this day.
The anti-war movement, while ultimately unsuccessful in preventing U.S. involvement, played a crucial role in shaping public opinion and forcing a reevaluation of government policies. It catalyzed a broader movement for social change, addressing issues such as racial inequality, women's rights, and environmental protection. Understanding the complex factors that led to the Vietnam War and the diverse perspectives of those who opposed it is essential for appreciating the lasting consequences of this conflict. By examining the past, we can better comprehend the challenges and opportunities of the present.
Understanding the complex factors that led to the Vietnam War and the diverse perspectives of those who opposed it is essential for appreciating the lasting consequences of this conflict. By examining the past, we can better comprehend the challenges and opportunities of the present.