Biogas generation and its methods
Biogas generation is the process of converting organic waste materials into a valuable source of renewable energy. It involves the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, a process known as anaerobic digestion. Biogas is primarily composed of methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and water vapor.
The first step in biogas generation is the collection of organic waste materials, which can include various types of biomass such as agricultural residues, animal manure, food waste, and sewage sludge. These waste materials are then fed into an anaerobic digester, which is a sealed container where the decomposition process takes place.
Inside the anaerobic digester, microorganisms break down the organic matter through a series of biological reactions. The decomposition occurs in several stages, carried out by different groups of bacteria. Initially, complex organic compounds are broken down into simpler molecules like sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids. Then, the bacteria convert these compounds into simpler substances such as acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide.
As the organic matter breaks down, methane-producing bacteria called methanogens thrive in the anaerobic environment and convert the acetic acid and hydrogen into methane gas. This methane, along with the carbon dioxide produced during the process, is the main component of biogas. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, so capturing and utilizing it as a fuel helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The produced biogas can be used in a variety of applications. It can be burned directly as a source of heat for cooking, heating, or electricity generation. Alternatively, the biogas can be upgraded to remove impurities, particularly carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, resulting in a higher purity methane gas known as biomethane. Biomethane has similar properties to natural gas and can be injected into the natural gas grid or used as a transportation fuel.
Apart from producing biogas, the anaerobic digestion process also generates a nutrient-rich byproduct called digestate. Digestate can be used as a high-quality organic fertilizer, returning valuable nutrients back to the soil and closing the nutrient cycle.
Biogas generation offers several environmental and economic benefits. By converting organic waste into energy, it helps to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, mitigates greenhouse gas emissions, and contributes to the transition towards a more sustainable energy system. Additionally, biogas generation provides a solution for waste management by diverting organic waste from landfills and reducing odor issues and environmental pollution associated with waste disposal.
The success of biogas generation depends on the availability of suitable feedstock, efficient anaerobic digestion systems, and proper management of the process. Factors such as temperature, pH levels, and retention time need to be carefully controlled to ensure optimal performance. Technological advancements and research in this field are continually improving the efficiency and viability of biogas generation systems.
In conclusion, biogas generation is a valuable process that harnesses the power of organic waste to produce renewable energy. By converting waste into a useful resource, it offers a sustainable solution for waste management while contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. With ongoing advancements, biogas generation has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Biogas can be generated through various methods. Here are some common methods of biogas generation:
1.Anaerobic Digestion
This is the most common method used for biogas production. Organic materials such as animal manure, crop residues, sewage sludge, and food waste are placed in an anaerobic digester, which is a sealed container. The organic matter breaks down in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.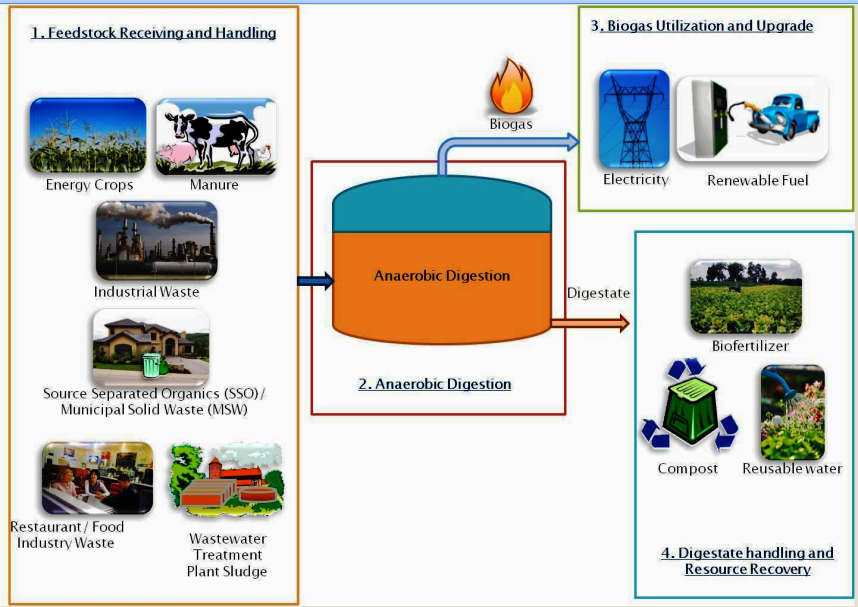
2.Landfill Gas Recovery
Landfills produce biogas naturally as organic waste decomposes. Landfill gas recovery systems collect and treat the gas emitted from landfills, which primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide. The collected gas can then be used for energy generation.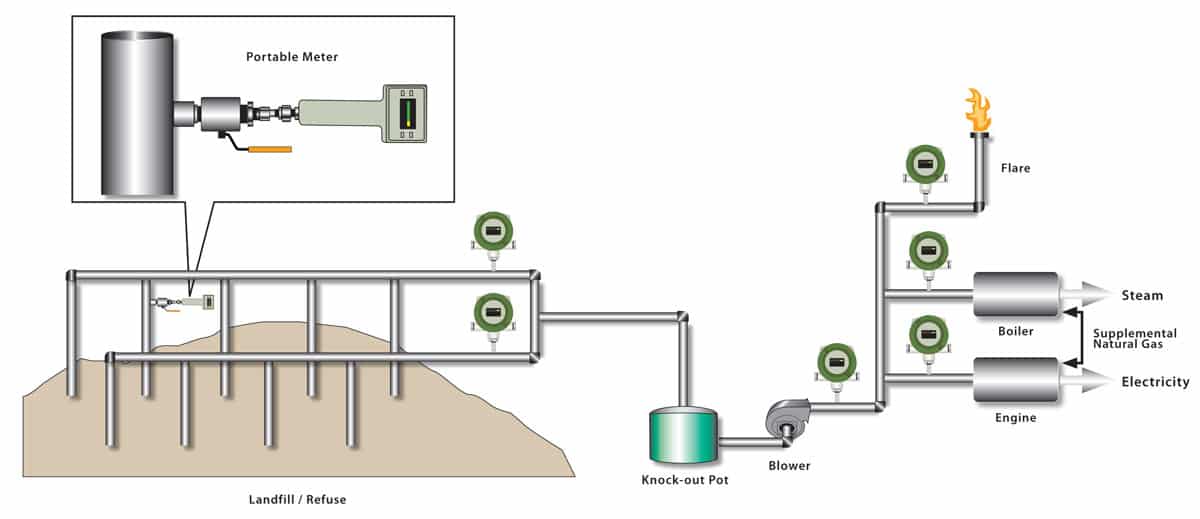
3.Sewage Treatment Plants
Biogas can be generated from sewage treatment plants where organic waste, including human waste, is treated. The anaerobic digestion process is employed to break down the waste, producing biogas.
4.Agricultural Residues
Agricultural residues like crop residues, straw, and stalks can be used as feedstock for biogas generation. These materials are collected and introduced into anaerobic digesters, where they undergo fermentation to produce biogas.
5.Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industries that produce large amounts of organic wastewater, such as breweries, distilleries, and food processing plants, can utilize anaerobic digesters to treat the wastewater. This process not only helps in treating the wastewater but also generates biogas.
6.Co-digestion
Co-digestion involves mixing different organic materials to enhance the biogas production process. For example, combining animal manure with food waste or agricultural residues can improve the methane yield and overall efficiency of the biogas generation.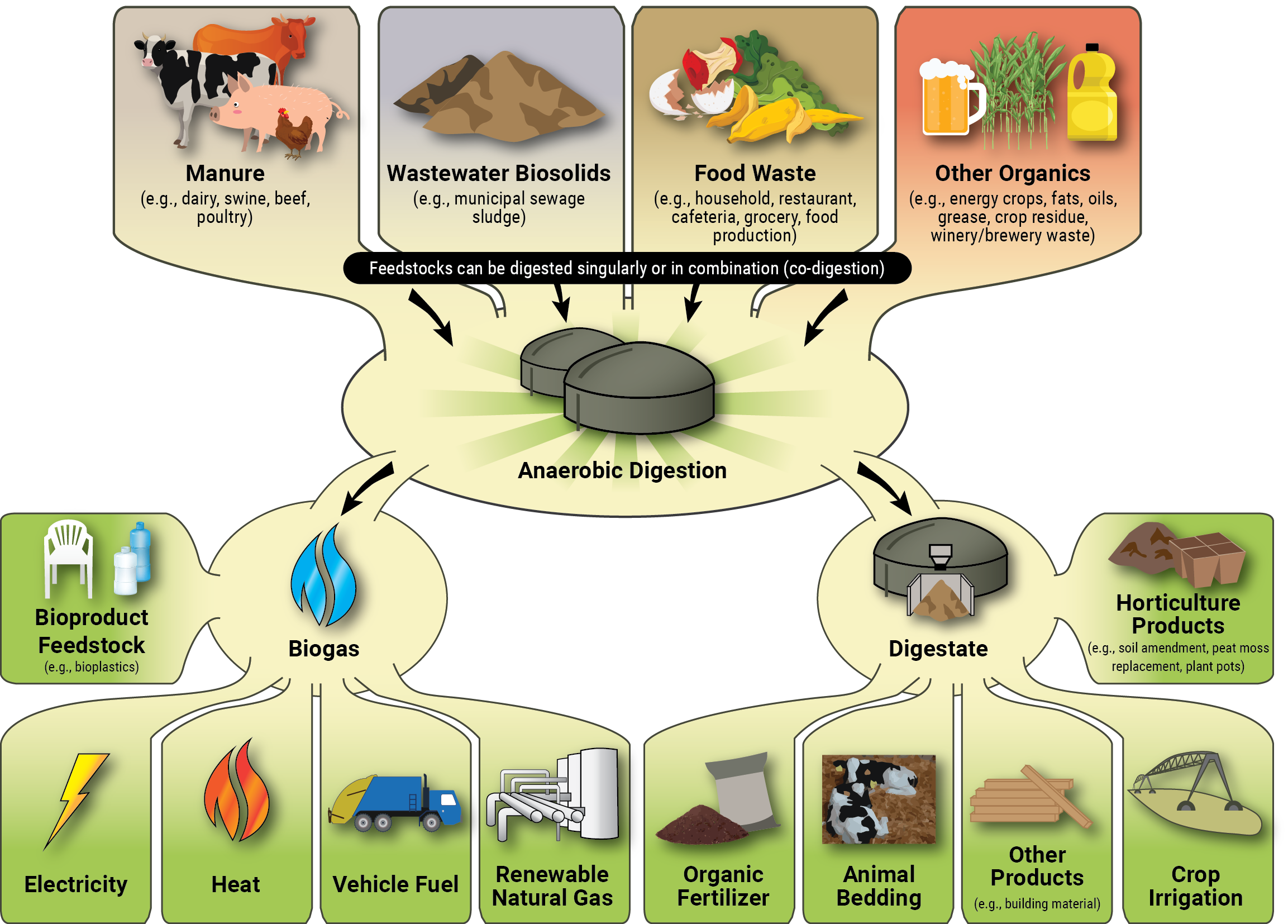 Biogas generation is a sustainable and renewable energy solution that involves the production of biogas through the decomposition of organic matter in an anaerobic environment. This process offers multiple benefits, including the generation of clean energy, waste management, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Biogas generation is a sustainable and renewable energy solution that involves the production of biogas through the decomposition of organic matter in an anaerobic environment. This process offers multiple benefits, including the generation of clean energy, waste management, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The most common method of biogas generation is anaerobic digestion. In this process, organic materials such as animal manure, crop residues, food waste, and sewage sludge are collected and introduced into an anaerobic digester. The digester is a sealed container where bacteria break down the organic matter in the absence of oxygen. As a result, biogas is produced, which primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and by capturing it through anaerobic digestion, we can reduce its release into the atmosphere.
Another method of biogas generation is landfill gas recovery. Landfills produce biogas naturally as organic waste decomposes. Landfill gas recovery systems collect and treat the gas emitted from landfills, primarily consisting of methane. This collected gas can be utilized for electricity generation or as a fuel source.
Sewage treatment plants also play a significant role in biogas generation. The organic waste, including human waste, is treated through anaerobic digestion, producing biogas. This not only helps in waste management but also generates energy.
Agricultural residues such as crop residues, straw, and stalks can be used as feedstock for biogas generation. These materials are collected and introduced into anaerobic digesters, where they undergo fermentation to produce biogas. Additionally, specific energy crops like maize and sugarcane can be grown specifically for biogas production.
Co-digestion is another approach where different organic materials are mixed to enhance biogas production. This method allows for the efficient utilization of multiple waste streams, improving the overall biogas yield.
Overall, biogas generation provides a sustainable solution for energy production while addressing waste management challenges. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, mitigates greenhouse gas emissions, and contributes to a circular economy by converting organic waste into valuable energy. The versatility of feedstock options and various biogas generation methods make it a flexible and adaptable solution for different regions and industries. With further advancements and investment in biogas technologies, it has the potential to play a significant role in achieving a greener and more sustainable energy future.































