Top ancient nations that appeared earliest in human history #1
Humans appeared on Earth about 200,000 years ago and went through many stages: tribes, primitive communes, city-states... until the formation of nations about 5,000 years ago. In history, there are many powerful ancient countries that are the cradle of civilization such as Egypt, India, Greece, China, Rome... Let's join Toplist to get to the Top 15 ancient countries appeared earliest in human history.
Ancient Egypt
Topping the list of ancient countries that appeared earliest in human history is ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt officially unified Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt with the ascension of the first Pharaoh around 3100 BC. The first Pharaoh's name was Narmer, often called Menes.
The territory of ancient Egypt included a large area of Northeast Africa following the Nile River basin to the Mediterranean. It is the fertile plains of the Nile River that have created favorable conditions for people to focus on developing agriculture, thereby creating a new step in the development of human society.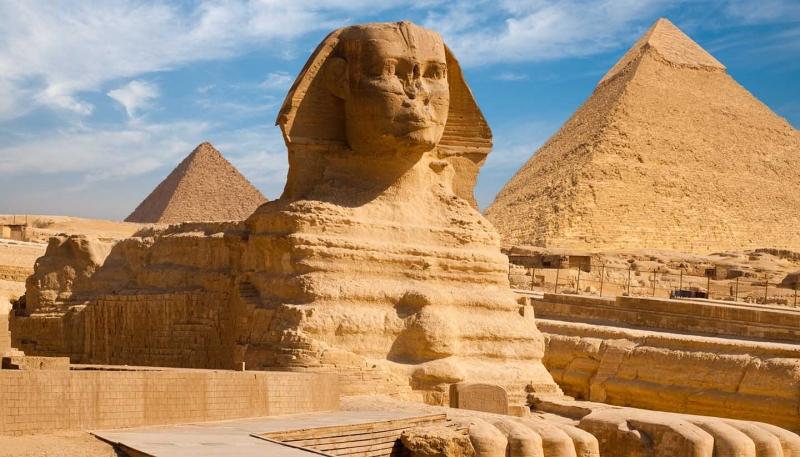
Ancient Egyptian history includes major periods: the Early Dynasty (3100-2686 BC), the Old Kingdom (2686-2181 BC), the First Intermediate (2181-2055 BC), the Middle Kingdom (2055- 1650 BC), Second Intermediate (1650-1550 BC), New Kingdom (1550-1069 BC), Third Intermediate (1069-664 BC) and Later Era (664-332 BC). In particular, ancient Egypt reached the peak of power, strength, and culture in the New Kingdom period, during the Ramsside (English: Ramsey) period (1186-1077 BC).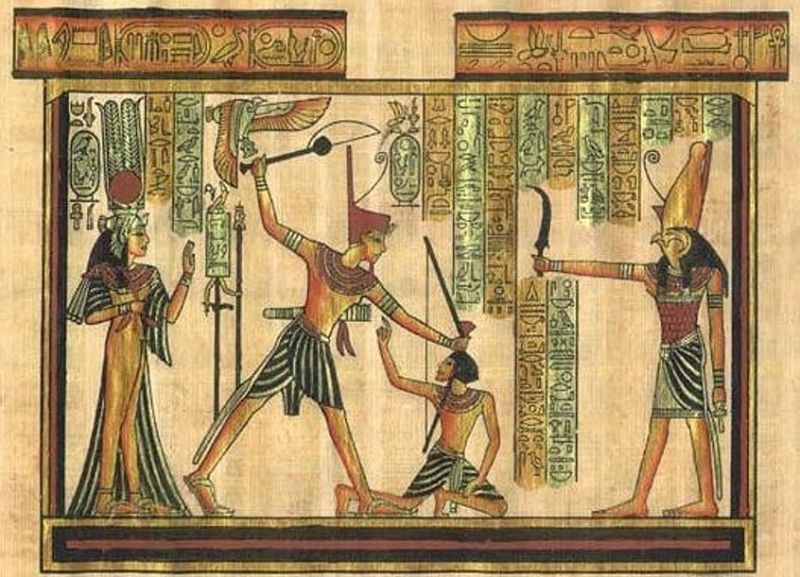
Ancient Egypt had many great civilizational achievements that are still preserved today. These are architectural works such as the Pyramids, the Sphinx, and temples; primitive mathematical system, primitive medical system, embalming techniques, paper making techniques and the first glass processing in the world. Among them, the most famous is Pharaoh Khufu's Giza Pyramid - recognized by UNESCO as 7 wonders of the ancient world.
Ancient India
Scientists have found that the "cradle of Asia" is ancient India in the Indus River basin around 3,000 BC. According to research, prehistoric humans appeared in India from about 200,000 to 500,000 years ago and modern humans settled in India at the end of the Ice Age, 12,000 years ago. The civilization of ancient India developed into a nation around 3,000 BC. This civilization featured the construction of terracotta cities, sewer systems, and multi-story buildings.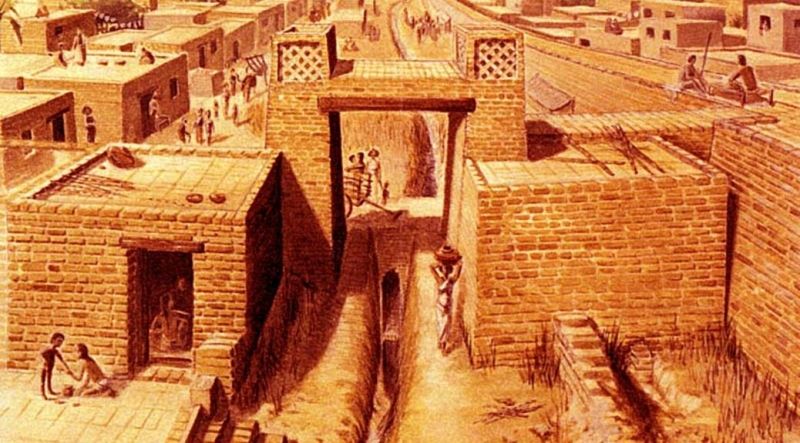
Ancient Indian history went through many overlapping events and periods, including an important historical milestone when the Aryans swept down from the North and built the Vedic period in India. ancient. 
The pinnacle of this culture is the Vedas - the oldest written text in existence, written in 1,500 BC. Around 625 BC, a great Indian was born, Siddhartha Gautama, also known as Buddha, the Buddha Shakyamuni - the founder of Buddhism. It can be said that ancient India had an extremely rich and strong religious culture that still has a profound influence until now, especially Buddhism is the most popular religion from South Asia to Asia. Winter.
Crete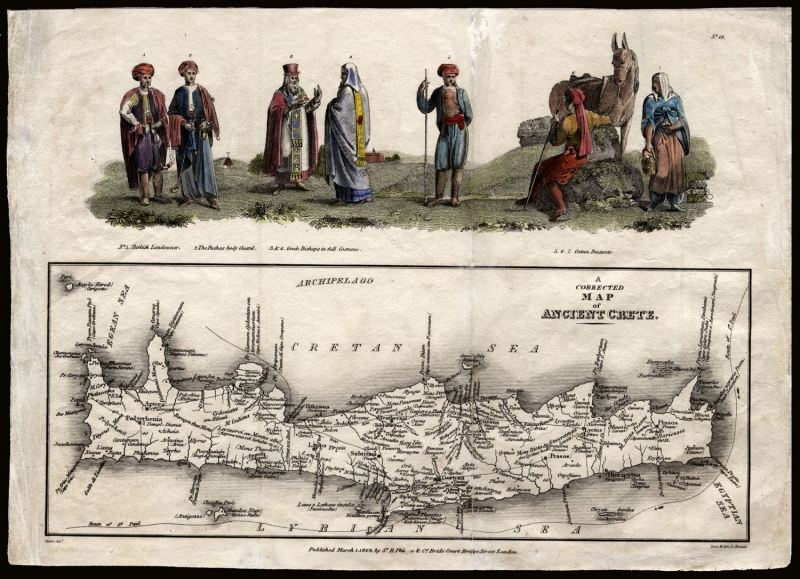
Crete is considered the cradle of ancient Greece, the first land of advanced Western civilization and the largest and most populous Greek island. Civilization on the island of Crete appeared very early before spreading to all of ancient Greece with brilliant development under the Minos civilization (about 2,700 BC). They are famous as pioneers and flourished in the maritime field because of their favorable location, located at the intersection of trade routes.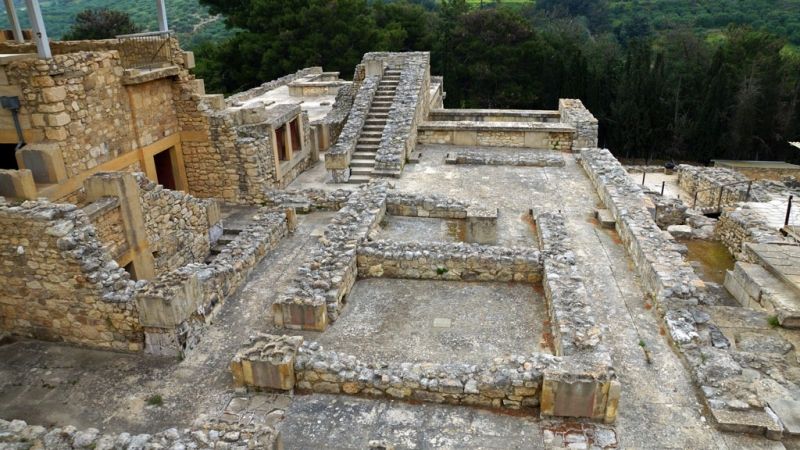
Because it was too primitive and rarely recorded in later history books, the history of Crete became stories in Greek mythology, such as the stories of King Minos, Theseus, and the Minotaur told by Homer - The greatest troubadour of ancient Greece (around the 8th century BC). Later, Crete became part of ancient Greece.
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire was the first ancient Semitic-speaking state, later mentioned in the Bible. In the 3rd millennium BC, Sumerian and Akkadian cultures interacted and Akkadian culture gradually replaced Sumerian culture.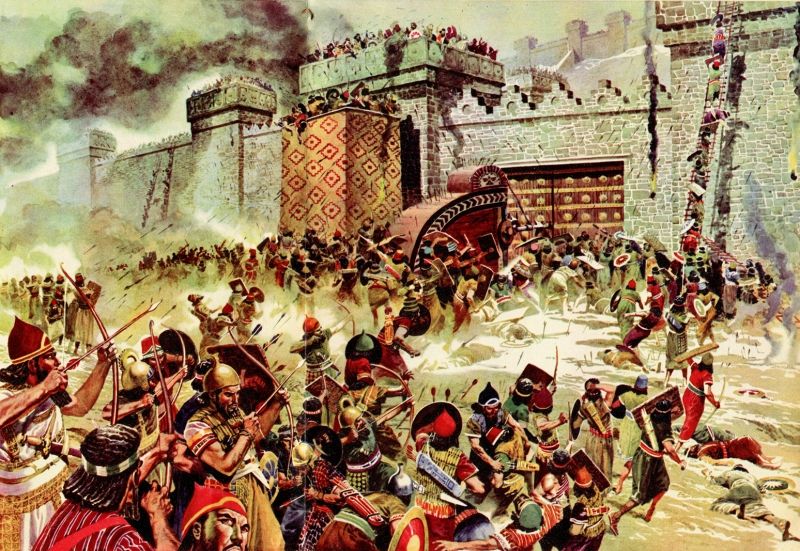 
The Akkadian Empire appeared around 2334 BC and lasted until around 2154 BC. The Akkad Empire is located in the Mesopotamia region, the capital of the Akkad empire belongs to the two countries of Syria and Iraq, and the neighboring lands that the Akkad empire conquered extended to Bahrain, Oman and part of modern Arabia. now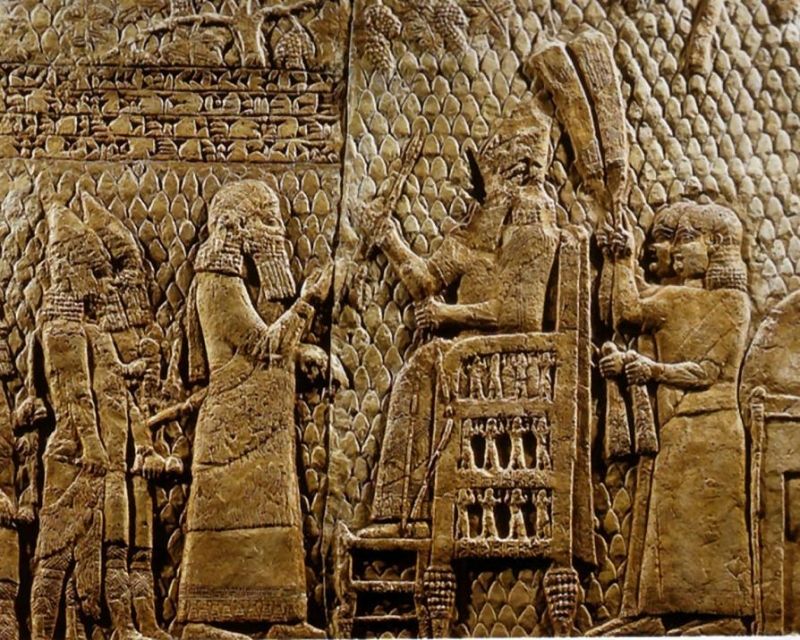
The Akkadian Empire ended its city-state period in Mesopotamia to usher in the first nation-state period in one of the cradles of humanity. The Akkadian Empire began with the conquest of King Sargon and ended with King Shu-turul. The Akkad Empire was also the predecessor of other famous ancient empires, Assyria and Babylon later
Assyrian Empire
Referring to the Top 15 ancient countries that appeared earliest in human history, it is indispensable to mention the Assyrian Empire - one of the very strong forces in ancient times. The Assyrian Empire inherited a large area of Mesopotamia when the Akkadian Empire collapsed. Under the Akkadian Empire, Assyria was just a small neighboring vassal. After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, Assyria gradually grew stronger, competing with other powers and became the Assyrian Empire from around 2,000 BC. The center of the Assyrian Empire was located at the headwaters of the Tigris River, in northern Mesopotamia, today northern Iraq.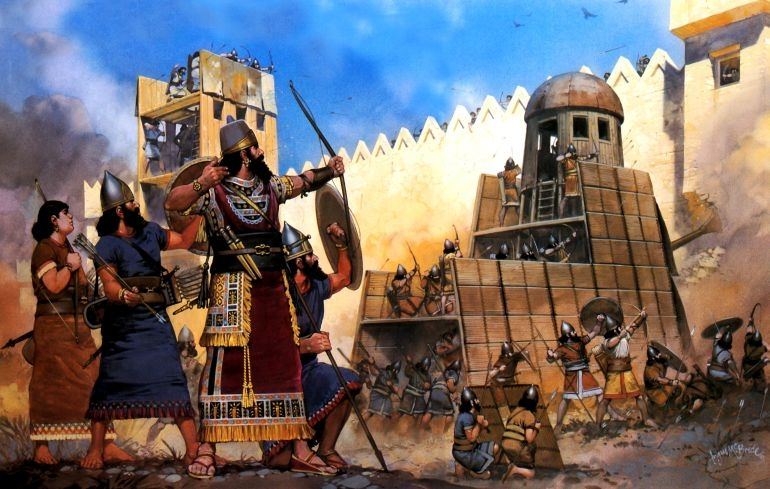
The collapse of the Akkad Empire caused many powers to emerge to compete with each other, including the Assyrian Empire, the Hittite Empire and ancient Babylon. Since the 19th century BC, the Assyrian Empire has expanded its territory, competing with the Hittite Empire in the North and ancient Babylon in the South. The prosperous period of the Assyrian Empire under King Shamshi-Adad I (1813-1791 BC) ended in 1756 BC when the Assyrian Empire was invaded and dominated by ancient Babylon, before the Assyrian Empire revived. returned and returned to invade and rule Babylon (911-609 BC).
This was the most prosperous period of the Assyrian Empire when the empire expanded throughout Mesopotamia, spreading to Asia Minor and the Mediterranean. However, its large territory with many colonies caused the Assyrian Empire to collapse, when it could not be controlled and was defeated by colonies, including Babylon, Scythia, Persia, and Yugoslavia.






![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: Veterans Affairs Labor repairs](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/1cbacfad-83d7-45aa-8b66-bde121dd44af/1)





















