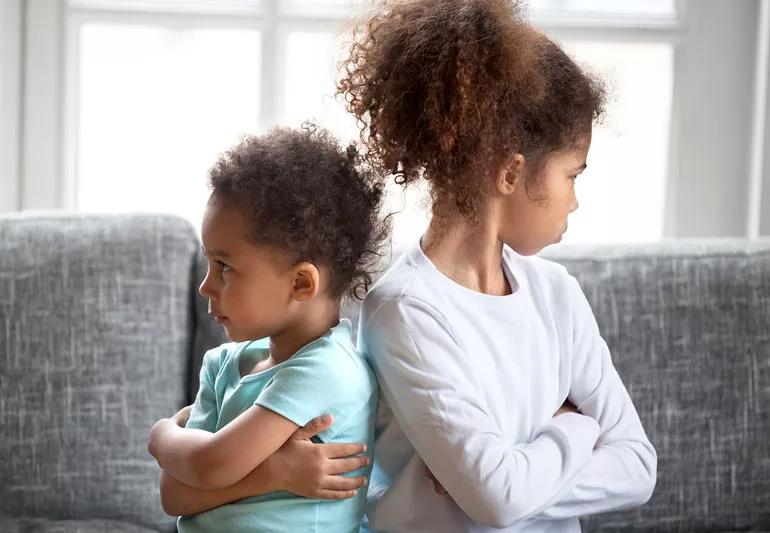
Factors That Lead to Rivalry Between Siblings
Sibling relationships are some of the most enduring connections in a person’s life. These bonds can be a source of love, support, and camaraderie. However, they are not immune to conflict, and rivalry between siblings is a dynamic that has persisted across cultures and generations. Understanding the factors that fuel sibling rivalry is essential to mitigating its impact and fostering healthier relationships within families.
This article delves into the underlying causes of sibling rivalry, exploring how family dynamics, individual differences, external influences, and parental involvement play critical roles.
Family Dynamics and Resource Allocation
At the heart of many sibling rivalries lies the question of resource distribution within the family. Resources can include tangible elements like parental attention, financial support, or physical possessions, as well as intangible ones such as emotional support and validation. When children perceive these resources as unequally distributed, feelings of resentment and competition often arise.
Birth order is a significant factor in this dynamic. The firstborn often enjoys undivided attention until the arrival of younger siblings, which can create feelings of displacement. Meanwhile, younger siblings may perceive older ones as having more privileges or greater autonomy. These perceptions, whether accurate or not, can sow seeds of rivalry. Furthermore, in larger families, the competition for parental recognition and time can intensify, exacerbating tensions between siblings.
Parental favoritism, whether real or perceived, further complicates family dynamics. Children are acutely aware of differences in how they are treated compared to their siblings. Even subtle actions, such as consistently praising one child’s achievements over another’s, can create a lasting sense of inequity. Over time, this can lead to persistent rivalries, as siblings vie for their parents’ approval and affection.
Individual Differences and Temperamental Clashes
Another critical factor in sibling rivalry is the inherent differences in personality, temperament, and interests. No two individuals are alike, and these differences can create friction, particularly when siblings are forced to share spaces, activities, or responsibilities.
Temperamental clashes are a common source of conflict. For instance, an extroverted, outgoing sibling might struggle to relate to a more introverted, reserved counterpart. Similarly, siblings with contrasting approaches to problem-solving or emotional expression may find it challenging to connect on a deeper level. These differences can be amplified during childhood and adolescence when identity formation and self-expression are paramount.
Competition in specific areas, such as academics, sports, or social standing, can also fuel rivalries. When one sibling excels in a domain where another struggles, feelings of inadequacy and jealousy often emerge. These emotions can strain the relationship, particularly if external comparisons from parents, teachers, or peers—reinforce the disparity. Additionally, siblings with overlapping interests may find themselves in direct competition, further intensifying feelings of rivalry.
External Influences and Social Pressures
While family dynamics and individual differences play significant roles in sibling rivalry, external factors can also contribute to tensions. Societal and cultural expectations often place undue pressure on siblings to conform to specific roles or standards, leading to comparisons and competition.
For example, in cultures where academic achievement is highly valued, siblings may feel pressured to outperform each other in school. Similarly, in families with a strong emphasis on financial success, siblings may compete to secure prestigious careers or accumulate wealth. These external pressures can create an environment where rivalry is not only inevitable but also normalized.
Peer relationships and social comparisons also influence sibling dynamics. Friends and classmates may inadvertently exacerbate rivalries by comparing siblings or favoring one over the other. Social media has further amplified these comparisons, as siblings’ achievements and lifestyles are often showcased and scrutinized in public forums. This constant exposure can heighten feelings of inadequacy or jealousy, fueling existing tensions.
The Role of Parental Involvement
Parents play a pivotal role in either mitigating or exacerbating sibling rivalry. Their actions, whether intentional or not, significantly influence the dynamics between siblings. The way parents handle conflicts, distribute responsibilities, and express affection can all impact the likelihood and intensity of rivalries.
One common issue is inconsistency in discipline or expectations. When parents enforce rules differently for each child, it can create a perception of favoritism or unfairness. For instance, a younger sibling who receives leniency for the same behavior that resulted in punishment for the older sibling may breed resentment. Similarly, assigning unequal responsibilities—such as expecting the older sibling to care for younger ones—can create imbalances that strain relationships.
Parental involvement in conflicts is another critical area. When parents take sides or fail to address disputes impartially, they risk deepening the divide between siblings. On the other hand, parents who actively encourage open communication and foster a sense of teamwork can help reduce rivalry. Modeling healthy conflict resolution and emphasizing the value of sibling bonds can go a long way in mitigating tensions.
It is also essential for parents to recognize and celebrate each child’s unique strengths and achievements. By fostering an environment where individuality is valued over comparison, parents can help their children develop self-confidence and reduce the need for rivalry. Providing opportunities for siblings to collaborate and build positive shared experiences can further strengthen their bond.
Conclusion
Sibling rivalry is a complex phenomenon influenced by a multitude of factors, including family dynamics, individual differences, external pressures, and parental involvement. While some level of rivalry is natural and even beneficial in fostering resilience and problem-solving skills, excessive or unresolved conflicts can have long-lasting effects on sibling relationships and overall family harmony. By understanding and addressing the root causes of rivalry, families can create an environment where siblings are more likely to support and uplift one another rather than compete. Ultimately, fostering healthy sibling relationships requires a combination of empathy, fairness, and proactive communication—qualities that benefit not only the siblings involved but the entire family unit.
References
- Coleman, J. (2020). Sibling Rivalry: Understanding and Managing Competition Among Brothers and Sisters. Family Psychology Press.
- Dunn, J. (2014). Sibling Relationships in Childhood and Adolescence. Harvard University Press.
- Kramer, L., & Conger, K. (2009). "What We Know About Sibling Rivalry and How to Address It." Journal of Family Research.
- Updegraff, K., & White, N. (2015). "The Role of Parents in Shaping Sibling Dynamics." Journal of Child Development.