Web3 in Action: DApps, Protocols, and the Evolution of the Internet
Introduction
1.What is Web3?
Web3 refers to the next evolutionary phase of the internet, emphasizing decentralization, blockchain technology, and user empowerment. Unlike its predecessor, Web2, which is characterized by centralized platforms and control over user data by large corporations, Web3 envisions a more democratized and user-centric online experience. At the core of Web3 is blockchain technology, providing a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger that underpins various applications and services. This enables trustless interactions through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies play a pivotal role in Web3, facilitating peer-to-peer transactions and powering decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Web3 also promotes the idea of user ownership of data, allowing individuals to have greater control over their digital identities and personal information. As the Web3 ecosystem continues to grow, it brings forth innovations such as decentralized applications (DApps), distributed storage solutions like IPFS, and the potential to reshape traditional industries. The journey into Web3 represents a shift towards a more inclusive, secure, and transparent internet experience.
2.Fundamental Principles of Web3
Web3 is built upon several fundamental principles that distinguish it from its predecessors. Decentralization stands as a cornerstone, aiming to distribute control and authority across the network rather than concentrating power in a few entities. Blockchain technology is pivotal, providing a transparent and tamper-resistant ledger that ensures trust and security in transactions and data handling. Interoperability is another key principle, fostering seamless interaction between different platforms and protocols within the Web3 ecosystem. Inclusivity is emphasized, aiming to create an internet where all participants, irrespective of geographical location or socioeconomic status, have equal access and opportunities. User sovereignty is a guiding principle, advocating for individuals to have ownership and control over their data, enabling them to decide how their personal information is utilized. Privacy and security are paramount, with an emphasis on protecting user data from unauthorized access. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, exemplify the automation principle, reducing reliance on intermediaries. As Web3 continues to evolve, these principles collectively contribute to a vision of a more democratic, transparent, and user-centric internet.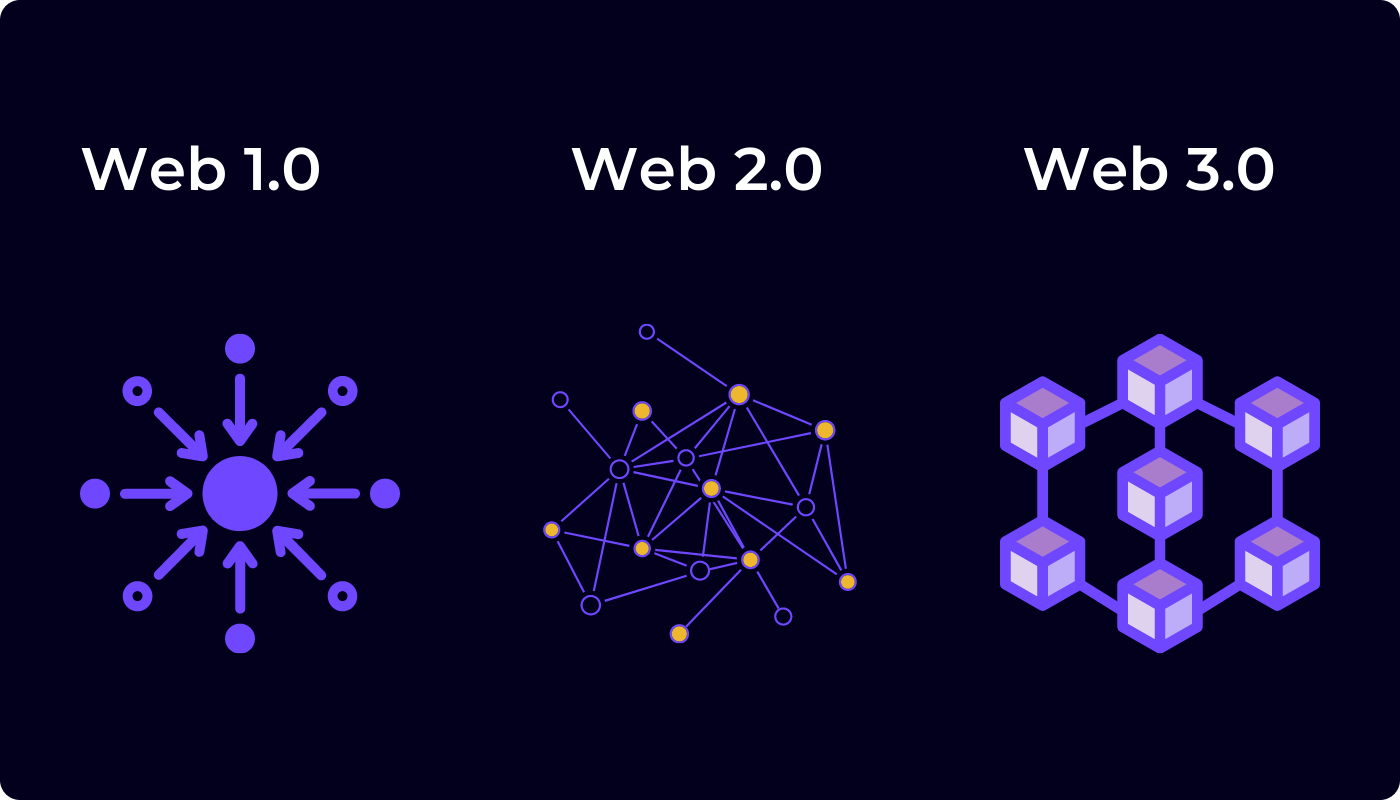
3.Differences Between Web3 and Web2
Web3 and Web2 represent distinct phases in the evolution of the internet, each characterized by different principles and functionalities. Web2, the current state of the internet, is dominated by centralized platforms where user data is controlled and monetized by a few major corporations. In contrast, Web3 strives for decentralization, seeking to distribute control and data ownership among network participants. Web2 relies heavily on intermediaries for various services, while Web3 leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable trustless, peer-to-peer interactions, reducing the need for middlemen. Data privacy is a significant differentiator; Web3 emphasizes user sovereignty, allowing individuals to own and control their data, in contrast to the data-centric business models of Web2. Moreover, Web3 promotes interoperability, fostering collaboration between different platforms and services, while Web2 platforms often operate in silos. The shift from Web2 to Web3 signifies a move towards a more inclusive, transparent, and user-empowered internet experience.
Blockchain Technology and Web3
1.What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that serves as the backbone of many decentralized systems, including cryptocurrencies and Web3 applications. At its core, a blockchain is a distributed and tamper-resistant ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure and transparent manner. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions and a unique identifier called a cryptographic hash, which is generated based on the content of the block. These blocks are linked together through cryptographic hashes, forming a continuous chain. One of the key features of blockchain is decentralization, meaning that no single entity has control over the entire network. Instead, consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, are employed to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger. This decentralized and secure nature of blockchain makes it resistant to fraud and censorship, providing a trustless environment for various applications, from peer-to-peer transactions to smart contracts in the Web3 ecosystem. Blockchain technology is a cornerstone of the shift towards more transparent, secure, and decentralized digital systems.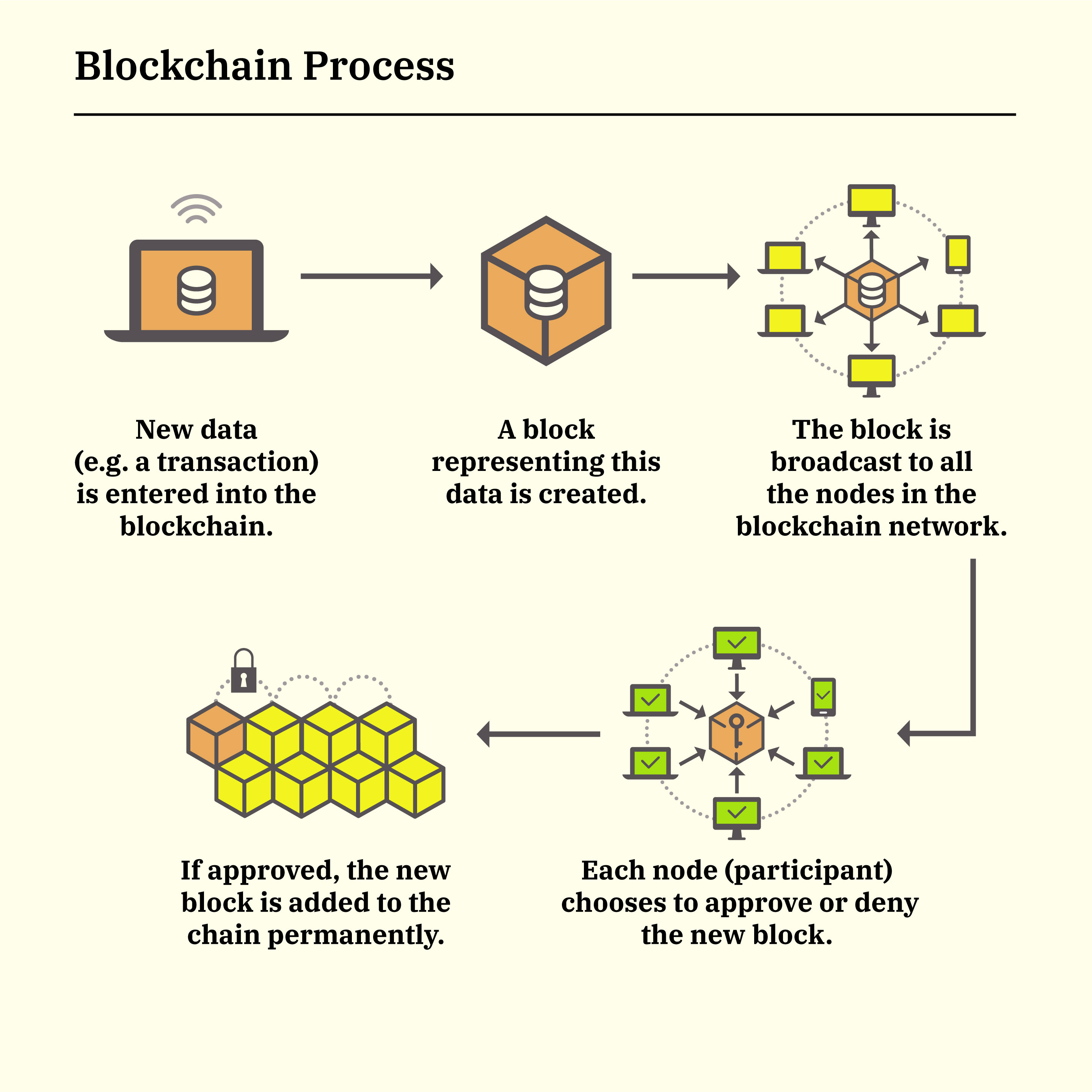
2.Smart Contracts and Web3
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, and they play a pivotal role in the evolution of Web3. Operating on blockchain technology, smart contracts enable automated and trustless execution of predefined agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries. In the Web3 ecosystem, platforms like Ethereum have popularized the use of smart contracts, allowing developers to create decentralized applications (DApps) that utilize these programmable agreements.
Smart contracts operate on the principles of decentralization and transparency. Once deployed on the blockchain, they are immutable and tamper-resistant, ensuring the integrity of the agreement. The terms of the contract are executed automatically when predefined conditions are met, providing a secure and efficient way to facilitate transactions and enforce agreements. Web3's reliance on smart contracts extends beyond financial transactions. They are utilized in various sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and even governance mechanisms within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Smart contracts contribute to the efficiency, security, and autonomy of Web3 applications, ushering in a new era of decentralized and automated interactions on the internet. As Web3 continues to evolve, smart contracts are poised to be a fundamental building block for a wide range of decentralized applications and services.
Web3's reliance on smart contracts extends beyond financial transactions. They are utilized in various sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and even governance mechanisms within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Smart contracts contribute to the efficiency, security, and autonomy of Web3 applications, ushering in a new era of decentralized and automated interactions on the internet. As Web3 continues to evolve, smart contracts are poised to be a fundamental building block for a wide range of decentralized applications and services.
3.Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT)
Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT) is a groundbreaking concept that underpins the core principles of decentralization in various technological applications, most notably in the development of blockchain. DLT operates as a distributed and synchronized database spread across multiple nodes or participants in a network. Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, DLT eliminates the need for a central authority, enabling peer-to-peer transactions and interactions.
The primary objective of DLT is to create a transparent, secure, and tamper-resistant record of transactions. This is achieved through consensus mechanisms that validate and agree upon the state of the ledger across the network. The decentralized nature of DLT ensures that no single entity has control over the entire system, enhancing trust and mitigating the risk of a single point of failure.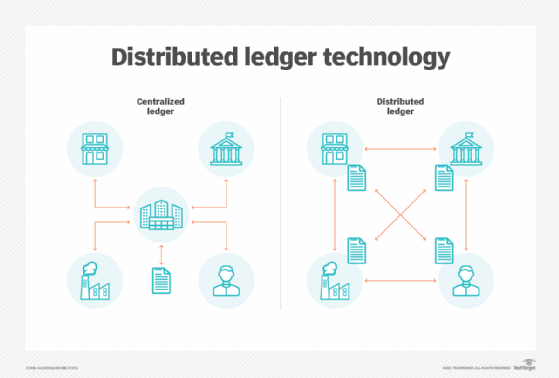 Blockchain, as a specific implementation of DLT, utilizes cryptographic techniques to link individual data blocks, creating an unbroken chain of information. This chain ensures an immutable record, making it extremely challenging for malicious actors to alter past transactions.
Blockchain, as a specific implementation of DLT, utilizes cryptographic techniques to link individual data blocks, creating an unbroken chain of information. This chain ensures an immutable record, making it extremely challenging for malicious actors to alter past transactions.
DLT has far-reaching implications beyond cryptocurrencies, extending its influence to sectors such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance. As a fundamental component of the Web3 ecosystem, DLT serves as the backbone for transparent and decentralized applications that are reshaping the way we interact, transact, and share information in the digital age.
Cryptocurrencies and Web3
1.The Role of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies play a crucial role in the transformative landscape of Web3 and decentralized systems. At the heart of this role is their function as digital assets designed to facilitate secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, often utilizing blockchain technology.
One of the primary functions of cryptocurrencies is to serve as a medium of exchange within decentralized ecosystems. They enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks, providing users with more direct control over their finances. Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, have emerged as pioneers in this space, showcasing the potential for decentralized financial systems.
In addition to their role as a means of exchange, cryptocurrencies are integral to the functioning of decentralized applications (DApps). They act as incentives for participants within these networks, encouraging users to contribute resources or services in exchange for cryptocurrency rewards. This incentivization model helps sustain the ecosystem and ensures active participation. Moreover, cryptocurrencies power the burgeoning field of decentralized finance (DeFi), where traditional financial services are recreated on blockchain networks. DeFi applications leverage cryptocurrencies for lending, borrowing, and trading, offering financial services without the need for traditional banking intermediaries.
Moreover, cryptocurrencies power the burgeoning field of decentralized finance (DeFi), where traditional financial services are recreated on blockchain networks. DeFi applications leverage cryptocurrencies for lending, borrowing, and trading, offering financial services without the need for traditional banking intermediaries.
As Web3 continues to evolve, the role of cryptocurrencies expands beyond mere transactions. They represent a fundamental building block, fostering decentralized and trustless environments across various applications and use cases, ultimately contributing to the broader vision of a decentralized and user-centric internet.
2.Major Cryptocurrencies Used in the Web3 Ecosystem
The Web3 ecosystem is powered by a diverse array of cryptocurrencies, each serving specific functions and roles within decentralized applications and platforms. Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, remains a foundational asset and a store of value within the Web3 space. Its decentralized nature, security features, and limited supply make it a popular choice for transactions and as a long-term investment.
Ethereum, another significant player, extends beyond a mere digital currency. It serves as a versatile platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts, enabling developers to create and deploy a wide range of decentralized services. Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, is not only a medium of exchange but also serves as gas – the fuel that powers transactions and computations on the platform.
Binance Coin (BNB) has gained prominence, particularly within the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem. BNB facilitates transactions and functions as a utility token within the Binance ecosystem, playing a pivotal role in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, token sales, and transaction fee payments. Ripple (XRP) stands out with its focus on facilitating fast and low-cost cross-border payments. Its consensus algorithm and partnerships with financial institutions contribute to its role in revolutionizing traditional finance.
Ripple (XRP) stands out with its focus on facilitating fast and low-cost cross-border payments. Its consensus algorithm and partnerships with financial institutions contribute to its role in revolutionizing traditional finance.
The decentralized finance (DeFi) movement has propelled tokens like Uniswap (UNI), Aave (AAVE), and Compound (COMP) into the spotlight. These tokens are integral to decentralized lending, borrowing, and liquidity provision within the DeFi space.
Overall, these major cryptocurrencies represent the diverse functionalities required in the Web3 landscape, from store of value and medium of exchange to enabling smart contracts, decentralized applications, and decentralized finance. Their combined impact reflects the dynamic and multifaceted nature of the evolving Web3 ecosystem.
3.Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Web3
Decentralized Finance, often abbreviated as DeFi, stands as a revolutionary force within the broader Web3 ecosystem, reshaping traditional financial systems through blockchain technology. At its core, DeFi refers to a set of financial services and applications built on decentralized networks, primarily blockchain platforms. The distinguishing feature of DeFi lies in its commitment to eliminating intermediaries, providing financial services directly to users, and fostering a more inclusive and accessible global financial system.
Smart contracts, a key component of Web3, play a central role in enabling DeFi applications. These self-executing contracts automate various financial processes, including lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming. Ethereum, as a leading Web3 platform, has been pivotal in the rise of DeFi, hosting a multitude of decentralized applications that operate without traditional banking intermediaries.
DeFi also introduces the concept of yield farming, where users can earn additional tokens by providing liquidity to decentralized platforms. This incentivization mechanism encourages active participation in the ecosystem.
The synergy between DeFi and Web3 represents a paradigm shift in how financial services are conceptualized and delivered. By leveraging blockchain's decentralization, transparency, and security, DeFi not only reduces reliance on traditional financial institutions but also fosters financial inclusivity on a global scale. As the Web3 ecosystem continues to evolve, DeFi is positioned to be a transformative force in shaping the future of finance.
Web3 Protocols
1.IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
IPFS, or the InterPlanetary File System, is a revolutionary protocol designed to create a more efficient and decentralized method of storing and sharing content on the internet. Unlike traditional file systems that rely on centralized servers, IPFS operates on a peer-to-peer network, utilizing a distributed approach to data storage. The fundamental idea behind IPFS is to assign content a unique hash identifier, making it addressable based on its content rather than its location.
In IPFS, files are broken down into smaller chunks, each assigned a cryptographic hash. These chunks are then distributed across a network of nodes, forming a distributed file system. When a user requests a file, the IPFS protocol retrieves the various chunks from the network, reconstructing the file locally. This not only improves redundancy and fault tolerance but also enhances data integrity as the content's hash ensures that it has not been tampered with during retrieval. IPFS is particularly notable for its potential to revolutionize how data is stored and accessed, offering benefits such as increased speed, reduced reliance on centralized servers, and improved censorship resistance. Additionally, IPFS aligns with the principles of Web3 by fostering a more decentralized and resilient internet infrastructure, making it a critical component in the broader movement toward a more open and transparent digital ecosystem. As the Web3 landscape continues to evolve, IPFS remains at the forefront, contributing to the vision of a more robust and decentralized internet.
IPFS is particularly notable for its potential to revolutionize how data is stored and accessed, offering benefits such as increased speed, reduced reliance on centralized servers, and improved censorship resistance. Additionally, IPFS aligns with the principles of Web3 by fostering a more decentralized and resilient internet infrastructure, making it a critical component in the broader movement toward a more open and transparent digital ecosystem. As the Web3 landscape continues to evolve, IPFS remains at the forefront, contributing to the vision of a more robust and decentralized internet.
2.Ethereum and Other Blockchain Protocols
Ethereum stands as a pioneering force in the realm of blockchain technology, distinguishing itself as a decentralized platform beyond its role as a cryptocurrency. Founded on the principles of Web3, Ethereum introduces the concept of smart contracts, self-executing agreements with code governing their execution. This innovation allows developers to create decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum blockchain, facilitating a wide array of functionalities beyond simple peer-to-peer transactions.
In addition to Ethereum, several other blockchain protocols contribute significantly to the diversity and evolution of the Web3 ecosystem. Binance Smart Chain (BSC) emerges as a notable competitor, offering compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and lower transaction fees. Polkadot introduces a multi-chain framework, enabling different blockchains to interoperate and share information seamlessly. Tezos focuses on self-amendment and on-chain governance, allowing the blockchain to evolve without hard forks. Cardano, recognized for its scientific and peer-reviewed approach, emphasizes scalability, sustainability, and interoperability. Solana, with its high-performance architecture, aims to provide fast and cost-effective decentralized applications. Avalanche introduces a consensus mechanism that facilitates sub-second finality, enhancing transaction speed.
Cardano, recognized for its scientific and peer-reviewed approach, emphasizes scalability, sustainability, and interoperability. Solana, with its high-performance architecture, aims to provide fast and cost-effective decentralized applications. Avalanche introduces a consensus mechanism that facilitates sub-second finality, enhancing transaction speed.
Despite the differences, these blockchain protocols share the common goal of decentralization, transparency, and security. Each protocol brings its unique features, fostering competition and innovation within the Web3 ecosystem. As the landscape continues to evolve, the collaboration and compatibility between these protocols contribute to the realization of a more interconnected, decentralized, and user-centric internet.
3.Solidity and Smart Contracts
Solidity serves as a pivotal programming language in the development of smart contracts, playing a central role in the broader Web3 ecosystem. Developed explicitly for the Ethereum blockchain, Solidity enables the creation of self-executing contracts that run on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). These contracts, known as smart contracts, are integral to decentralized applications (DApps) and various other functionalities within the Web3 space.
Solidity's syntax is designed for expressing the logic of smart contracts, incorporating elements from widely-used programming languages such as JavaScript and C++. Developers utilize Solidity to define the rules and conditions under which a smart contract executes. The language supports data structures, libraries, and other features essential for building complex decentralized applications. One of Solidity's distinguishing features is its compatibility with Ethereum's blockchain. Smart contracts written in Solidity can be deployed on the Ethereum network, where they become part of the decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger. This process introduces automation and trustlessness to various sectors, including finance, supply chain, and governance.
One of Solidity's distinguishing features is its compatibility with Ethereum's blockchain. Smart contracts written in Solidity can be deployed on the Ethereum network, where they become part of the decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger. This process introduces automation and trustlessness to various sectors, including finance, supply chain, and governance.
Despite its power and flexibility, Solidity is not without challenges. The potential for vulnerabilities, such as the notorious DAO incident, has led to ongoing improvements and security best practices within the Solidity development community.
In summary, Solidity stands as a crucial tool for developers seeking to build decentralized applications and deploy smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Its role in shaping the landscape of Web3, through secure and transparent programmable agreements, is emblematic of the transformative potential of blockchain technology.






































