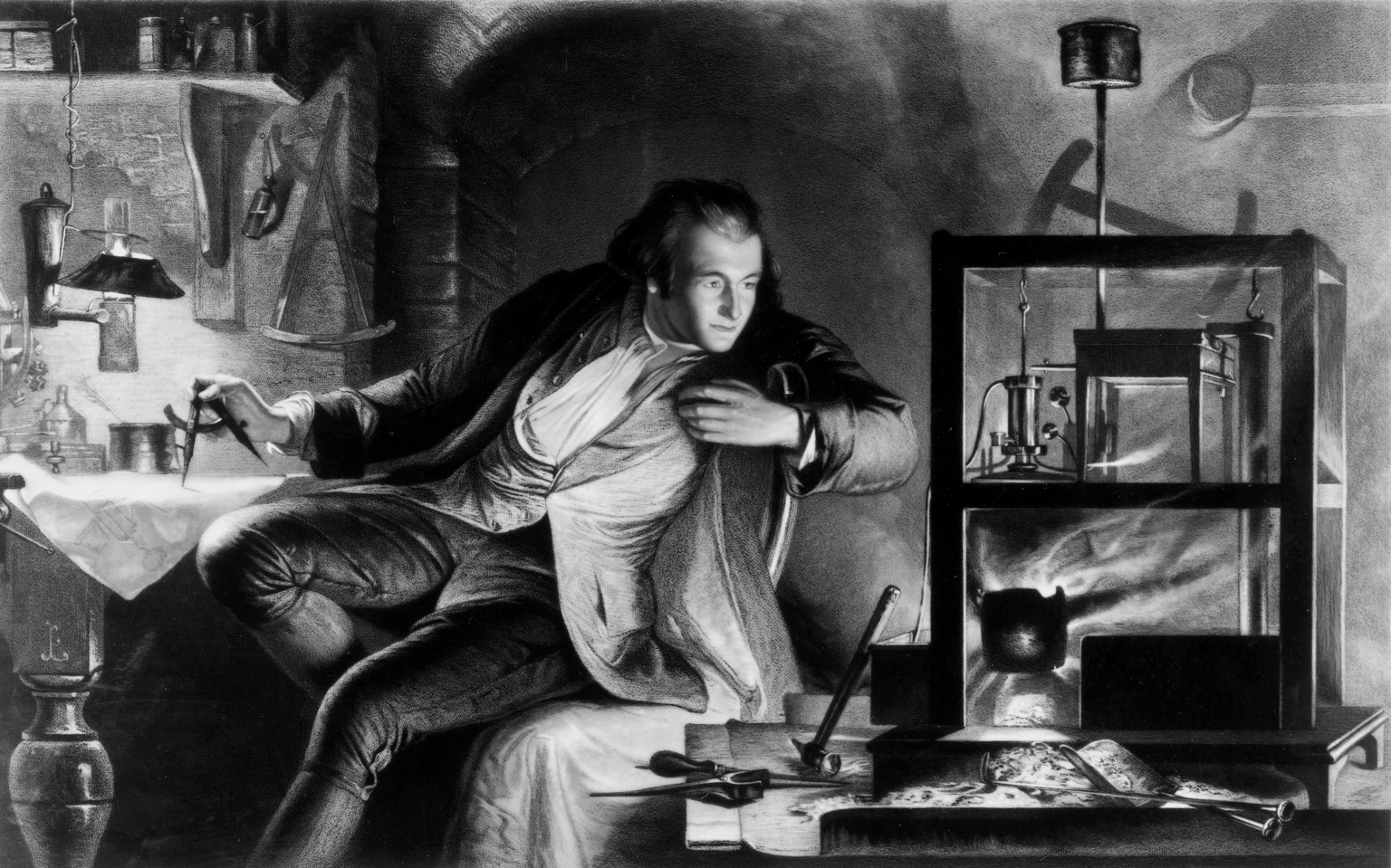
Who is James Watt?
James Watt (1736–1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist, best known for his significant improvements to the steam engine, a key development during the Industrial Revolution. Here is an overview of the story of James Watt:
Early Life and Education:
- James Watt was born on January 19, 1736, in Greenock, Scotland, into a family of relatively modest means.
- He showed an early aptitude for mathematics and engineering.

Steam Engine Improvements:
- In the early 1760s, Watt was employed as an instrument maker at the University of Glasgow, where he encountered the Newcomen steam engine.
- He recognized the inefficiencies of the existing steam engines and set out to improve their design.

Separate Condenser:
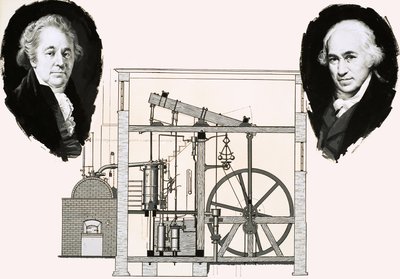
- One of Watt's key innovations was the development of a separate condenser in 1765.
- In the earlier Newcomen engines, steam was condensed in the same cylinder as it was used for power, leading to significant energy losses. Watt's separate condenser improved efficiency by allowing the cylinder and condenser to operate at different temperatures.

Rotary Motion and Double-Acting Engine:
- Watt continued to refine his steam engine design, introducing the rotary motion and the double-acting engine, which produced power on both the up and down strokes.
- These innovations made the steam engine more versatile and applicable to various industrial processes.
Partnership with Matthew Boulton:
- In 1774, Watt entered into a partnership with Matthew Boulton, a Birmingham manufacturer, forming the famous engineering firm Boulton and Watt.
- Boulton provided financial support, and their collaboration led to the widespread adoption of Watt's steam engine.
Patents and Legal Battles:
- Watt secured patents for his steam engine innovations, and the Boulton and Watt firm actively defended these patents.
- Legal battles ensued, and the firm took action against those who attempted to replicate or use the steam engine without proper authorization.
Later Years and Legacy:
- James Watt continued to work on various inventions throughout his life, including improvements to surveying instruments and the development of the watt, a unit of power named in his honor.
- He retired from active business in the early 1800s and died on August 25, 1819, in Heathfield, Staffordshire, England.
James Watt's contributions to the steam engine played a pivotal role in the advancement of industry and transportation during the Industrial Revolution. His innovations had a profound impact on the development of machinery and were crucial to the widespread adoption of steam power. The unit of power, the watt, is named in recognition of his significant contributions to engineering and technology.
Private Life
James Watt, known for his groundbreaking work in steam engine development, had a private life that included personal relationships, family, and various aspects beyond his professional endeavors. Here are some details about James Watt's private life:
Family:
- James Watt was married twice. His first wife was his cousin Margaret Miller, whom he married in 1764. They had two children, but unfortunately, Margaret died in 1773.
- After Margaret's death, Watt married Ann MacGregor in 1776. They had two sons and two daughters.
Children:
- James Watt's children included James Jr., who became a notable engineer and surveyor, and Gregory, who later became a famous geologist.
Health Issues:
- Watt faced various health challenges throughout his life. He suffered from periods of poor health, including bouts of depression and nervousness.
- Despite his health issues, Watt remained dedicated to his work and continued to make significant contributions to engineering.
Personal Interests:
- Beyond his engineering pursuits, Watt had interests in a wide range of subjects. He was known for his intellectual curiosity and involvement in various scientific and philosophical discussions of his time.
Retirement:
- James Watt retired from active business in the early 1800s, allowing him more time for personal interests and family.
While Watt is primarily remembered for his pioneering work in steam engine development and his contributions to the Industrial Revolution, his private life also included the joys and challenges of family, health, and personal interests. His legacy extends beyond the realm of engineering, and the impact of his inventions continues to be felt in the modern world.
https://youtu.be/ecFTXRDm_vA