What is a Money Manager ? Type Of Money Managers
 Investing is a risky and time-consuming process that can either enhance financial stability or lead to significant debt if not managed properly. To avoid considerable losses, a detailed financial plan is a must.
Investing is a risky and time-consuming process that can either enhance financial stability or lead to significant debt if not managed properly. To avoid considerable losses, a detailed financial plan is a must.
However, developing an effective and beneficial investment strategy may require some assistance. Money managers, among others, offer investment advice, day-to-day trading, performance monitoring, and long-term planning services, ensuring that your portfolio is well-managed and not left in serious debt.
What is a money manager, and how do you choose one? Read on because selecting the right expert can significantly impact your financial situation.
Key Takeaways
- A money manager is responsible for handling financial assets for individuals or enterprises.
- Portfolio managers employ various strategies to meet client’s financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Money managers offer their services for a percentage or a commission-based fee.
- To become a financial manager, you should acquire a certain degree of education, as well as have a profound knowledge of the financial markets and relevant certification.
What is a Money Manager?
A money manager, or portfolio or investment manager, is a person or entity responsible for managing financial assets for individuals or institutional investors.
They assist clients in achieving financial goals by buying and selling securities, settling transactions, measuring performance, tracking expenses, creating budgets, managing taxes and reporting to regulators.
Their clients can have different goals, such as ensuring principal safety, maximising returns, or seeking value or growth investments.
A money manager in a corporation provides personalised advice, manages clients’ portfolios, and is responsible for choosing investments with their client’s best interests in mind. These managers may have access to areas of the capital markets that clients may not have.
Money managers handle portfolios for both individuals and organisations and can be found in traditional financial institutions, hedge funds, pension funds, private equity funds, or mutual funds. 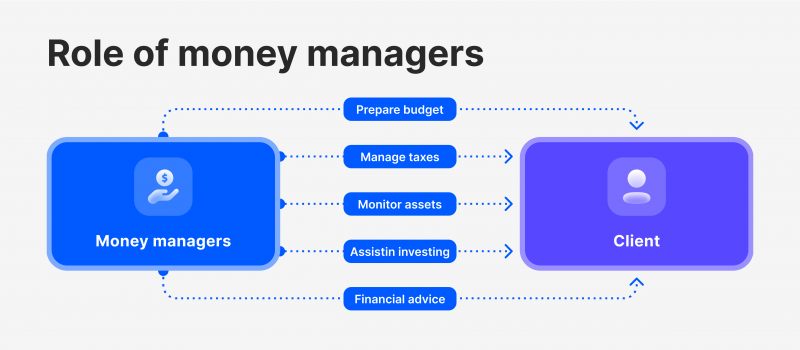 Money managers use various portfolio management schemes to achieve their goals, depending on the type of fund or management style. For instance, mega-funds, like the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, diversify asset classes like equities, fixed income, real estate, infrastructure, and private equity.
Money managers use various portfolio management schemes to achieve their goals, depending on the type of fund or management style. For instance, mega-funds, like the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, diversify asset classes like equities, fixed income, real estate, infrastructure, and private equity.
Those focused on increasing returns may invest in riskier assets. Retail money managers collaborate with clients to understand their goals and risk adversity, creating an investment portfolio. As economic data is released, money managers adjust their portfolios to suit their goals and client’s best interests, as they have a fiduciary responsibility.
Money managers are professionals with a CFA or degree in finance, accounting, economics, or business who analyse financial performance and make better decisions. They use their research skills, expertise, and experience to maximise client benefits.
Famous money managers include Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham, Peter Lynch, and Sir John Templeton, while top investment management firms include Goldman Sachs, BlackRock, USB, Morgan Stanley, Vanguard Group, and J.P. Morgan & Co.
Fast Fact
Types of Money Managers
Money managers have diverse expertise and specialities, with some common types including the following:
Financial Advisors
Financial advisors offer expert guidance on various financial matters, helping clients manage their finances, make informed decisions, and achieve their financial goals.
Mutual Fund Managers
Mutual fund managers manage mutual funds, which are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They select securities, manage the portfolio, and ensure the fund meets its investment objectives.
Asset Managers
Asset managers, acting on behalf of institutions like pension funds, endowments, and foundations, manage investments to optimise returns and manage risk, utilising various asset classes like equities, fixed income, and alternative investments.
Alternative Asset Managers
Alternative asset managers are professionals who manage investments in different asset classes like real estate, private equity, and hedge funds.
Institutional Asset Managers
Institutional asset managers, acting on behalf of institutions like pension funds, endowments, and foundations, manage investment portfolios using their financial market expertise to optimise returns and manage risk for long-term investment goals.
Private Wealth Managers
Private wealth managers manage high-net-worth individuals’ finances, offering services like investment management, financial planning, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management.
Portfolio Managers
Portfolio managers manage investment portfolios, make decisions, and execute trades to achieve clients’ investment objectives. They collaborate with clients to understand their goals and risk tolerance, developing tailored investment strategies.
Investment Fund Managers
Investment fund managers manage mutual funds, ETFs, and hedge funds, making investment decisions on behalf of investors and managing the fund’s assets.
Hedge Fund Managers
Hedge fund managers manage investment vehicles that use various strategies like leverage and short-selling to generate high returns, typically charging performance-based fees.