Contemporary Issues in Environment Globalization and Cross Cultural Issues Globalization
Introduction:
This report aims to provide an overview of contemporary issues in the areas of environment, globalization, cross-cultural issues, public-private partnership (PPP), safety, risk and benefit analysis, and development and environment. It covers key concepts, benefits, effects, and the importance of Public-Private Partnerships, along with discussions on safety, risk, and benefit analysis, and sustainable development.
Globalization and Cross Cultural Issues:
Globalization:
- Definition: Globalization refers to the free movement of goods, services, capital, and information across national boundaries, leading to the integration of regional economies, societies, and cultures through a global network.
- Causes: Advancements in transportation and communication are key drivers.
- Benefits:Increase in innovation
- Rich cultural exchange
- Improved living standards
- High average income
- Access to a global market
- Effects:Permanent economic shift
- Increasing homogeneity
- Job insecurity in developed countries
- Price fluctuations due to competitive markets
- Cultural degradation due to the influence of modern culture

Cross Culture:
- Definition: Cross-culture involves initiatives to understand different groups or societies for effective communication and marketing efforts beyond traditional markets.
- Importance: Successful international trade relies on smooth interactions between employees from different cultures, emphasizing the need for positive cross-cultural experiences.
- Cross-Cultural Competence: Adaptability in cross-cultural environments is crucial for individuals, ensuring effective communication and collaboration.

Public-Private Partnership (PPP):
Definition:
- Public-Private Partnership involves a collaboration between a public sector authority and one or more private sector companies to operate and fund government services or private businesses.

Importance of PPP:
- Efficient and cost-effective development of public sector infrastructure.
- Unique collaborative approach for public management.
- Facilitates globalization by fostering cooperation between the public and private sectors.
- Ensures a balance between risk and reward through a risk-sharing mechanism.
Safety, Risk, and Benefit Analysis:
Safety:
- Definition: Safety refers to protection from various forms of harm, ensuring controlled mechanisms to achieve acceptable risk levels.
- Importance: It is a top priority in engineering product development to prevent harm to individuals or society.
Risk:
- Definition: Risk is the potential that a chosen action will lead to a loss.
- Management: Involves identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and coordinating to minimize, monitor, and control project risks.
- Sources of Risk: Financial uncertainty, project failure, legal liabilities, accidents, natural disasters, etc.
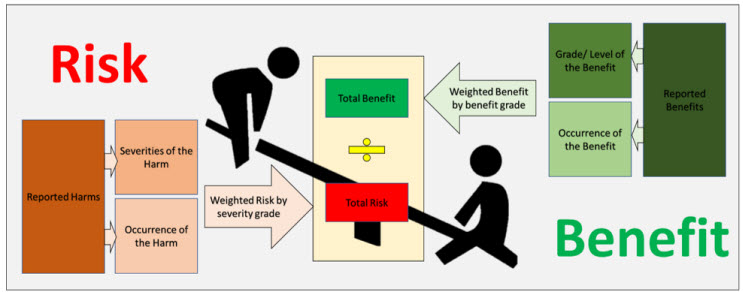
Risk-Benefit Analysis:
- Definition: The analysis compares the risk of a situation to its related benefits.
- Acceptable Risk: Projects are undertaken if the risk is at an acceptable level and yields more benefits.
Development and Environment:
Sustainable Development:
- Definition: Development activities that meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, focusing on both economic growth and environmental concerns.

Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA):
- Definition: Assessment of the positive and negative impacts a proposed project may have on the environment.
- Process: Involves screening, scoping, prediction and mitigation, management and monitoring, and post-implementation audit.

SWOT Analysis:
- Definition: SWOT analysis evaluates Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats in a project, identifying internal and external factors affecting project objectives.
Conflict and Dispute Management:
- Dispute Definition: A dispute occurs when one party's claims or demands contradict the other party's position.
- Resolution Process:Amicable settlement
- Adjudication
- Dispute resolution board
- Arbitration
- Litigation (Court)

- Prevention: Disputes should ideally be settled amicably. If not, an adjudicator or dispute resolution committee should be involved. Arbitration is pursued if satisfaction is not achieved through the initial steps.
Conclusion:
This report provides a comprehensive overview of contemporary issues in the environment, globalization, cross-cultural interactions, public-private partnerships, safety, risk and benefit analysis, and development. The understanding of these concepts is essential for fostering sustainable development, effective conflict management, and global cooperation.



























































