"Taking Steps for the Future of a Planet: Fighting Climate Change and Sustainability"
Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Strategies
Climate change is one of the greatest threats facing our planet. It is causing a number of adverse effects, including global warming, sea level rise, extreme weather events, and droughts. These impacts are putting a great strain on human and natural ecosystems.
Some of the key impacts of climate change include:
- Global warming: The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the Industrial Revolution. This warming is causing glaciers to melt, sea levels to rise, and extreme weather events to become more frequent.
- Sea level rise: Sea levels have risen by about 20 cm during the 20th century. This rise is making coastal areas more vulnerable to flooding and erosion.
- Extreme weather events: Droughts, floods, storms, and hurricanes are becoming more frequent and severe due to climate change. These events are causing significant property damage and loss of life.
- Droughts: Droughts are leading to water scarcity and food insecurity in many regions. Droughts also increase the risk of wildfires.
Adaptation to climate change is necessary to cope with this threat. Adaptation strategies include:
- Building seawalls and levees to protect coastal areas
- Growing drought-resistant crops
- Conserving and using water resources efficiently
- Developing emergency plans and being prepared for disasters
- Investing in clean energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions
 Adaptation to climate change is an urgent priority at the national and international levels. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to address this threat.
Adaptation to climate change is an urgent priority at the national and international levels. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to address this threat.
For more information:
Sustainable Energy Sources and Technologies
 Sustainable energy sources are energy sources that are derived from natural resources that are not depleted or can be replenished. These sources are critical to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable energy sources are energy sources that are derived from natural resources that are not depleted or can be replenished. These sources are critical to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
Some of the key benefits of sustainable energy sources include:
- Environmental friendliness: Sustainable energy sources do not produce greenhouse gas emissions and therefore do not contribute to climate change.
- Renewability: Sustainable energy sources are derived from natural resources and therefore are not depleted.
- Reliability: Sustainable energy sources can increase energy security and reduce countries' dependence on energy imports.

- Solar energy: Solar energy is used to generate electricity from sunlight. Solar panels are used to convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Wind energy: Wind energy is used to generate electricity from the kinetic energy of the wind. Wind turbines are used to convert the power of the wind into electrical energy.
- Hydroelectric energy: Hydroelectric energy is used to generate electricity from the kinetic energy of flowing water. Hydroelectric power plants are used to convert the power of flowing water into electrical energy.
- Geothermal energy: Geothermal energy is used to generate electricity and heat from the heat of the Earth's interior. Geothermal power plants are used to convert the heat of the Earth's interior into electrical and thermal energy.
- Biomass energy: Biomass energy is used to generate electricity and heat from organic matter. Biomass power plants are used to convert organic matter into electrical and thermal energy.
 Sustainable energy technologies are rapidly developing. These developments are making sustainable energy sources cheaper and more efficient.
Sustainable energy technologies are rapidly developing. These developments are making sustainable energy sources cheaper and more efficient.
The transition to sustainable energy is necessary to address climate change and increase energy security. Governments, businesses, and individuals should support this transition by investing in and using sustainable energy sources.
For more information:
Protecting Forests and Managing Renewable Resources:

Forests are vital to our planet. They help to protect biodiversity, regulate the climate, conserve water resources, and prevent soil erosion. They also provide a livelihood and recreation for many people.
However, forests are under many threats:
- Illegal logging: Illegal logging is devastating forests in many parts of the world.
- Forest fires: Forest fires can cause extensive damage to forests and destroy biodiversity.
- Agricultural and urban expansion: The clearing of forests for agricultural land and urban areas is a widespread problem.
- Climate change: Climate change is making forests more vulnerable to drought, insect infestations, and other threats.
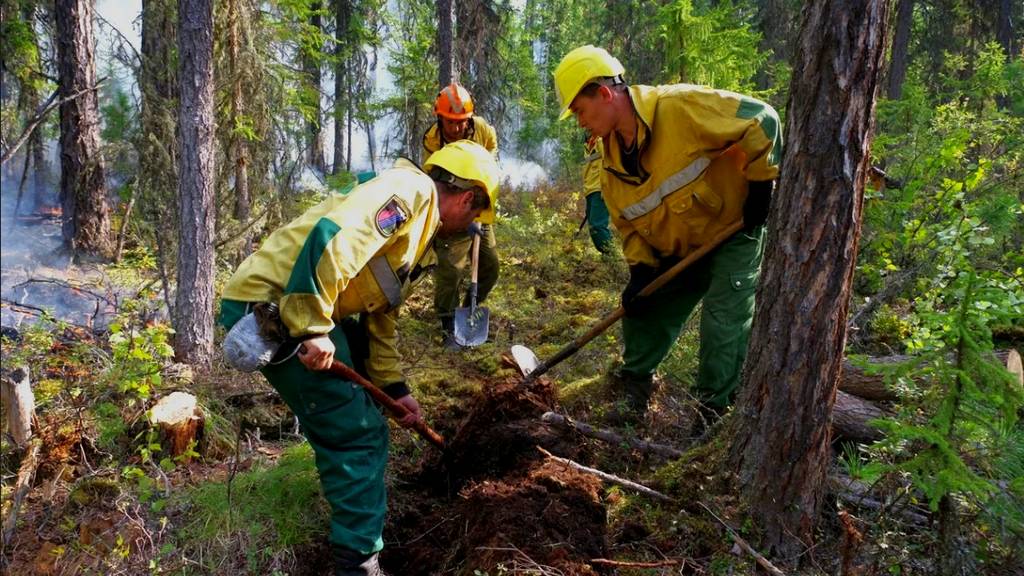 To protect forests and manage renewable resources:
To protect forests and manage renewable resources:
- Sustainable forest management practices: Managing forests sustainably is the best way to ensure their protection for future generations.
- Preventing illegal logging: Governments need to strengthen law enforcement and sanctions to prevent illegal logging.
- Preventing and controlling forest fires: Education and awareness programs are important for preventing and controlling forest fires.
- Reforestation: Reforesting degraded forests can help to restore biodiversity and reestablish the functions of forests.
- Use of renewable energy sources: We need to use renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
Protecting forests and managing renewable resources is everyone's responsibility. We must do all we can to help protect forests and preserve them for future generations.
For more information:
Climate Change and Food Security

Climate change is one of the most significant threats to food security. The effects of climate change, such as drought, floods, storms, and extreme weather events, are negatively impacting agricultural production and food supply.
The impacts of climate change on food security include:
- Reduced agricultural production: Droughts, floods, and extreme weather events are causing significant losses in agricultural production. This can lead to higher food prices and food shortages.
- Water scarcity: Climate change is causing water resources to diminish and droughts to increase. This can lead to less water available for agricultural irrigation and make food production more difficult.
- Soil erosion: Extreme weather events are increasing soil erosion. This reduces soil fertility and negatively impacts food production.
- Increased diseases and pests: Climate change is causing an increase in plant and animal diseases and pests. This damages agricultural production and threatens food security.
 To mitigate the impacts of climate change on food security:
To mitigate the impacts of climate change on food security:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions: It is crucial to take urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the primary cause of climate change.
- Develop adaptation strategies in agricultural production: It is important to develop new methods to grow drought-resistant crops, improve irrigation systems, and reduce risks in agricultural production.
- Prevent food waste: Food waste is a major threat to food security. It is important to raise awareness and promote more efficient use of food resources to prevent food waste.
- International cooperation: Climate change and food security are global problems. International cooperation and solidarity are essential to address these issues.
Understanding the relationship between climate change and food security and taking necessary actions is critical to creating a healthy and sustainable food system for future generations.
For more information:
Protecting the Seas and Oceans:

Seas and oceans cover about 70% of the Earth's surface and are vital to our planet. They harbor a vast majority of biodiversity, regulate the climate, produce oxygen, and provide food.
However, the seas and oceans are under many threats:
- Pollution: Pollutants such as plastic, oil, chemicals, and wastewater are causing significant damage to the seas and oceans.
- Overfishing: Fish stocks are being depleted due to overfishing. This disrupts the balance of the marine ecosystem.
- Climate change: Climate change is causing the seas and oceans to warm and acidify. This poses a great threat to marine life.
 To protect the seas and oceans:
To protect the seas and oceans:
- Preventing pollution: It is important to establish wastewater treatment plants, reduce plastic and chemical use, and avoid dumping waste into the seas to prevent pollution.
- Sustainable fishing: Promoting sustainable fishing practices and preventing overfishing are crucial for the conservation of fish stocks.
- Addressing climate change: Addressing climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions is of critical importance to protecting the seas and oceans.
Protecting the seas and oceans is everyone's responsibility. We must do our part to help protect the seas and oceans and preserve them for future generations.
For more information:
- https://www.greenpeace.org/international/
- https://www.wwf.org/
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/oceans/
Urbanization and Sustainable Urban Planning:

Urbanization is rapidly increasing with the growing world population and the tendency towards urbanization. This puts a significant strain on the infrastructure and resources of cities. Sustainable urban planning is necessary for cities to withstand this pressure and create a livable environment for future generations.
The basic principles of sustainable urban planning are:
- Compact cities: Planning cities in a compact way reduces the need for transportation and energy consumption.
- Protection of green spaces: Preserving green spaces in cities and creating new ones is important for maintaining air quality and biodiversity.
- Promoting public transportation: Encouraging public transportation reduces private vehicle use and traffic congestion.
- Energy efficiency: Designing buildings and infrastructure in an energy-efficient way reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste management: Recycling and reusing waste saves resources and protects the environment.
 Sustainable urban planning helps cities become more livable:
Sustainable urban planning helps cities become more livable:
- Improved air quality: Preserving green spaces and energy efficiency contribute to improved air quality.
- Reduced traffic congestion: Encouraging public transportation and compact cities reduce traffic congestion.
- More green spaces: Preserving green spaces in cities and creating new ones provides more recreational space for residents.
- Lower energy costs: Energy efficiency reduces energy costs in buildings and infrastructure.
Sustainable urban planning is a significant investment in the future of cities. It is important for public, private, and civil society organizations to work together to help cities become more livable and sustainable.
For more information:
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/cities/
- https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview
- https://www.c40.org/
Climate Justice and Social Equity:
 Introduction:
Introduction:
Climate change and social inequality are two of the most important and pressing issues of our time. These two issues are closely linked and must be addressed together.
What is Climate Justice?
Climate justice is a concept that advocates for a fair distribution of the burdens and harms caused by climate change. It focuses on protecting developing countries and poor communities that have historically contributed the least to greenhouse gas emissions and are most affected by the impacts of climate change.
What is Social Inequality?
Social inequality refers to the disparities in income, wealth, education, health, and other areas that exist between different groups in society. These inequalities increase vulnerability to the impacts of climate change.
The Link Between Climate Justice and Social Inequality:
Climate change exacerbates inequalities and disproportionately affects poor and marginalized communities. These communities are often more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and have fewer resources to cope with them.
What Can Be Done for Climate Justice and Social Equity?
- Take urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions: It is necessary to drastically reduce emissions to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
- Provide financial resources to developing countries: Financial resources should be provided to help developing countries adapt to the impacts of climate change and finance mitigation activities.
- Reduce social inequalities: Policies should be developed to reduce inequalities in education, health, and other areas.
- Adopt a sustainable development model: A development model that integrates economic development, social justice, and environmental sustainability should be adopted.
 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
Climate justice and social equity are two important interconnected issues that must be addressed together. It is necessary to take urgent action and work together to build a sustainable future that solves these problems.
Resources:
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/climate-action/
- https://www.greenpeace.org/international/campaigns/climate-change/
Zero Waste and Circular Economy:
Introduction:
Zero waste and circular economy are two critical approaches to protecting our resources and building a sustainable future. These approaches promote preventing waste generation, reusing and recycling generated waste, and using resources in a circular manner.
What is Zero Waste?
Zero waste aims to prevent waste generation and to reuse or recycle generated waste to recover its value. This approach is crucial for conserving resources, preventing environmental pollution, and saving energy.
What is a Circular Economy?
A circular economy is an economic system that aims to keep products and materials in use for as long as possible and preserve their value. This system aims to prevent waste generation, promote reuse and recycling, and use more sustainable methods in production processes.
The Link Between Zero Waste and Circular Economy:
Zero waste and circular economy are two complementary approaches. Zero waste is the foundation of a circular economy. On the other hand, the circular economy provides the necessary tools to achieve the zero waste goal.
What Can Be Done to Transition to Zero Waste and Circular Economy?
- Raising awareness: Education and awareness-raising activities should be carried out to increase awareness and understanding of zero waste and circular economy.
- Making legal arrangements: Laws and regulations should be enacted to promote zero waste and circular economy.
- Providing economic incentives: Economic incentives such as tax breaks and subsidies should be offered to encourage the transition to zero waste and circular economy.
- Utilizing technology: The development and use of new technologies that support zero waste and circular economy should be encouraged.
Conclusion:
Zero waste and circular economy are two essential approaches needed to conserve our resources and build a sustainable future. It is crucial for all stakeholders to cooperate to transition to these approaches.
Resources:
- https://steamcommunity.com/discussions/forum/1/1480982338947210062/
- https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/
Climate Change and Health:
 Introduction:
Introduction:
Climate change is one of the greatest global threats of our time and it has a significant impact on human health. The effects of climate change, such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and water scarcity, lead to various health risks.
Health Impacts of Climate Change:
- Respiratory problems: Air pollution contributes to the increase in respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
- Heat stress: Rising temperatures can lead to heat fatigue, heat stroke, and death.
- Infectious diseases: It causes the spread of infectious diseases such as malaria, dengue, and Zika by expanding the spread of vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks.
- Water-borne diseases: Extreme weather events such as floods and droughts can lead to the spread of water-borne diseases.
- Mental health problems: Climate change can lead to mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
The Role of the Health Sector in Combating Climate Change:
- Raising awareness: Raising awareness among the public and health professionals about the health effects of climate change.
- Conducting research: Researching the health effects of climate change and developing new solutions.
- Putting into practice: Developing and implementing policies and programs to reduce the health effects of climate change.
Conclusion:
Climate change poses a serious threat to human health. The health sector has a significant role to play in combating this threat. We must work to reduce the health effects of climate change by raising awareness, conducting research, and putting it into practice.
Resources:
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-and-health
- https://www.cdc.gov/climateandhealth/effects/default.htm
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/climate-action/
Climate Change Policies and International Cooperation:
 Introduction:
Introduction:
Climate change is a global threat that requires international cooperation to address. In this article, we will examine the importance of climate change policies and how international cooperation can help.
Climate Change Policies:
Climate change policies are policies that aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the effects of climate change. These policies can include:
- Transitioning to renewable energy: Investing in renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
- Increasing energy efficiency: Using energy more efficiently in buildings and industrial facilities.
- Protecting forests: Forests play a vital role in combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Transforming transportation systems: Investing in public transportation and electric vehicles.
The Importance of International Cooperation:
Climate change is a global problem that cannot be solved by any single country. Therefore, it is crucial for countries to work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. International cooperation can provide:
- Knowledge and resource sharing: Countries can share best practices and technologies for combating climate change.
- Setting common goals: Countries can set common goals for limiting global warming and work together to achieve these goals.
- Providing finance: Developed countries can provide financial resources to developing countries to help them adapt to the effects of climate change.
Examples of International Cooperation:
- The Paris Agreement: The Paris Agreement is an international agreement that aims to keep global warming well below 2°C, preferably to 1.5°C, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- The Green Climate Fund: The Green Climate Fund is a fund that provides financial resources to developing countries to help them adapt to the effects of climate change.
Conclusion:
Climate change policies and international cooperation are vital in the fight against climate change. Countries must work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the effects of climate change.
Resources:
- https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paris_Agreement
- https://www.greenclimate.fund/


































































