Electricity Generation Plants
Energy production plants are factory structures that produce electrical energy from various energy sources. These power plants are used to meet electrical energy needs, support industrial processes and meet the electricity demands of society.
Now let's examine the facilities operating according to different energy sources:
Thermal Power Plants
Thermal power plants are facilities that use thermal energy to produce electrical energy. These power plants produce electricity by producing steam, usually using fossil fuels (coal, natural gas or oil) or nuclear energy.
Thermal power plants are generally large facilities and play an important role in meeting energy needs. Thermal energy generated by the burning of fossil fuels provides the production of water vapor. This steam causes a type of turbine to rotate, and as the turbine rotates, electrical energy is produced by a generator. This process involves converting thermal energy into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy. 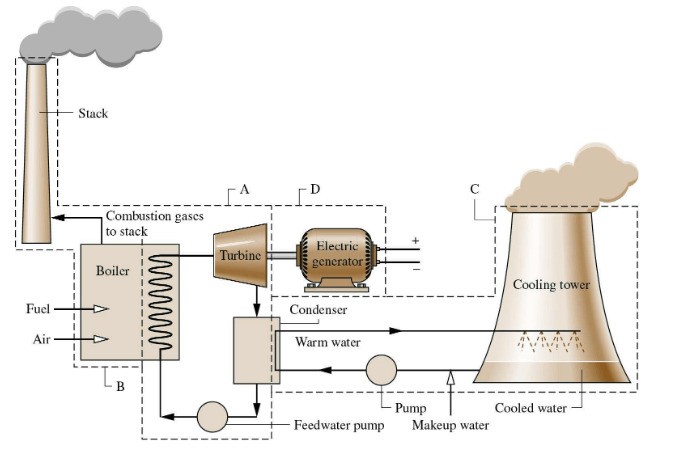
Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants are facilities that produce electrical energy using thermal energy obtained from nuclear fission (splitting of atomic nuclei) reactions. These power plants generally use nuclear fuels such as uranium or plutonium. Nuclear fission reactions release large amounts of energy as atomic nuclei split.
Nuclear power plant operation generally includes these steps:
- Fuel Element: The fuel used in nuclear reactors is usually enriched uranium (usually uranium-235). This fuel is arranged in rods or plates.
- Reactor Core: In the nuclear reactor, fuel elements are brought together and the reaction is controlled through control rods.
- Fission Reactions: Nuclear fission reactions occur as a result of the splitting of uranium nuclei. During these reactions, large amounts of heat and radiation are released.
- Heat Exchanger and Steam Production: The resulting thermal energy is transferred through a heat exchanger and provides steam production. Turbine and Generator: The resulting steam causes a turbine to rotate. As the turbine rotates, a generator operates and electrical energy is produced.
- Cooling System: Excess heat generated in the reactor is controlled through cooling systems. These systems often use water or other coolants.
Nuclear power plants can have high capacity and continuous electricity generation capacity. However, the use of nuclear energy is controversial due to environmental and safety risks. Issues such as the storage of radioactive waste, the possible risks of nuclear accidents, and nuclear weapons proliferation concerns are issues that criticize the use of nuclear energy. Therefore, nuclear energy is a political issue and each country may have a different approach to this issue in its energy strategy.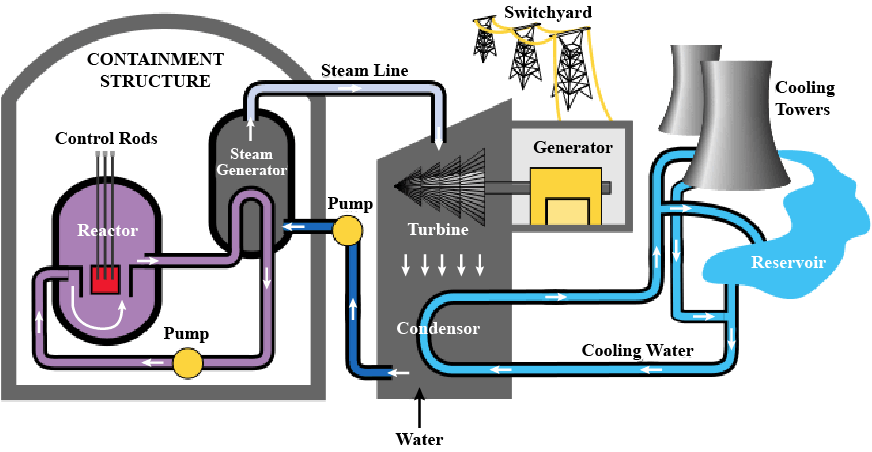
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants are facilities where the kinetic or potential energy of water is converted into electrical energy. These power plants generally take water from rivers or ponds and convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through turbines. Hydroelectric energy is a clean and sustainable source of energy and is considered environmentally friendly.
The operating principle of hydroelectric power plants includes the following steps:
- Water Intake and Elevation Difference: Water is taken from rivers or ponds and this water is accumulated at a high point. This increases the potential energy of water.
- Water Discharge and Turbines: Water is directed to the turbines with the help of control valves. Turbines convert the kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy.
- Generator: Mechanical energy produced by turbines is converted into electrical energy by rotating a generator. The generator produces electric current using a coil rotating in a magnetic field.
- Transformer and Distribution: The produced electrical energy is transmitted by adjusting the voltage level through transformers and then transferred to the energy distribution system.
- Cooling and Recycling: The heat generated during electricity production is generally controlled through cooling systems. After the water passes through the turbines, it can return to the stream or pond, creating a loop.
Hydroelectric power plants have several advantages due to their environmental impact and low greenhouse gas emissions. However, ecosystem changes associated with large dams can also bring about some environmental and social problems, such as water management and displacement of communities. Nevertheless, many countries around the world use hydroelectric energy as an important component of their energy portfolios.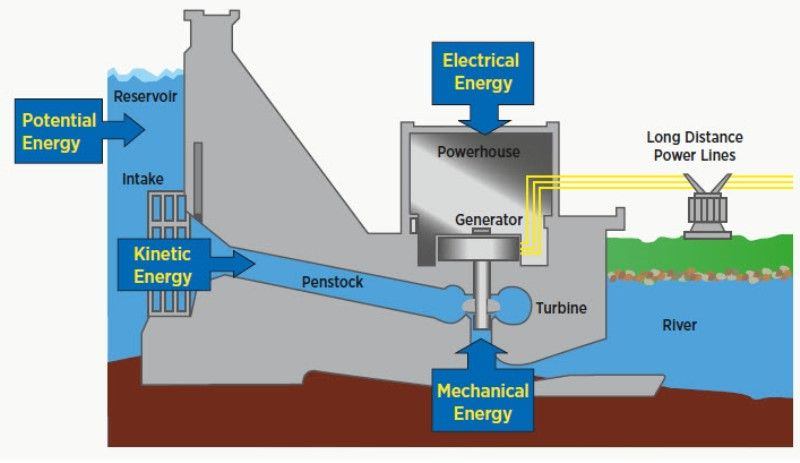
We examined three energy production facilities and their working methods. In our next article: We will examine Wind Power Plants, Solar Power Plants, Geothermal Power Plants, Wave and Tidal Energy Power Plants, Biomass Energy Power Plants.






































































