Evolution of Automotive Technology: From Self-Driving to Sustainable Solutions
Evolution of Automotive Technology: From Self-Driving to Sustainable Solutions
Introduction
The automotive industry has witnessed a remarkable evolution, marked by groundbreaking inventions that have transformed transportation. Among these innovations are self-driving cars, electric vehicles (EVs), and compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles. This article explores the inception, development, and future prospects of these technologies, along with insights into the future of fossil fuels in the automotive sector.
The Invention of Self-Driving Cars
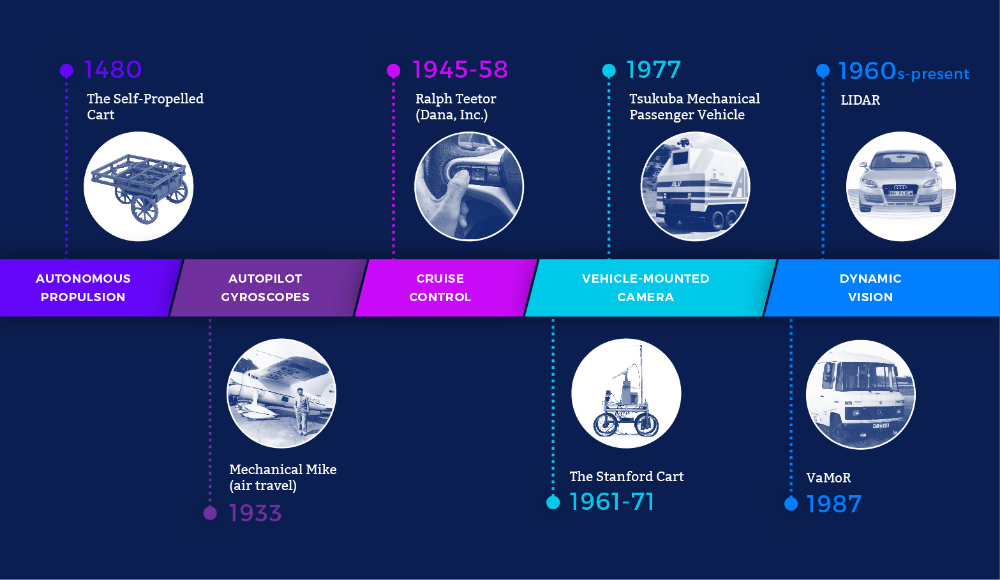
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles (AVs), represent a pinnacle of automotive innovation. The concept of self-driving cars dates back to the 1920s when engineers began exploring automated driving systems. However, significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), sensor technology, and computing power in recent decades have propelled the development of fully autonomous vehicles.
Key Milestones
The DARPA Grand Challenge: In 2004, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) organized the first Grand Challenge, a competition to stimulate the development of autonomous vehicle technology. Although no vehicle completed the course, it laid the foundation for future advancements.
Google's Self-Driving Car Project: Google's Waymo, formerly known as the Google Self-Driving Car Project, emerged as a pioneering effort in autonomous driving. It introduced prototypes equipped with sensors and AI algorithms, demonstrating the feasibility of self-driving technology.
Commercial Deployment: Companies like Tesla, Uber, and General Motors have made significant strides in deploying semi-autonomous and autonomous vehicles for commercial use. These vehicles utilize a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and AI to navigate roads safely.
Future Prospects
The future of self-driving cars holds promises of enhanced safety, reduced congestion, and increased mobility for people with disabilities and the elderly. However, challenges related to regulatory frameworks, cybersecurity, and public acceptance need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles have gained momentum as a sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. The transition to electric mobility aims to mitigate environmental concerns, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Historical Context
The concept of electric vehicles dates back to the 19th century, with early prototypes introduced in the late 1800s. However, the mass adoption of EVs was hindered by limitations in battery technology, range anxiety, and infrastructure challenges.
Key Developments
Technological Advancements: Advances in lithium-ion battery technology have significantly improved the energy density, range, and charging capabilities of electric vehicles. Companies like Tesla have played a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of EV performance and innovation.
Government Initiatives: Governments worldwide have implemented policies to promote electric vehicle adoption, including incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and investment in charging infrastructure.
Market Expansion: The EV market has witnessed rapid growth, with established automakers and new entrants introducing electric models across various vehicle segments. This expansion reflects increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly transportation options.
Future Outlook
The future of electric vehicles hinges on continued advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and cost reduction. With ongoing efforts to decarbonize the transportation sector, EVs are poised to play a central role in achieving these sustainability goals.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Vehicles:
Compressed natural gas vehicles utilize natural gas as a fuel source, offering environmental and economic benefits compared to traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles. CNG is composed primarily of methane and is considered a cleaner alternative fuel.
Advantages of CNG Vehicles
Reduced Emissions: CNG vehicles produce lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter compared to gasoline and diesel vehicles.
Cost Savings: Natural gas prices are often lower and less volatile than gasoline and diesel prices, resulting in potential cost savings for fleet operators and consumers.
Abundance and Accessibility: Natural gas reserves are abundant globally, promoting energy security and reducing dependence on imported oil. Additionally, CNG refueling infrastructure is expanding, facilitating broader adoption of CNG vehicles.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its advantages, the widespread adoption of CNG vehicles faces challenges such as limited refueling infrastructure, higher upfront costs for vehicle conversion or purchase, and concerns about methane leakage and fugitive emissions.
Future Trends
The future of CNG vehicles may be influenced by advancements in renewable natural gas (RNG) production, which involves capturing methane emissions from organic waste sources. RNG has the potential to further reduce the carbon footprint of CNG vehicles and enhance their environmental credentials.
The Future of Fossil Fuels in Automotive Technology
The automotive industry is at a crossroads, grappling with the transition from fossil fuel-dependent vehicles to sustainable alternatives. While fossil fuels continue to power the majority of vehicles on the road, the shift towards electrification and alternative fuels is reshaping the automotive landscape.
Key Trends
Electrification: The electrification of transportation, driven by concerns over climate change and air quality, is accelerating the decline of fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Electric vehicles are projected to gain market share rapidly, particularly as battery costs decline and charging infrastructure expands.
Renewable Fuels: The integration of renewable fuels such as biofuels, hydrogen, and synthetic fuels holds potential for reducing the carbon intensity of transportation. These fuels can be produced from sustainable sources and offer compatibility with existing combustion engine technology.
Carbon Neutrality Goals: Automakers are setting ambitious targets to achieve carbon neutrality across their operations, including vehicle production and fleet emissions. This shift necessitates a transition away from fossil fuels towards cleaner alternatives to meet sustainability objectives.
Conclusion
The automotive industry is undergoing a transformative shift driven by innovations in self-driving technology, electric vehicles, and alternative fuels like compressed natural gas. While challenges remain, the collective pursuit of sustainability and technological advancement is shaping the future of transportation towards a cleaner, more efficient, and interconnected mobility ecosystem.
References
1. Waymo: https://waymo.com/
2. Tesla: https://www.tesla.com/
3. U.S. Department of Energy: https://afdc.energy.gov/
4. International Energy Agency (IEA): https://www.iea.org/topics/transport
5. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): https://www.nrel.gov/vehicles-and-fuels/