AR, VR, MR – Differences and Applications
In the fascinating world of immersive technologies, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are two pillars, each offering different experiences and applications. The latest trend on the market is to combine both functions through Mixed Reality (MR).
This guide delves into these technologies’ essence, highlighting their differences and applications.
Augmented Reality (AR): Combining Physical and Digital World
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a game-changer, blurring the lines between real and virtual worlds. AR enhances our real-world environment by superimposing computer-generated information – images, text, or interactive data – onto our objective worldview.
Let’s dive into what AR is, its myriad applications, and look at some examples of AR glasses pushing this technology’s boundaries.
Understanding Augmented Reality
At its core, Augmented Reality involves overlaying digital content onto the real-world environment. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates an immersive virtual environment, AR enhances reality without replacing it.
This is achieved using various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and specialized AR glasses. AR can be as simple as a text notification or as complex as an interactive 3D model appearing in the physical space around you.
Augmented Reality Applications: Transforming Industries and Experiences
Retail and Shopping: Augmented Reality is revolutionizing the retail experience. Customers can use AR to virtually try on clothes or accessories or see how furniture might look in their homes before purchasing.
Industry: AR is pivotal in Industry 4.0, which denotes manufacturing technologies’ ongoing automation and data exchange. AR serves several crucial functions in industry and manufacturing, like enhanced training and skills development, maintenance and repair, and real-time data visualization.
Education and Training: Broadly understood education and training are the main tasks of AR. Many industrial sectors use augmented Reality to train employees in a structured way in the context of repetitive activities that can be documented thanks to appropriate applications.
Onboarding a new employee using AR glasses is a standard in many organizations.
Healthcare: AR is making strides in healthcare by assisting in complex surgeries, providing real-time data overlay for surgeons, and enhancing patient care with more interactive and personalized treatment plans.
Tourism and Travel: Tourists can use augmented Reality for enhanced travel experiences, such as interactive maps, historical information overlayed on landmarks, and real-time translation of signs and menus.
Games and Entertainment: AR games such as the popular Pokémon GO have already demonstrated the potential of Augmented Reality in creating immersive gaming experiences. In entertainment, AR can bring stories to life in the user’s environment, creating a more immersive experience.
Arts and Culture: In 2021, the National Museum of Natural History in Paris introduced an augmented reality experience as part of the “REVIVRE” project. Visitors could encounter virtual representations of extinct animals. Such an undertaking greatly inspires Augmented Reality’s broader use in art museums.
Examples of AR Glasses: The Pioneers of Augmented Reality
Microsoft HoloLens 2: The HoloLens 2 is one of the most well-known AR headsets for various gaming and industrial applications. It offers a high-quality Augmented Reality experience with advanced features like gesture recognition and spatial mapping.
RealWear Navigator 520: The RealWear Navigator 520 is an industrial-grade wearable computer designed primarily for frontline workers in various industries, such as manufacturing, field services, and construction. It’s a head-mounted device that combines robust construction with advanced technology to assist workers in hands-free operations.
To use AR, in many cases, a smartphone or tablet is enough – appropriate software allows you to use everyday tools to enter Augmented Reality.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is not just a technological novelty; it’s a tool transforming how we interact with the world around us. From enhancing everyday experiences to revolutionizing professional industries, AR is opening up new possibilities and redefining Reality as we know it.
As AR technology evolves, we can anticipate more innovative applications and immersive experiences, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms.
Virtual Reality (VR): Immersing in New
Digital Dimensions
In advanced technology, virtual Reality (VR) has created immersive digital environments distinct from our physical world. VR immerses users in a wholly digital experience, differing significantly from Augmented Reality (AR), which blends real and virtual worlds.
Let’s explore the intricacies of VR, its diverse applications, and some leading VR headsets that are redefining the boundaries of this technology.
Delving into Virtual Reality
Defining VR
Virtual Reality encompasses the creation of immersive digital, new environments that users can interact with, typically using VR headsets. Unlike AR, which enhances the real world, the VR experience replaces the natural environment with a virtual one, completely depriving us of contact with the outside world.
Technology Behind VR
VR technology uses headsets with special screens and sound systems, often including hand controllers, to provide a fully interactive experience. These devices track the user’s movements and adjust the virtual environment in real-time, creating a sense of presence in the digital world.
Applications of VR: Broadening Horizons Across Sectors
Gaming and Entertainment: VR has revolutionized gaming and entertainment, offering unparalleled immersion. Users can experience being in the heart of the action, exploring virtual worlds, and interacting with digital characters in ways never before possible.
Education and Simulation: VR provides immersive learning experiences in education, making complex subjects more accessible and engaging. It’s widely used in virtual vocational training, offering a risk-free environment to develop skills.
Therapy and Rehabilitation: VR is increasingly used in therapeutic settings, such as treating phobias or PTSD, by exposing patients to controlled virtual environments.
Virtual Travel and Exploration: VR allows users to explore distant locations or historical sites from their homes, opening up new possibilities for virtual tourism and exploration.
Leading VR Headsets: Pioneering the Virtual Experience
Meta Quest 2: The Meta Quest 2, formerly known as the Oculus Quest 2, is a popular standalone virtual reality (VR) headset. Its versatility and user-friendly design make it accessible to many users, from casual gamers to VR enthusiasts.
Valve Index: The Valve Index is a high-end virtual reality (VR) headset developed and produced by Valve Corporation. It’s known for its impressive specifications and features that cater to VR enthusiasts and gamers looking for a premium VR experience.
Oculus Rift S: The Oculus series, including the Rift and Quest, are among the most popular VR headsets. They offer high-quality graphics, precise tracking, and a vast library of games and applications.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality represents a leap into new digital dimensions, offering experiences that were once the realm of science fiction. From gaming to education, therapy, and beyond, VR is not just altering our entertainment options; it’s changing how we learn, experience, and interact with the world.
Mixed Reality (MR): A Hybrid of Real and Virtual
Mixed Reality (MR) has emerged as a groundbreaking development, seamlessly merging the physical and digital worlds. Building upon the foundations of Augmented Reality (AR), MR overlaps digital content onto the natural world and allows for interaction between digital and physical elements. This fusion creates a hybrid environment where virtual and real-world elements coexist and interact in real time.
Let’s explore the fascinating world of MR, its diverse applications, and some pioneering MR devices that are expanding the horizons of this technology.
Understanding Mixed Reality
The Essence of MR
Mixed Reality (MR) combines Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) best. While AR overlays digital content onto the real world, and VR immerses the user in a completely virtual environment, MR blends these two, creating interactive environments where physical and digital objects coexist and interact.
Technological Framework
Mixed Reality is experienced through advanced headsets and glasses with sensors, cameras, and sophisticated software. These devices track the user’s movements and the physical environment, integrating this information to create interactive, immersive experiences.
Applications of MR: Transforming Realities Across Sectors
Industrial Design and Manufacturing: MR is revolutionizing industry design and production processes. Engineers and designers can interact with 3D models of their creations, making adjustments and seeing their effects in real time.
Healthcare and Medical Training: Mixed Reality (MR) enhances medical training and surgeries by providing doctors with interactive 3D visualizations of the human body. Surgeons can practice procedures in a mixed reality environment before performing actual surgeries.
Education and Training: MR offers an interactive and immersive learning experience, allowing students to engage with educational content in a more hands-on way. This technology benefits technical and scientific education, where understanding complex concepts is crucial.
Gaming and Entertainment: MR is taking gaming and entertainment to new levels, allowing users to interact with digital content within their physical space offering a more immersive and interactive experience.
Retail and Commerce: Mixed Reality (MR) can enhance the shopping experience by allowing customers to visualize products in their natural environment and interact with them before purchasing.
Leading MR Devices: Pioneering a New Reality
Oculus Meta Quest 3: Quest 3 is a professional glass with the most powerful processor. The glasses enable you to intelligently understand and interact with objects in physical space with new and improved mixed reality features.
Magic Leap: Magic Leap has made headlines with its advanced MR headset, designed for various applications, from gaming to professional use. Its ability to create lifelike digital objects interacting with the physical environment is awe-inspiring.
Apple Vision Pro: The Apple Vision Pro MR glasses represent a significant step forward in mixed reality technology. These glasses blend augmented and virtual Reality, offering users a highly immersive experience. Apple Vision Pro uses a breakthrough ultra-high-resolution display system with 23 million pixels across two displays, more than a 4K TV for each eye, offering incredible sharpness and clarity.
Conclusion
Mixed Reality is not just a technological innovation but a transformative experience that blurs the lines between the physical and digital worlds. It combines AR and Virtual Reality applications and is becoming a new trend in the technology market.
From streamlining professional workflows to revolutionizing entertainment and education, MR opens up new possibilities for interaction and immersion.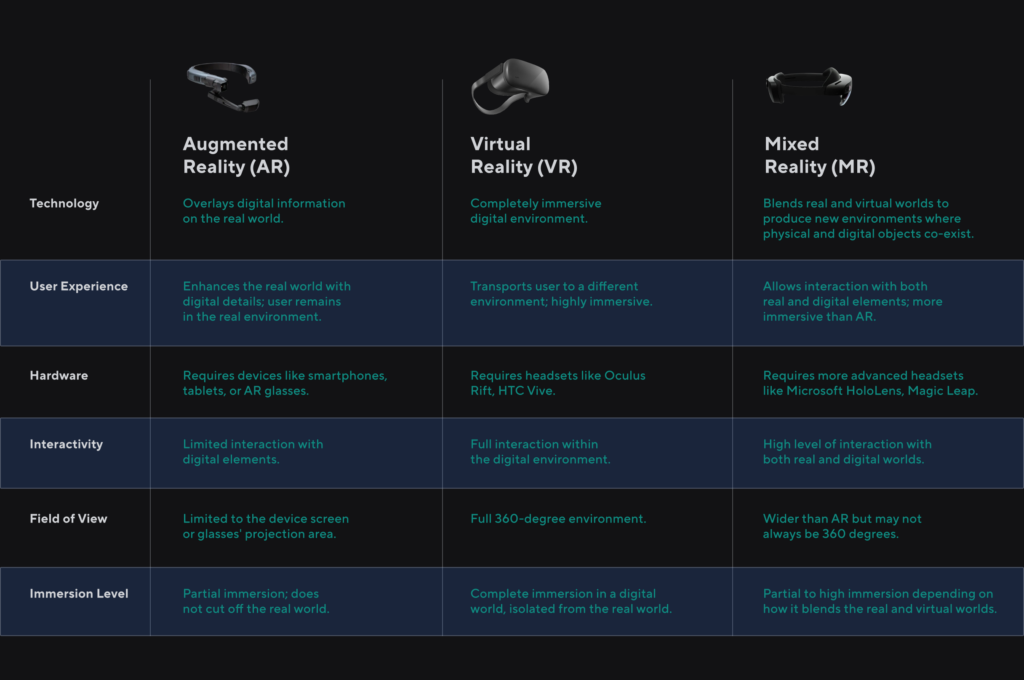
AR, VR, MR: Differences in Equipment
Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are three immersive technologies, each with unique characteristics and equipment. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Augmented Reality (AR)
- AR typically uses devices like smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens 2, Google Glass).
- These devices are generally less bulky and more integrated with everyday tech than VR and MR.
- AR glasses or headsets have transparent lenses that allow users to see the real world while overlaying digital information.
Virtual Reality (VR)
- VR requires headsets that completely cover the eyes (e.g., Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR).
- These headsets are often tethered to a computer or gaming console, though standalone versions like Oculus Quest are available.
- VR equipment includes controllers or gloves for interacting within the virtual environment. The main goal of VR is to provide entertainment in the form of immersion in the digital world.
Mixed Reality (MR)
- MR combines elements of AR and VR, using headsets like Apple Vision Pro or Oculus Meta Quest 3
- These headsets have transparent, see-through displays allowing interaction with virtual environments.
- MR devices are typically equipped with more advanced sensors and cameras for spatial mapping and physical object recognition, and moving between the physical and digital worlds is done through options on the device.
Conclusion
While AR, VR, and MR have overlapping qualities, they each offer unique experiences:
- AR enhances the real world with digital overlays and is the most accessible.
- VR provides an entirely immersive virtual experience, often used for gaming and simulations.
- MR blends real and virtual worlds, allowing interactions with digital objects as if they were real, and is particularly useful for professional and educational applications.
As technology advances, the lines between these technologies might blur, leading to more integrated and sophisticated immersive experiences.



















![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - Is Trump Dying? Or Only Killing The Market?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/a129e75e-4fa1-46cc-80b6-04e638877e46/1)







































