Isaac Newton: The Genius Who Transformed Science
Isaac Newton, one of the most brilliant minds in human history, stands as a towering figure in the realms of physics, mathematics, and astronomy. His groundbreaking contributions laid the foundation for modern science, revolutionizing our understanding of the universe. Through his meticulous observations, rigorous experiments, and groundbreaking theories, Newton transformed the way we perceive the world around us. In this exploration, we delve into the life, achievements, and enduring legacy of this extraordinary polymath. Born on January 4, 1643, in Woolsthorpe, England, Isaac Newton's early life was marked by hardship and adversity. His father died before his birth, leaving his mother to raise him in modest circumstances. Despite these challenges, Newton displayed exceptional intellectual curiosity from a young age, showing a keen interest in mechanical devices and scientific phenomena.
Born on January 4, 1643, in Woolsthorpe, England, Isaac Newton's early life was marked by hardship and adversity. His father died before his birth, leaving his mother to raise him in modest circumstances. Despite these challenges, Newton displayed exceptional intellectual curiosity from a young age, showing a keen interest in mechanical devices and scientific phenomena.
Newton's academic journey began at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he immersed himself in the study of mathematics and natural philosophy. His brilliance quickly became apparent, and he was appointed Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the age of just 26. It was during this time that Newton made his groundbreaking discoveries in optics, formulating his theory of colors and inventing the reflecting telescope, which revolutionized astronomical observation. However, it was Newton's work in mechanics and gravitation that would cement his place in history. In 1687, he published his magnum opus, the "Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica" (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), commonly known as the Principia. In this monumental work, Newton laid out his laws of motion and universal gravitation, providing a mathematical framework that explained the motion of celestial bodies and earthly objects alike. The Principia remains one of the most influential scientific texts ever written, shaping the course of physics for centuries to come.
However, it was Newton's work in mechanics and gravitation that would cement his place in history. In 1687, he published his magnum opus, the "Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica" (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), commonly known as the Principia. In this monumental work, Newton laid out his laws of motion and universal gravitation, providing a mathematical framework that explained the motion of celestial bodies and earthly objects alike. The Principia remains one of the most influential scientific texts ever written, shaping the course of physics for centuries to come.
Newton's laws of motion, encompassing concepts such as inertia, force, and acceleration, laid the groundwork for classical mechanics, providing a unified explanation for the behavior of objects in motion. His law of universal gravitation, which states that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics.
Newton's influence extended far beyond the realm of academia. As President of the Royal Society and Master of the Mint, he played a central role in shaping the scientific and intellectual landscape of his time. His work laid the foundation for the scientific revolution, inspiring generations of scientists and thinkers to explore the mysteries of the natural world.
Despite his towering intellect and prodigious achievements, Newton was a complex and enigmatic figure, prone to fits of temper and bouts of melancholy. He lived a largely solitary existence, consumed by his work and driven by an insatiable thirst for knowledge. Yet, behind the facade of the austere scientist lay a deeply spiritual man, whose belief in a divine creator informed his understanding of the universe. Isaac Newton's legacy endures to this day, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and inspiring future generations to push the boundaries of human knowledge. His profound insights into the laws of nature laid the groundwork for the scientific revolution, paving the way for centuries of progress and discovery. As we gaze upon the stars and contemplate the mysteries of the universe, we owe a debt of gratitude to the towering intellect of Isaac Newton, the man who transformed our understanding of the world.
Isaac Newton's legacy endures to this day, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and inspiring future generations to push the boundaries of human knowledge. His profound insights into the laws of nature laid the groundwork for the scientific revolution, paving the way for centuries of progress and discovery. As we gaze upon the stars and contemplate the mysteries of the universe, we owe a debt of gratitude to the towering intellect of Isaac Newton, the man who transformed our understanding of the world.
Newton's impact extended well beyond his lifetime, shaping not only the course of science but also influencing philosophy, theology, and the broader cultural landscape. His emphasis on empirical observation and mathematical rigor set a new standard for scientific inquiry, ushering in an era of unprecedented progress and discovery.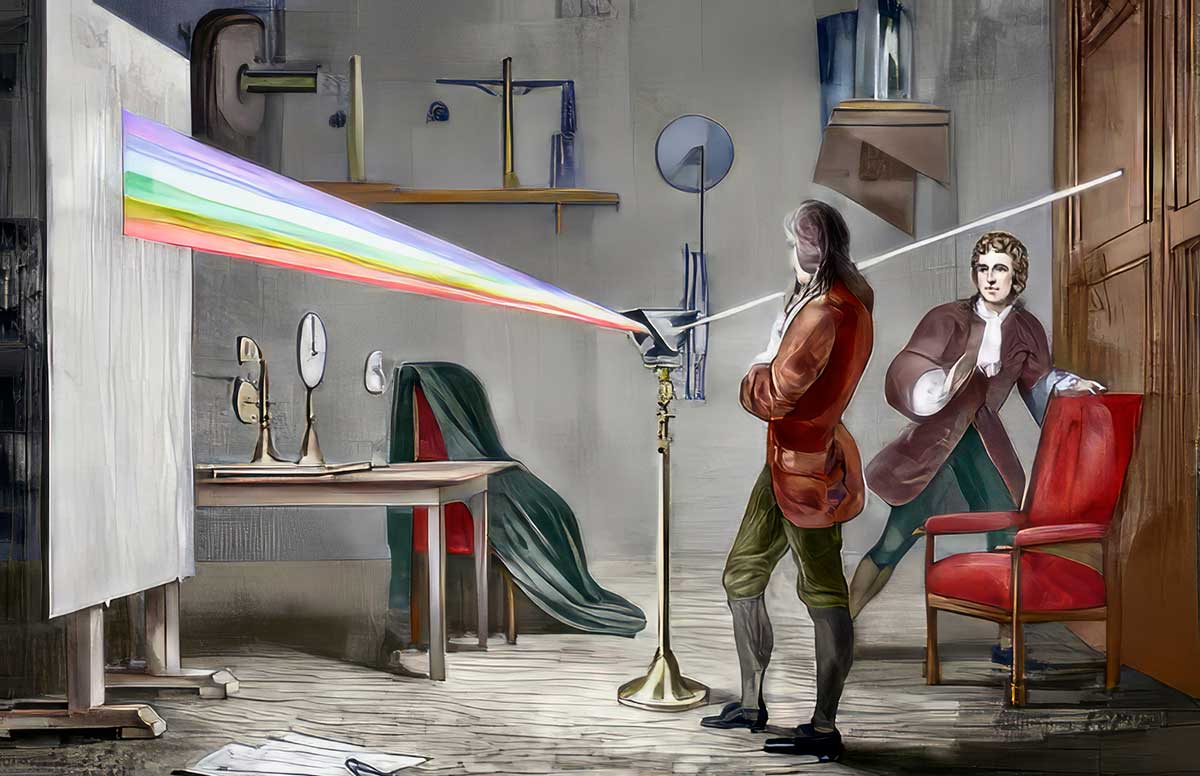 One of Newton's enduring legacies is his conception of the universe as a vast, ordered system governed by precise mathematical laws. His mechanistic worldview, which viewed the cosmos as a giant machine operating according to deterministic principles, laid the groundwork for the modern scientific worldview. By demonstrating that the same laws of motion and gravitation govern both earthly and celestial phenomena, Newton demolished the traditional distinction between the terrestrial and celestial realms, ushering in a new era of scientific inquiry.
One of Newton's enduring legacies is his conception of the universe as a vast, ordered system governed by precise mathematical laws. His mechanistic worldview, which viewed the cosmos as a giant machine operating according to deterministic principles, laid the groundwork for the modern scientific worldview. By demonstrating that the same laws of motion and gravitation govern both earthly and celestial phenomena, Newton demolished the traditional distinction between the terrestrial and celestial realms, ushering in a new era of scientific inquiry.
Newton's work also had profound implications for our understanding of human nature and the nature of reality itself. His deterministic worldview, which posited that the universe operates according to fixed laws that can be understood through reason and observation, challenged traditional notions of divine intervention and supernatural agency. By emphasizing the power of human reason to unlock the secrets of the universe, Newton paved the way for the Enlightenment and the rise of modern science. Yet, despite his towering intellect and unparalleled contributions to human knowledge, Newton was also a deeply flawed and complex individual. His intense rivalry with fellow scientists, including Robert Hooke and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, often descended into acrimony and petty squabbling. His dogged pursuit of intellectual dominance sometimes led him to prioritize personal vendettas over the pursuit of scientific truth.
Yet, despite his towering intellect and unparalleled contributions to human knowledge, Newton was also a deeply flawed and complex individual. His intense rivalry with fellow scientists, including Robert Hooke and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, often descended into acrimony and petty squabbling. His dogged pursuit of intellectual dominance sometimes led him to prioritize personal vendettas over the pursuit of scientific truth.
Moreover, Newton's views on theology and metaphysics were often at odds with his scientific principles. Although he believed in a divine creator who had designed the universe according to rational principles, he also harbored unorthodox beliefs, such as his rejection of the doctrine of the Trinity and his fascination with alchemy and biblical prophecy. Newton's complex relationship with religion reflects the tensions between faith and reason that have animated Western thought for centuries.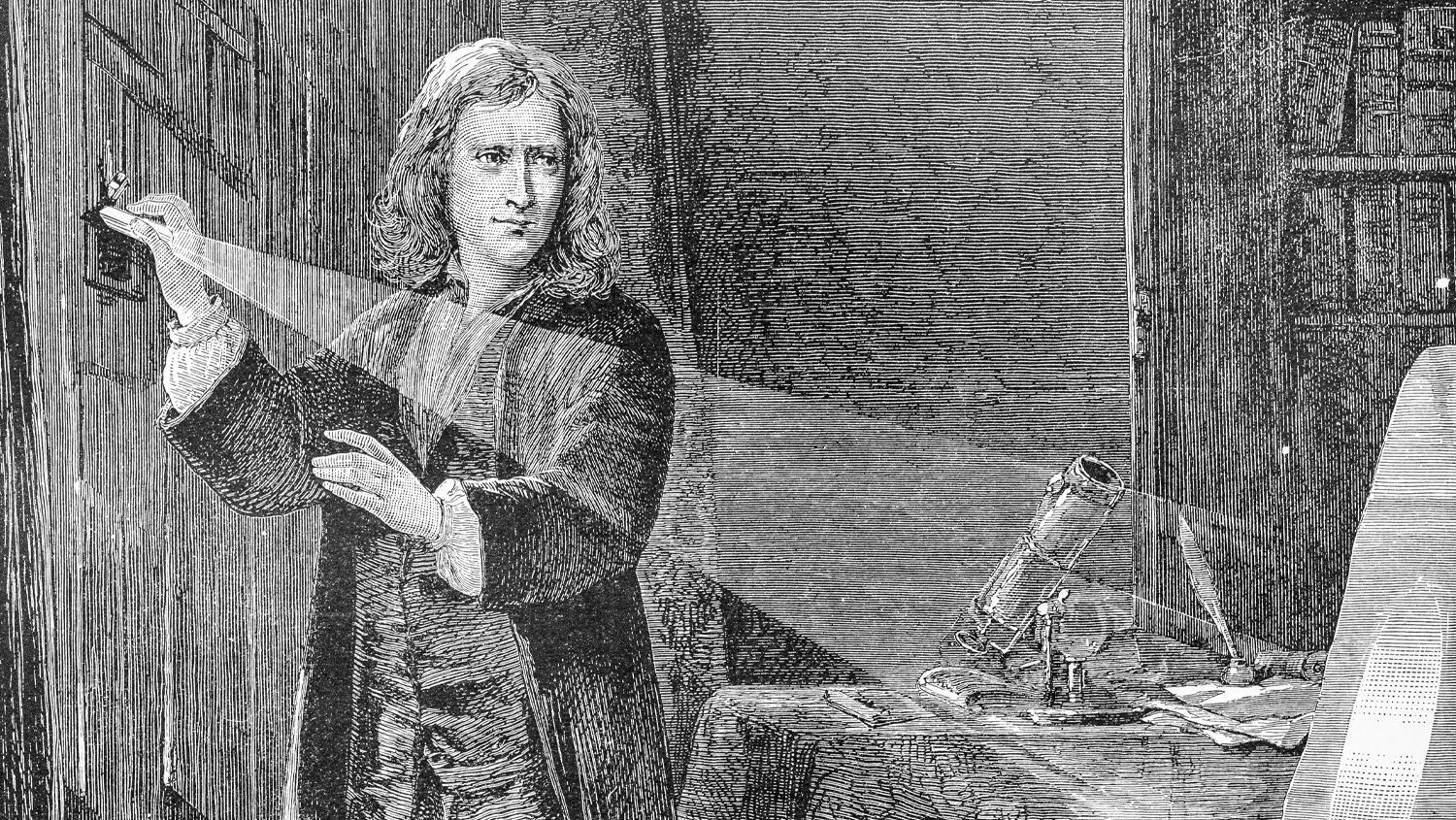 Nevertheless, Newton's profound impact on the course of human history cannot be overstated. His towering intellect, groundbreaking discoveries, and relentless pursuit of knowledge transformed our understanding of the universe and laid the foundation for the modern scientific revolution. As we continue to grapple with the mysteries of the cosmos and strive to unlock the secrets of the natural world, we stand on the shoulders of giants like Isaac Newton, whose legacy continues to inspire and enlighten us to this day.
Nevertheless, Newton's profound impact on the course of human history cannot be overstated. His towering intellect, groundbreaking discoveries, and relentless pursuit of knowledge transformed our understanding of the universe and laid the foundation for the modern scientific revolution. As we continue to grapple with the mysteries of the cosmos and strive to unlock the secrets of the natural world, we stand on the shoulders of giants like Isaac Newton, whose legacy continues to inspire and enlighten us to this day.