The Impact of Sugar on Health and Well-being
10
The Bittersweet Effects of Sugar
Sugar is hard to resist. Yet many of us eat and drink far more of the sweet stuff than we should without realizing the health implications. This article explores some of the notable effects that high sugar intake has on the body and mind.
- Hooking Our Brains: When you take a bite of a glazed doughnut or sip a soda, sugar sparks activity in the reward centers of your brain. You likely feel an initial rush of pleasure as your brain is bathed in feel-good dopamine. Food manufacturers have capitalized on sugar’s ability to hijack this neural circuitry, using sweeteners to make products more crave-worthy and addictive.
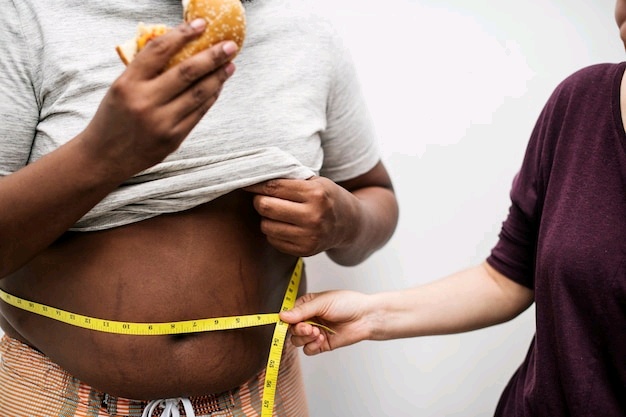
- Padding On The Pounds: The pleasurable high caused by sugar usually fades fast, leaving you feeling hungry as blood sugar plummets. This sets off a vicious cycle of sugar cravings and energy crashes that can easily lead to weight gain over time. Studies show people who consume more added sugar tend to carry more visceral fat – the dangerous kind that wraps around organs deep in the belly. This raises risks for chronic illness.
- Tooth Decay And Gum Disease: Bad bacteria thrive on the sugars left behind after you eat that red velvet cupcake or candy bar. The bugs release acids that erode tooth enamel and irritate gums. So a high-sugar diet promotes tooth decay, cavities, gum inflammation and eventual tooth loss if not treated promptly.
- Skin Woes: That refined sugar rush also spells trouble for your complexion. Sugary foods lead to spikes in blood glucose and insulin, which can stimulate oil production and inflammation. The result can be more frequent acne breakouts and accelerated skin aging over time due to glycation, the sticking of sugars to collagen fibers.
- Inflammation And Disease: A diet high in added sugar can trigger widespread inflammation, a known catalyst for most chronic diseases. Eating lots of sweets repeatedly floods the liver with fructose, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Excess sugar also makes blood more viscous and abrasive to artery walls. This raises risks for high blood pressure, atherosclerosis and subsequent heart attack or stroke.
- Mood Swings: There’s no denying a sugary pick-me-up can provide a short-term mood boost and energy lift. But you pay for it later when that surge fades, plummeting your mood and energy levels. Studies also link high sugar consumption to poorer mental health including higher risks for depression and anxiety disorders compared to people who avoid added sweeteners.
The Bitter Truth
While satisfying a sweet tooth may start as a neurological delight, overdoing sugar sets off a cascade of negative effects in the body and brain. Consuming added sweeteners sparingly is key to avoiding addictive eating behaviors, obesity, chronic illness, cognitive declines and mood disorders over the long-term. When a sugar craving strikes, reach for a naturally sweet whole food like fruit instead. Your body and mind will thank you.