Future Technology: The Journey of Innovation
Technology, as a rapidly evolving field, continues to shape future transformations. Here are some important points about the technology of the future:
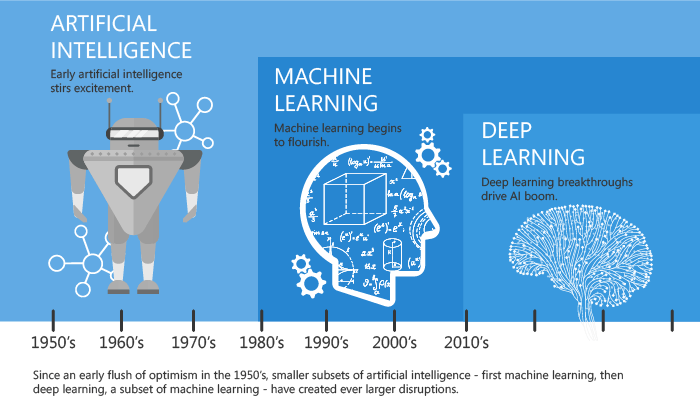
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (MO) are used to provide learning and decision-making capabilities to computer systems. In the future, the capabilities of AI and MO to handle more complex tasks will increase, having major impacts on many industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, etc.
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are making significant impacts across various sectors.
1. Healthcare Sector:
AI is transforming the healthcare sector in various areas, from disease diagnosis to treatment planning. For instance, deep learning algorithms can enhance expertise in medical imaging, providing faster and more accurate diagnoses.
2. **Industrial Automation:** AI and robotic systems can increase industrial process automation, improving production efficiency and enabling humans to focus on more complex tasks.
3. Automotive Industry:
The technology behind autonomous vehicles relies on the integration of AI and sensors. This can enhance traffic safety and make transportation more efficient.
4. Financial Services:
AI is applied in the finance sector for fraud detection, optimizing trading strategies, and personalizing customer services.
5. Education:
AI is used to assess student performance and provide personalized learning experiences.
6. Natural Language Processing:
Developments in understanding and generating language are utilized in various applications such as virtual assistants, language translation, and customer service.
AI has the potential to offer advantages in nearly every industry, shaping the future technological transformation. However, it is crucial to address ethical and security considerations along with these advancements.
2. Quantum Computers:
Quantum computers have the potential to perform calculations at astronomical speeds compared to traditional computers. This technology could revolutionize fields such as encryption, materials science and artificial intelligence.
Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize computing by performing complex calculations at speeds previously unimaginable.
1. Unprecedented Processing Power:
Quantum computers can handle highly complex computations exponentially faster than traditional computers. This capability opens doors to solving problems in fields like cryptography, material science, and optimization in ways that were once thought impractical.
2. Cryptography and Security:
Quantum computing threatens traditional cryptographic methods. On the flip side, quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms are being developed to secure information in the age of quantum computers.
3. Simulation and Modeling:
Quantum computers excel in simulating quantum systems, allowing scientists to better understand and design new materials, drugs, or even study complex biological processes with remarkable precision.
4. Financial Modeling:
Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data simultaneously can enhance financial modeling, optimizing investment portfolios and risk management strategies.
5. Supply Chain Optimization:
Quantum computers can efficiently handle complex optimization problems, such as supply chain management, leading to more efficient distribution, reduced costs, and improved overall performance.
6. Artificial Intelligence:
Quantum computing has the potential to enhance machine learning algorithms, enabling quicker data processing and more sophisticated pattern recognition.
Quantum computers represent a new frontier in computing, promising groundbreaking applications across various disciplines. As research and development progress, quantum computers may become integral in solving challenges that are currently beyond the reach of classical computing.
3. Internet of Things (IoT):
The Internet of Things allows devices to communicate with each other and exchange data. In the future, IoT will bring greater integration and effective use in many areas, from smart cities to the healthcare sector.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technological landscape where interconnected devices communicate and share data, leading to a multitude of applications across diverse sectors.
1. Smart Homes:
IoT devices enable the creation of smart homes, where interconnected appliances, lighting, heating, and security systems can be controlled and monitored remotely through smartphones or other devices.
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT):
In manufacturing and industry, IoT facilitates the implementation of smart factories. Sensors and devices collect real-time data, optimizing production processes, predicting equipment failures, and enhancing overall efficiency.
3. Healthcare Monitoring:
Wearable devices and medical sensors connected to the IoT provide continuous health monitoring. This allows for remote patient care, early detection of health issues, and personalized treatment plans.
4. Smart Cities:
IoT plays a crucial role in the development of smart cities. Connected infrastructure, such as smart traffic lights and waste management systems, contributes to improved energy efficiency, reduced congestion, and enhanced public services.
5. Agriculture:
IoT devices in agriculture, often referred to as "smart farming," monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. This data-driven approach helps farmers optimize irrigation, fertilization, and overall crop management.
6. Logistics and Supply Chain:
IoT enhances logistics and supply chain management by providing real-time tracking of goods, optimizing routes, and ensuring the integrity of transported products through sensors and monitoring devices.
The IoT ecosystem continues to expand, fostering innovation and improving efficiency across various domains. As the number of connected devices grows, so does the potential for transformative impact on how we live, work, and interact with the world
4. BioTechnology and Genetic Editing:
Biotechnology and genetic editing are used in a wide range of areas, from the treatment of diseases to genetic improvements for plants and animals. This field can lead to revolutionary changes in the healthcare industry.
Advancements in biotechnology and genetic editing have far-reaching implications for fields ranging from medicine to agriculture, unlocking new possibilities and ethical considerations.
1. Precision Medicine:
Biotechnology enables the development of personalized treatments tailored to an individual's genetic makeup. This approach, known as precision medicine, holds the potential to revolutionize disease prevention and treatment.
2. Gene Therapy:
Genetic editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, allow for the modification of genes to treat or prevent genetic disorders. This groundbreaking approach opens the door to addressing previously incurable diseases at their root.
3. Agricultural Innovation:
Genetic modification of crops enhances agricultural productivity and resilience. Drought-resistant, pest-resistant, and nutritionally enriched crops are being developed to address global food security challenges.
4. Synthetic Biology:
Biotechnology contributes to the emerging field of synthetic biology, where organisms are engineered to perform specific functions. This has applications in biofuel production, environmental cleanup, and the creation of novel materials.
5. Stem Cell Research:
Biotechnology plays a crucial role in stem cell research, offering potential treatments for various degenerative diseases and injuries by harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells.
6. Ethical Considerations:
The ability to edit genes raises ethical questions about the potential misuse of technology, unintended consequences, and the moral implications of altering the human genome.
As biotechnology continues to evolve, striking a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility becomes paramount. The profound impacts of these advancements underscore the importance of thoughtful regulation and consideration of the societal implications.
5. Space Exploration:
Advances in space exploration may make it possible for humans to travel to Mars and beyond in the future. Additionally, the potential for space mining and exploitation of its resources may also increase.
Space exploration, with its continuous technological advancements, opens new frontiers and possibilities for humanity, spanning scientific discovery, resource utilization, and the potential for human colonization.
1. Mars Exploration:
Ambitious missions aim to explore and potentially colonize Mars. This involves sending robotic probes, conducting experiments, and preparing for human missions, marking a significant leap in interplanetary exploration.
2. Space Mining:
The concept of extracting resources from celestial bodies, such as asteroids and the Moon, is gaining traction. Space mining could provide essential materials for further space exploration and address resource shortages on Earth.
3. Satellite Technology:
Satellites play a crucial role in communication, Earth observation, and scientific research. Advancements in miniaturization and efficiency contribute to the deployment of increasingly sophisticated satellite networks.
4. International Collaboration:
Space exploration often involves collaborative efforts between countries and space agencies. International cooperation in space missions promotes shared knowledge, cost distribution, and the pooling of resources.
5. Commercial Space Ventures:
Private companies are actively participating in space exploration, driving innovation and reducing launch costs. Commercial space ventures include satellite launches, space tourism initiatives, and plans for lunar exploration.
6. Beyond the Solar System:
Scientific endeavors aim to explore exoplanets and potentially habitable celestial bodies beyond our solar system. This expands our understanding of the universe and the potential for extraterrestrial life.
Space exploration not only pushes the boundaries of human knowledge but also fosters technological advancements with applications on Earth. As we continue to explore the cosmos, the prospects for discovering new worlds and harnessing space resources for the benefit of humanity remain captivating.
6. Environmental Technology:
Future technology will also focus on environmental sustainability and combating climate change. Renewable energy sources, energy storage systems and environmental monitoring technologies can provide significant developments in this world
Environmental technology focuses on developing innovative solutions to address pressing ecological challenges, promoting sustainability, and mitigating the impact of human activities on the planet.
1. Renewable Energy Sources:
Advancements in solar, wind, and hydropower technologies contribute to the transition toward cleaner and sustainable energy. These sources reduce reliance on fossil fuels, combating climate change and decreasing environmental pollution.
2. Energy Storage Systems:
Efficient energy storage solutions, such as advanced batteries and grid-scale storage, support the integration of renewable energy into existing power grids. This helps address the intermittency of renewable sources and ensures a stable energy supply.
3. Smart Grids:
Smart grid technologies optimize energy distribution, enhance efficiency, and reduce energy losses. These systems enable real-time monitoring, efficient load balancing, and the integration of decentralized energy sources.
4. Water Purification and Treatment:
Innovative water purification technologies address the global challenge of clean water scarcity. From advanced filtration systems to desalination techniques, these solutions contribute to ensuring access to safe and clean drinking water.
5. Waste Management and Recycling:
Technological advancements in waste management facilitate the recycling and repurposing of materials, reducing the environmental impact of landfills. Smart waste collection systems optimize resource utilization and minimize pollution.
6. Environmental Monitoring:
IoT devices and sensor networks aid in environmental monitoring, providing real-time data on air quality, biodiversity, and climate change. This information is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive environmental conservation efforts.
Environmental technology plays a pivotal role in creating a more sustainable and resilient future. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, the development and implementation of these technologies become essential for preserving the planet for futureqt
Future technological advances will profoundly change societies and industries. However, it is important that these advances are also approached carefully regarding ethical and security issues.