Deep Review of Cosmos Blockchain Protocol
Introduction
Cosmos is a decentralized network of independent, scalable, and interoperable blockchains, built on a modular and adaptable architecture. It aims to solve the scalability, usability, and interoperability issues faced by many existing blockchain platforms. In this review, we will delve into the key features, components, consensus mechanism, governance model, and use cases of the Cosmos blockchain protocol.
Key Features
- Interoperability: Cosmos enables different blockchains to communicate and transact with each other through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.
- Scalability: By utilizing a modular architecture, Cosmos allows for the creation of multiple parallel blockchains, known as zones, which can scale independently.
- Adaptability: The modular design of Cosmos allows developers to easily customize and upgrade their blockchain applications.
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus: Cosmos uses a PoS consensus mechanism called Tendermint, which offers fast transaction finality and high security.
- Cosmos SDK: Developers can build custom blockchains and decentralized applications (dApps) using the Cosmos SDK, a framework that provides tools and libraries for blockchain development.

Components
- Tendermint Core: The Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus engine used by Cosmos to secure the network and achieve fast block finality.
- Cosmos Hub: The main hub of the Cosmos network, responsible for connecting various blockchains and facilitating interoperability.
- IBC Protocol: The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol enables secure and trustless communication between different blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem.
- Cosmos SDK: A powerful framework for building custom blockchains and decentralized applications on the Cosmos network.
- Cosmos Governance: A decentralized governance model that allows stakeholders to propose and vote on network upgrades, parameter changes, and funding allocations.
Consensus Mechanism
Cosmos uses the Tendermint Core consensus algorithm, which is a Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) consensus protocol. Tendermint ensures fast block finality, high security, and efficient transaction processing. Validators in the network take turns proposing and validating blocks, with the consensus being reached through a voting process.
Governance Model
Cosmos has a decentralized governance model where stakeholders can submit governance proposals, vote on network upgrades, parameter changes, and funding allocations. This model ensures that the network remains adaptable and responsive to the needs of its community.
Use Cases
- Cross-Chain Token Transfers: Cosmos enables seamless token transfers between different blockchains, allowing users to exchange assets across various networks.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Developers can build DeFi applications on Cosmos, leveraging its interoperability and scalability features to create innovative financial products.
- Enterprise Solutions: Cosmos's modular architecture and customizable features make it suitable for building enterprise-grade blockchain solutions that require high performance and interoperability.
Benefits of Cosmos Ecosystem:
- Scalability: Cosmos provides a scalable platform for building decentralized applications that can handle a high volume of transactions.
- Interoperability: The IBC protocol allows different blockchains within the Cosmos ecosystem to communicate and transfer assets seamlessly.
- Decentralized Governance: Cosmos enables community-driven governance through on-chain voting mechanisms, giving stakeholders a say in the future development of the ecosystem.
- Security: With the Tendermint consensus mechanism, Cosmos ensures a high level of security and finality for transactions on the network.
- Innovation: The Cosmos SDK makes it easy for developers to create custom blockchains and applications, fostering innovation within the ecosystem.
- Cross-chain DeFi: Cosmos enables the creation of decentralized finance applications that can interact with multiple blockchains, opening up new possibilities for financial services.
- Community Engagement: The Cosmos community is vibrant and active, providing support and resources for developers and users to participate in the ecosystem.
The Cosmos ecosystem offers a range of benefits for both developers and users, making it an attractive platform for blockchain innovation and collaboration.
Limitations of Cosmos Ecosystem:
- Complexity: Setting up and maintaining a Cosmos blockchain can be complex, especially for new developers, due to the various components and configurations involved.
- Centralization Concerns: While Cosmos aims to be a decentralized platform, there are concerns about centralization, particularly with validators and governance, which could potentially impact the security and trustworthiness of the ecosystem.
- Scalability Challenges: Despite its scalability features, Cosmos may face challenges as the network grows in size and complexity, potentially leading to congestion and slower transaction speeds.
- Security Risks: Like any blockchain platform, Cosmos is not immune to security vulnerabilities, and the interconnected nature of the ecosystem through IBC could introduce additional attack vectors.
- Interoperability Limitations: While IBC allows for interoperability between blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem, compatibility issues may arise when connecting with external blockchains that do not support the protocol.
- Ecosystem Fragmentation: With the ability to create custom blockchains using the Cosmos SDK, there is a risk of ecosystem fragmentation, where different projects operate independently, potentially hindering collaboration and interoperability.
- Governance Challenges: Decentralized governance on Cosmos relies on active community participation, which can sometimes lead to governance disputes and decision-making inefficiencies.
Despite these limitations, the Cosmos ecosystem continues to evolve and address these challenges to improve the overall user experience and functionality of the platform.
Partnerships in the Cosmos Ecosystem:
- Tendermint Inc: The company behind the development of the Tendermint Core consensus engine, which serves as the foundation for many Cosmos-based blockchains.
- Interchain Foundation: A non-profit organization that supports the development and growth of the Cosmos ecosystem through grants, funding, and community initiatives.
- All in Bits (dba Tendermint): A team of developers and engineers working on various projects within the Cosmos ecosystem, including the Tendermint Core protocol.
- Binance: Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges, has shown support for Cosmos by listing its native token ATOM and promoting projects within the ecosystem.
- Coinbase: Coinbase, a popular cryptocurrency exchange, has also listed ATOM on its platform, providing more accessibility for users to trade the token.
- Figment Networks: A company providing infrastructure and tools for developers building on Cosmos, offering staking services, APIs, and other resources.
- Althea Network: A project utilizing Cosmos technology to create decentralized internet infrastructure, enabling users to share and sell excess bandwidth.
- Regen Network: A blockchain project focused on ecological regeneration, utilizing Cosmos technology to create a marketplace for ecological assets and services.
These partnerships and collaborations help strengthen the Cosmos ecosystem, drive innovation, and expand the reach of Cosmos technology into various industries and applications.
Future Integrations in the Cosmos Ecosystem:
- DeFi Protocols: As decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to grow in popularity, we can expect more integrations of DeFi protocols within the Cosmos ecosystem. This could include lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and other financial applications built on Cosmos technology.
- Cross-Chain Communication: Improving interoperability between different blockchains is a key focus for the Cosmos ecosystem. Future integrations may involve enhancing cross-chain communication protocols to enable seamless transfer of assets and data between different blockchains.
- Enterprise Solutions: Cosmos technology has the potential to be adopted by enterprises looking to leverage blockchain for various use cases. Future integrations may involve partnerships with enterprise solutions providers to create tailored blockchain solutions for businesses.
- IoT and Supply Chain: Integrating Cosmos technology with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and supply chain management systems could enable new use cases such as tracking and tracing of goods, automated supply chain management, and secure data exchange between devices.
- Governance and DAOs: Improved governance mechanisms and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are integral to the Cosmos ecosystem. Future integrations may involve enhancements to governance models and tools to empower community decision-making within the ecosystem.
- NFT Marketplaces: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have gained significant attention in the blockchain space. Future integrations within the Cosmos ecosystem could involve NFT marketplaces, digital art platforms, and other applications that leverage NFT technology.
- Scaling and Privacy Solutions: With a growing focus on data privacy and security, future integrations in the Cosmos ecosystem may involve privacy-focused solutions such as zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation, and other cryptographic techniques to enhance data protection on the blockchain.
- Identity Management: Integrating identity management solutions within the Cosmos ecosystem could enable secure and decentralized identity verification processes. This could have applications in areas such as KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures, access control, and user authentication.
- Green and Sustainable Solutions: As environmental concerns become more prominent, future integrations in the Cosmos ecosystem may focus on green and sustainable blockchain solutions. This could involve energy-efficient consensus algorithms, carbon offset initiatives, and other sustainability measures.
- Education and Adoption: To drive widespread adoption of Cosmos technology, future integrations may include educational platforms, developer tools, and community-building initiatives to empower more users and developers to participate in the ecosystem.

Conclusion
Cosmos is a promising blockchain protocol that addresses the scalability, interoperability, and governance challenges of the current blockchain ecosystem. With its innovative technology stack, including the Cosmos SDK, IBC protocol, and Tendermint consensus mechanism, Cosmos provides a robust platform for developers to build scalable and interoperable decentralized applications.
As the Cosmos ecosystem continues to grow and evolve, it is expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of blockchain technology. Whether it's facilitating cross-chain communication, enabling decentralized finance applications, or empowering governance through its voting mechanisms, Cosmos offers a wide range of possibilities for blockchain innovation.
Meanwhile, Cosmos stands out as a promising project that aims to create a more connected and efficient blockchain ecosystem. By focusing on scalability, interoperability, and decentralized governance, Cosmos is well-positioned to drive the next wave of blockchain adoption and innovation.
The future of integrations in the Cosmos ecosystem looks promising, with a focus on enhancing interoperability, scalability, security, and usability to support a wide range of applications and use cases.

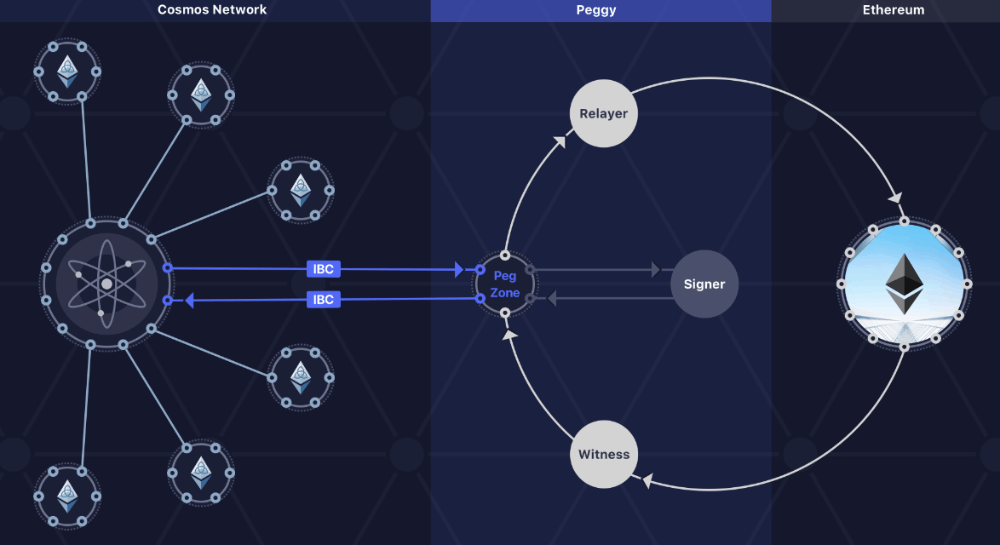
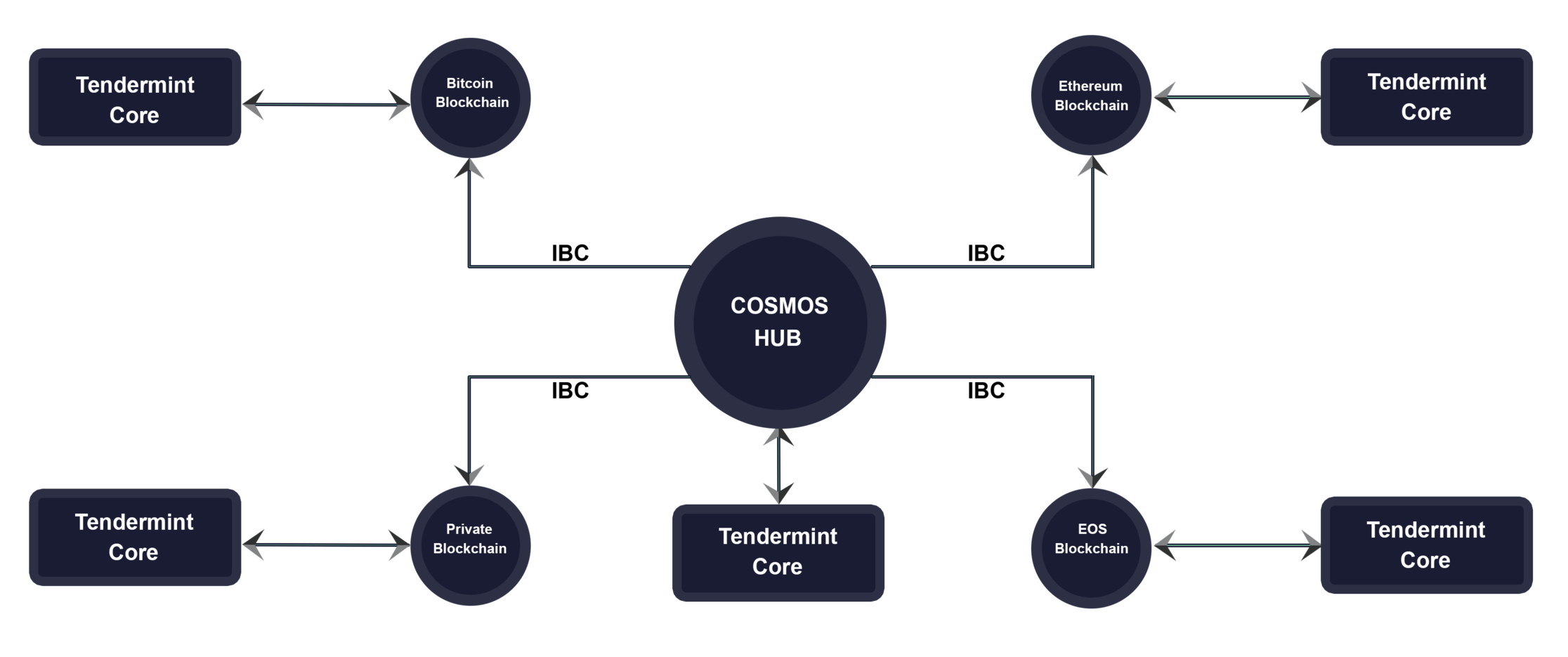








































![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - Is Trump Dying? Or Only Killing The Market?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/a129e75e-4fa1-46cc-80b6-04e638877e46/1)



















