Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Clash of the Crypto Titans
In the ever-evolving landscape of the crypto economy, Bitcoin and Ethereum stand out as the two most mature assets, each commanding a unique position and purpose. Traditionally, the roles were distinct: Bitcoin emerged as the quintessential store of value, while Ethereum, with its versatile platform, became the backbone for the burgeoning Decentralized Finance (DeFi) sector. However, the last few market cycles have blurred these lines, ushering in a new era where the functionalities and perceptions of these cryptocurrencies overlap more than ever before.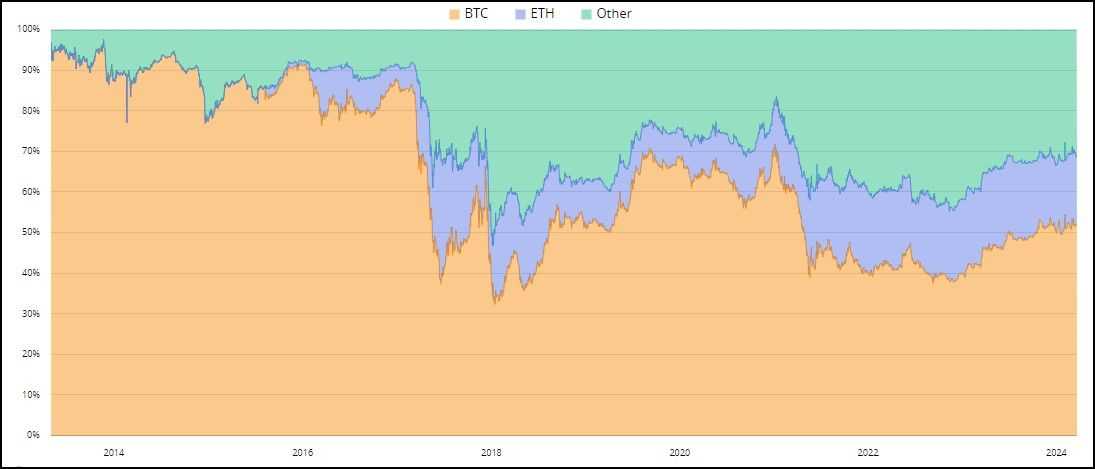
Recent technological advancements and shifts in investor sentiment have significantly altered how we view and use these assets. Bitcoin is no longer just a digital gold; it's making inroads into DeFi, demonstrating its versatility beyond a mere store of value. Concurrently, Ethereum is witnessing a transformation, with its native token, Ether, increasingly being viewed as a potential store of value, a shift driven by its growing commodification and integral role in the crypto ecosystem.
In light of these developments, this analysis aims to provide an updated perspective on the Bitcoin vs Ethereum debate. Our objective is not to declare a victor but to offer a nuanced analysis of how these assets evolve, highlighting their growing similarities and persistent differences as they become more deeply ingrained in the fabric of digital finance.
What is Bitcoin?

Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, revolutionized the digital world when it was introduced in 2009 by an individual or group known under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. This groundbreaking digital asset operates on distributed ledger technology on a Proof of Work blockchain. It underpins its integrity and security by requiring miners to solve complex computational problems to validate transactions and create new blocks.
Renowned for its scarcity and decentralized nature, Bitcoin is often lauded as the premier store of value in the digital asset realm, drawing parallels to gold. It shares key characteristics with precious metals, such as limited supply and durability, but in a digital format, offering a modern twist on the concept of a “safe-haven” asset. Bitcoin stands out as the only digital asset that has received an official classification as a commodity, underscoring its unique status and the widespread recognition of its value proposition.
In recent developments, Bitcoin has seen significant technological enhancements that augment its functionality. Implementing Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot upgrades has introduced a new level of scriptability to Bitcoin, opening the door to smart contract capabilities and enhancing its efficiency and privacy. The emergence of Ordinals and BRC20s illustrates the evolving landscape of Bitcoin, indicating a shift towards more versatile applications. Furthermore, the launch of Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) in the USA and the cryptocurrency's surge to new all-time high price levels underscore its growing acceptance and maturation as a mainstream financial asset.
What is Ethereum?

Ethereum, conceived by Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015, marked a significant evolution in blockchain technology by introducing a platform designed to execute smart contracts and build decentralized applications (DApps). Originally operating on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, Ethereum underwent a monumental transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) with "The Merge," aligning with its sustainability goals and enhancing its efficiency and scalability.
As the most widely adopted smart contract platform, Ethereum stands at the forefront of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) movement, providing the foundational infrastructure that powers many applications and layer-2 ecosystems. Ether, Ethereum's native cryptocurrency, serves a critical function beyond a mere store of value; it's the lifeblood of the network, utilized to pay for on-chain computation in the form of gas fees, enabling the execution of smart contracts and transactions.
Moreover, Ethereum underpins dynamic layer-2 ecosystems, where various scaling solutions flourish, significantly enhancing transaction throughput while reducing costs. A notable recent advancement in Ethereum's technological evolution is the introduction of proto-danksharding in the Dencun upgrade. This development marks a pivotal step in Ethereum's scalability roadmap, drastically reducing layer-2 fees and further solidifying Ethereum's position as a leading, innovative blockchain platform, continually adapting to meet the growing demands of its diverse and expanding user base.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Technical Comparison
This section will cover the technical features of the networks and contrast them with one another.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin was designed as a distributed ledger (to track BTC transactions) and a peer-to-peer network (to exchange BTC without any counter-party), providing a decentralized solution for financial transactions without traditional banking systems. Its underlying technology facilitates a secure and transparent ledger of transactions, promoting trust among users.
- Architecture: Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW) consensus is foundational to its security, requiring miners to compete in solving complex mathematical problems, requiring expensive hardware and electricity. This process secures the network and introduces new bitcoins into the system, mimicking the process of mining precious metals.
- Block Size and Timing: The roughly 1 MB block size limit in Bitcoin is a design choice that balances transaction throughput with network decentralization. The 10-minute interval for block creation aims to ensure network stability and security, though it can lead to variability in transaction confirmation times.
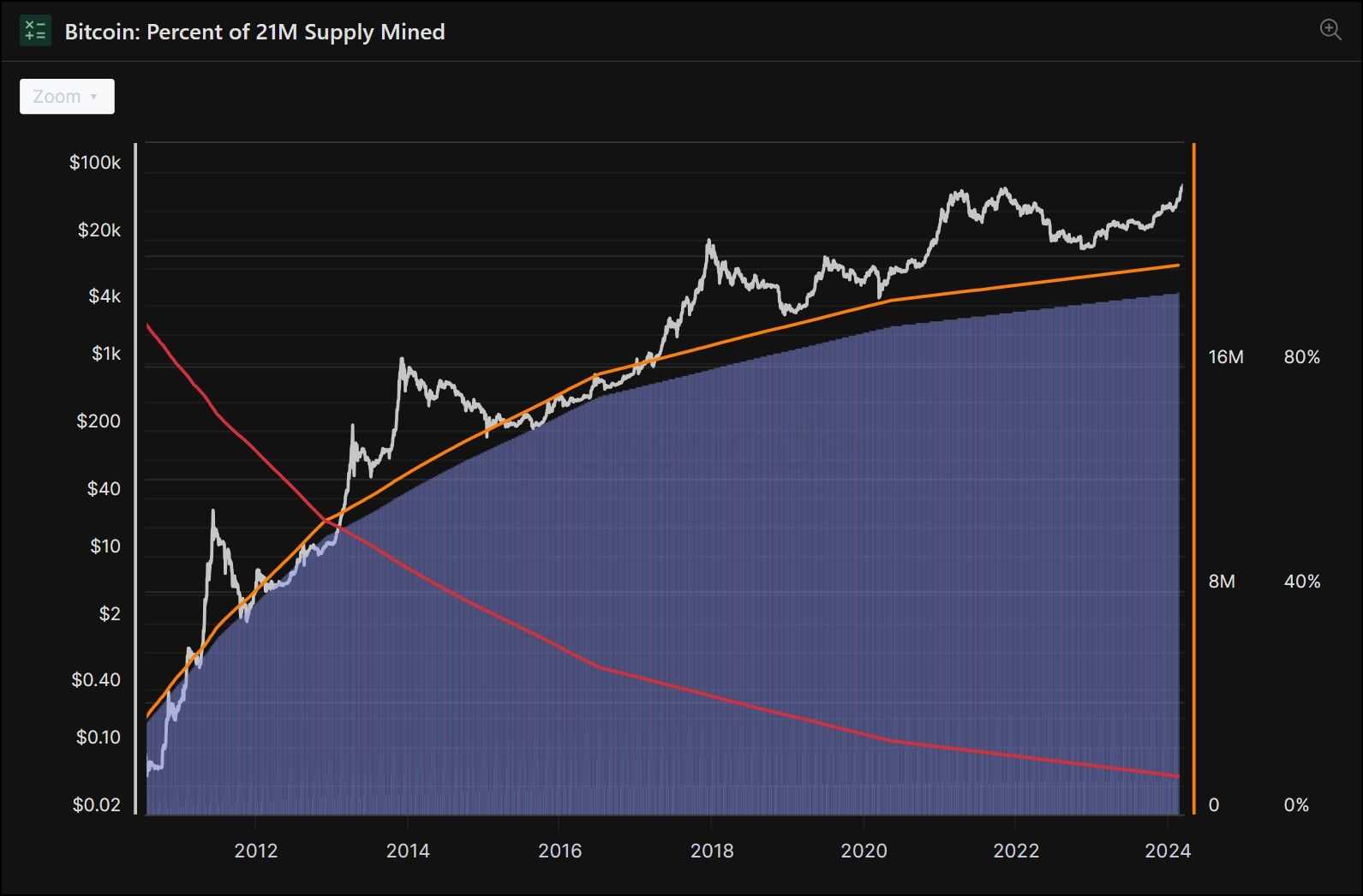
- Supply and Inflation: The fixed supply cap of 21 million BTC is a key feature that underpins Bitcoin's value proposition as "digital gold." The halving events half the BTC issuance rate every four years, simulating a form of digital scarcity that influences its market value.
- Mining: Bitcoin mining has evolved into a highly competitive industry, with participants investing in specialized hardware (ASICs) to improve their chances of success. This competition contributes to the network's security, acting as a deterrent to malicious behaviour.
Ethereum
Beyond a distributed ledger, Ethereum is a platform for continuous general-purpose computation (executing smart contracts), such as building decentralized applications. This flexibility has established Ethereum as a cornerstone of the DeFi and broader blockchain ecosystem.
- Architecture: The transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) with Ethereum's Merge represented a significant shift towards energy efficiency and scalability. In PoS, validators' chances of creating a block and receiving rewards are proportional to their stake (with a minimum requirement of 32 EH), replacing Bitcoin's resource-intensive architecture of block creation with a capital-intensive structure.
- Block Size and Timing: Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum's block size adapts based on network usage, allowing it to handle fluctuations in demand more dynamically. An Ethereum block is complete when the validators do a threshold quantity of transactions. This flexibility supports Ethereum's role as a platform for various applications, from simple transactions to complex smart contracts. For more details on Ethereum block dynamics, refer to the Ethereum Transactions Overview on The Coin Bureau.
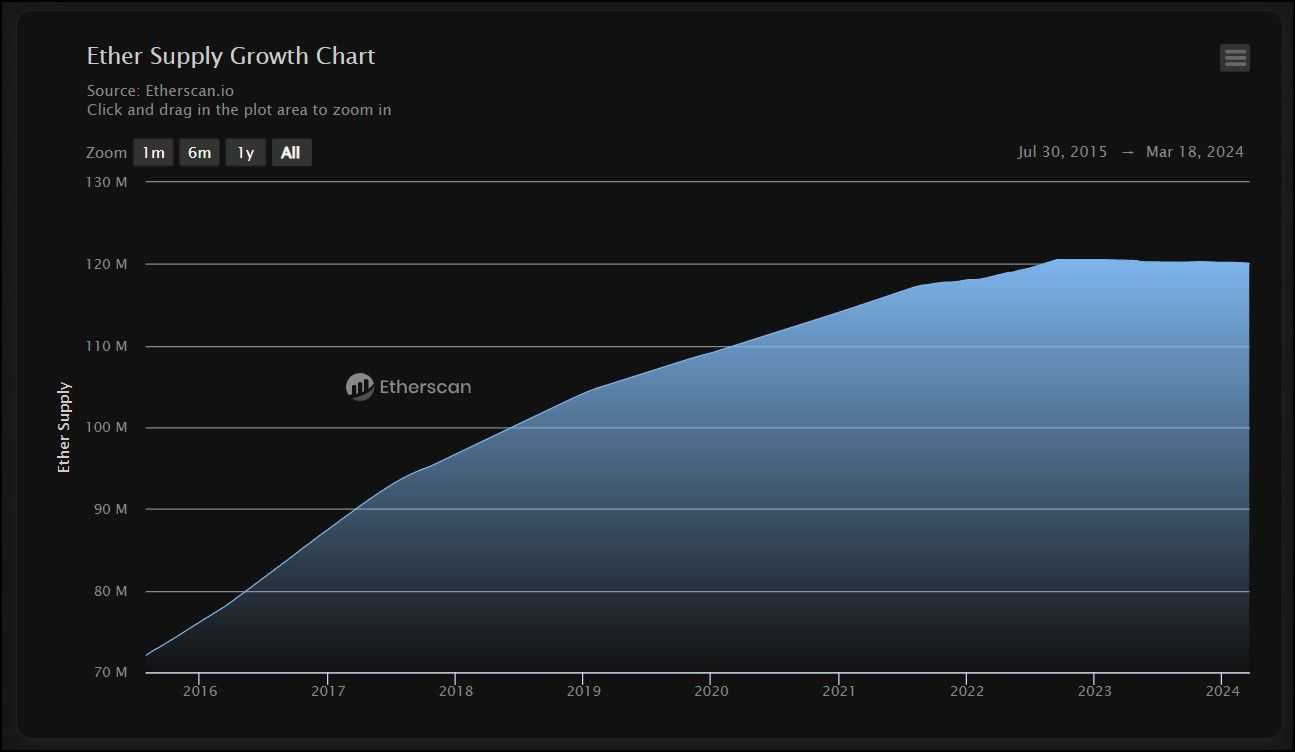
- Supply and Inflation: Ethereum's variable supply mechanism is designed to adapt to the network's needs, supporting its utility while managing inflation. The shift to a PoS consensus has further implications for Ethereum's supply dynamics, potentially leading to net deflation during periods of high network activity.
- Staking and Liquid Staking: The introduction of staking in Ethereum democratizes network participation, allowing a broader range of participants to contribute to network security. Liquid staking enhances this by providing liquidity to staked assets, enabling participants to engage with the network without locking in their resources.
Bitcoin and Ethereum in the Real World
In the real world, Bitcoin and Ethereum have transcended their digital origins to impact various sectors and industries, showcasing their versatility and growing acceptance.
Bitcoin's Real-World Use Cases:
- Investment Vehicle: Bitcoin has cemented its status as a sought-after investment asset, with instruments like futures and exchange traded funds (ETFs) allowing investors to speculate on its price without holding the actual cryptocurrency. These financial products have introduced Bitcoin to traditional investment markets, broadening its investor base.
- Legal Tender: El Salvador adopted Bitcoin as legal tender in a groundbreaking move, demonstrating its potential to function as an everyday currency alongside traditional fiat. This adoption signifies a monumental step in Bitcoin's journey, highlighting its capacity to facilitate daily transactions and financial inclusion.
Ethereum's Real-World Use Cases:
- Real-World Assets (RWAs): Ethereum's smart contracts enable the tokenization of real-world assets, allowing them to be bought, sold, and traded on the blockchain. This process enhances liquidity and accessibility, bridging the gap between physical assets and digital finance.
- Blockchain-Based Identification Systems: Leveraging its decentralized nature, Ethereum provides solutions for secure and verifiable identification systems, reducing fraud and enhancing privacy.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Ethereum supports the creation of DAOs, enabling community-led governance structures where decisions are made collectively without a centralized authority, fostering transparency and engagement.
Through these applications, Bitcoin and Ethereum are pioneering new financial paradigms and providing innovative solutions to longstanding problems across various industries.
Environmental Impact of Bitcoin and Ethereum
Bitcoin's environmental footprint has been a topic of considerable debate, largely due to its Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which requires substantial computational power and, consequently, a significant amount of electricity.
Critics often highlight Bitcoin's energy consumption as a key concern, especially when considering the sustainability of digital assets. However, it's crucial to contextualize this consumption by comparing it to the energy requirements of traditional financial systems, including banking networks, interbank payments, and global remittances, where Bitcoin's usage appears less significant.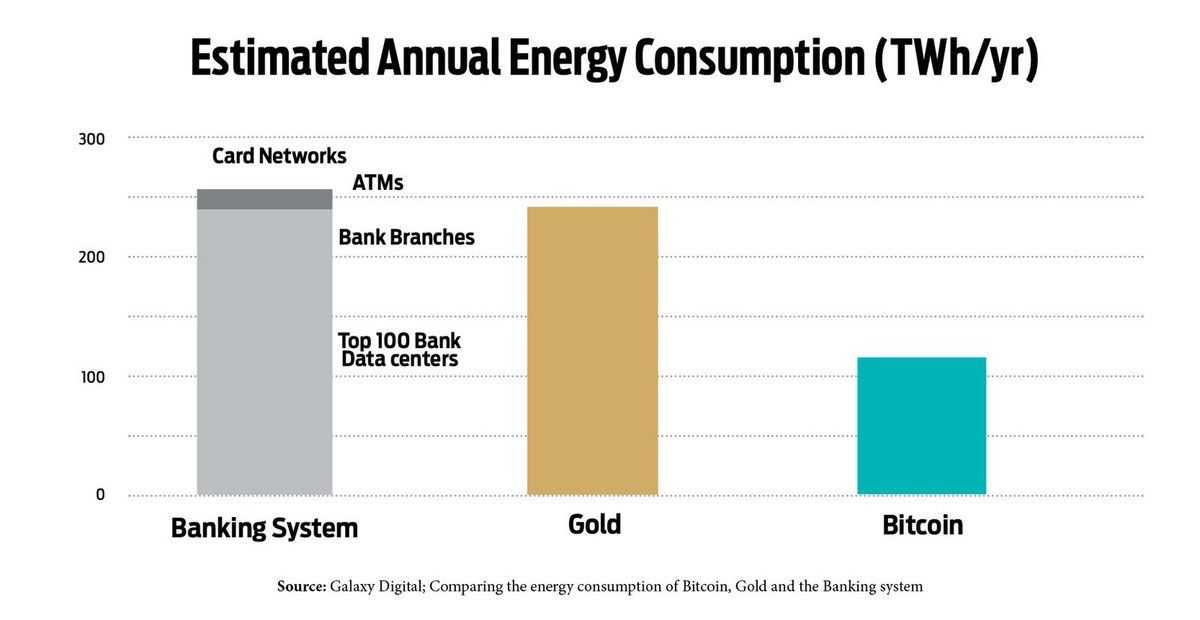
On the other side, Ethereum's transition to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism markedly reduced its energy consumption. By eliminating the need for energy-intensive mining, Ethereum's energy usage decreased by an estimated 99%, positioning it as a more environmentally friendly blockchain network. This shift not only addressed the growing concerns around the carbon footprint of cryptocurrency operations but also set a precedent for other blockchain networks to consider more sustainable consensus mechanisms.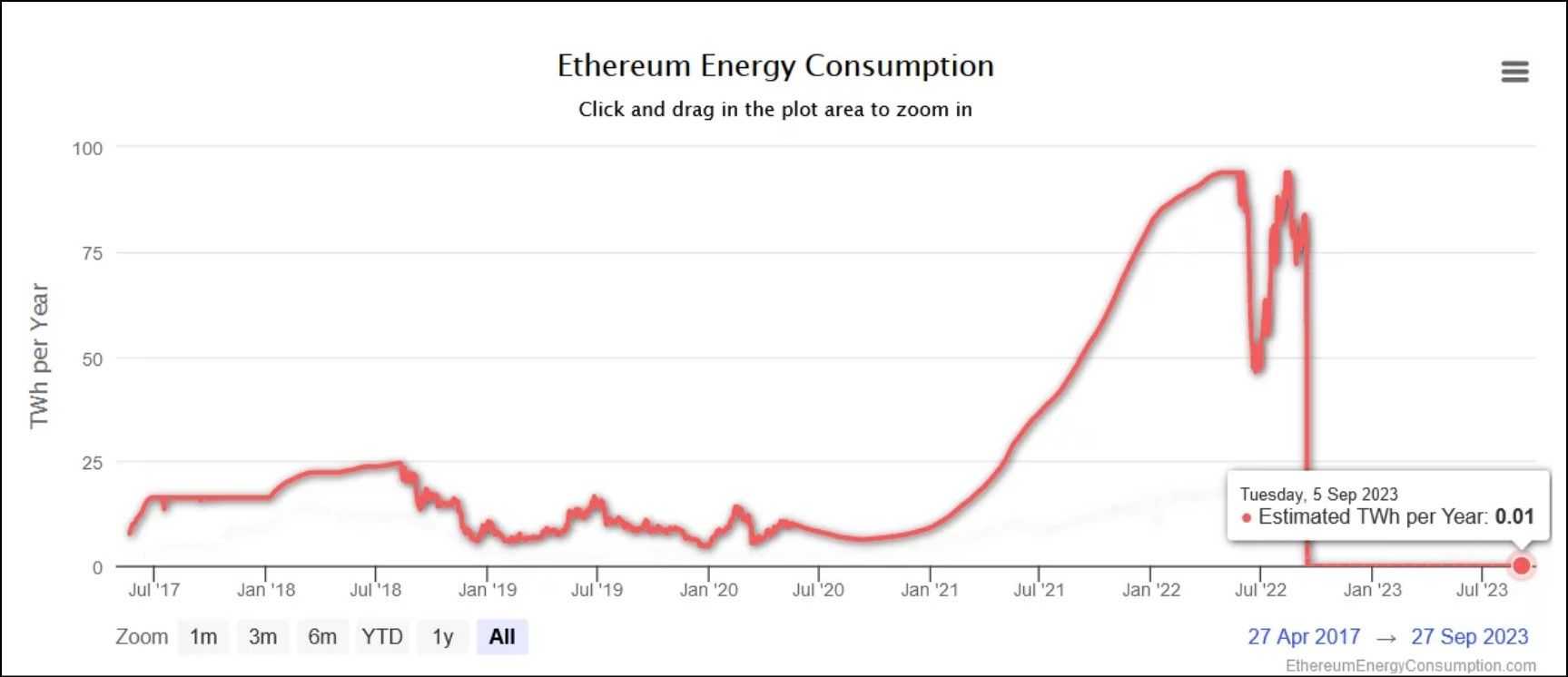
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications
Here's how Bitcoin and Ethereum compare across smart contracts and DApps.
Ethereum’s Smart Contract Capabilities
At the heart of Ethereum's innovation is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This powerful execution layer functions akin to an operating system for decentralized applications. Developers can deploy arbitrary applications written in Solidity, a programming language designed specifically for Ethereum, enabling a permissionless environment for innovation.
This flexibility has established Ethereum as the primary hub for DeF) developments, where most new ideas and applications are first introduced and tested. The EVM's capability to support complex smart contracts and composable elements fosters a vibrant ecosystem for developers and users alike.
Bitcoin’s Smart Contract Capabilities
Bitcoin's initial design focused on its role as a peer-to-peer payment system, with limited scope for additional functionalities. However, introducing the Taproot upgrade marked a significant milestone, introducing enhanced scripting capabilities. While this development has paved the way for a degree of smart contract functionality—illustrated by projects like Ordinals and the potential for building sidechains—Bitcoin's capabilities in this domain remain relatively limited. Its non-Turing complete nature restricts it from supporting complex logical constructs or developing composable smart contracts, a stark contrast to the flexibility offered by Ethereum's development environment.
Legal and Regulatory Environment
Bitcoin and Ethereum, as leading figures in the cryptocurrency space, are at the forefront of discussions concerning regulatory clarity. Their widespread adoption and significant market presence have drawn increased attention from regulatory bodies seeking to establish clear frameworks for digital assets.
Bitcoin enjoys a relatively settled position in the regulatory landscape, being the only digital asset with a definitive classification as a commodity in the United States. This clarity largely stems from Bitcoin's straightforward design and its primary function as a store of value, akin to digital gold, which aligns with the characteristics of commodities.
Ethereum's regulatory status, however, is more complex and is currently a subject of debate among key regulatory authorities. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have both asserted jurisdiction over Ethereum, with differing views: the SEC treats it as a security, while the CFTC considers it a commodity. This division reflects the multifaceted nature of Ethereum, especially given its utility in powering smart contracts and decentralized applications on the EVM.
Despite the regulatory uncertainties surrounding Ethereum, a significant portion of the cryptocurrency community advocates Ether as a commodity. They argue that Ether, like oil, is a fuel for the EVM, essential for executing operations and supporting the network's functionality, reinforcing its commodity-like characteristics. This perspective aligns with the broader view of cryptocurrencies as new asset classes that necessitate nuanced regulatory approaches.
Community and Developer Ecosystem
The community and developer ecosystem surrounding Bitcoin and Ethereum are vibrant and continually evolving, with each blockchain hosting a unique set of applications and innovations.
For Bitcoin, the introduction of Ordinals and the BRC-20 token standard represents a significant shift in its ecosystem. Ordinals have introduced a way to inscribe digital data directly on Bitcoin, creating a new category of NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain. This innovation has spurred interest and activity within the Bitcoin community, attracting new developers and projects.
Additionally, the BRC-20 token standard, akin to Ethereum's ERC-20, allows for the creation and transfer of tokens on the Bitcoin network, further expanding its use cases. Moreover, Layer 2 solutions and DeFi projects built on Bitcoin's network, like Stacks and Rootstock, demonstrate the growing breadth of Bitcoin's functionality, extending beyond its original use as a digital currency.
On the Ethereum side, the network remains the most widely adopted platform for smart contracts and DApps, hosting a multitude of projects across various sectors. Ethereum's flexible and robust programming environment, supported by the EVM, continues to be a significant draw for developers. This has fostered a diverse ecosystem where innovations in finance, gaming, identity verification, and more are commonplace.
Ethereum's ability to support complex smart contracts and its pivotal role in the DeFi space underscore its position as a dynamic and influential platform in the blockchain community.
These developments highlight the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the blockchain space, with both Bitcoin and Ethereum playing crucial roles in shaping the future of decentralized technology and applications.
Roadmap
Here's what the roadmap looks like for two leading cryptos.
Bitcoin
The evolution of Bitcoin's ecosystem is intentionally gradual, reflecting its foundational design as a basic, secure, and stable network. Major updates or hard forks are rare but impactful, with notable events including the contentious Bitcoin Cash split and significant upgrades like SegWit and Taproot. These developments have shaped Bitcoin's trajectory, enhancing its capabilities and security. Looking ahead, a pivotal event on the horizon is the April 2024 halving, set to reduce Bitcoin's block reward from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC, a change that historically influences the network's economics and miner dynamics.
Ethereum
In contrast, Ethereum's development landscape is bustling and rapid, underscored by its transition to Proof of Stake. This monumental shift was followed by the Dencun upgrade in March 2024, introducing proto-danksharding — a significant step forward in enhancing Layer 2 scalability and throughput.
The next milestone on Ethereum's roadmap is the full implementation of Danksharding, which is expected to consolidate and amplify the benefits of proto-danksharding, further boosting the network's capacity and efficiency. This trajectory underscores Ethereum's commitment to continuous improvement and innovation, aiming to fortify its position as a leading platform for decentralized applications and finance.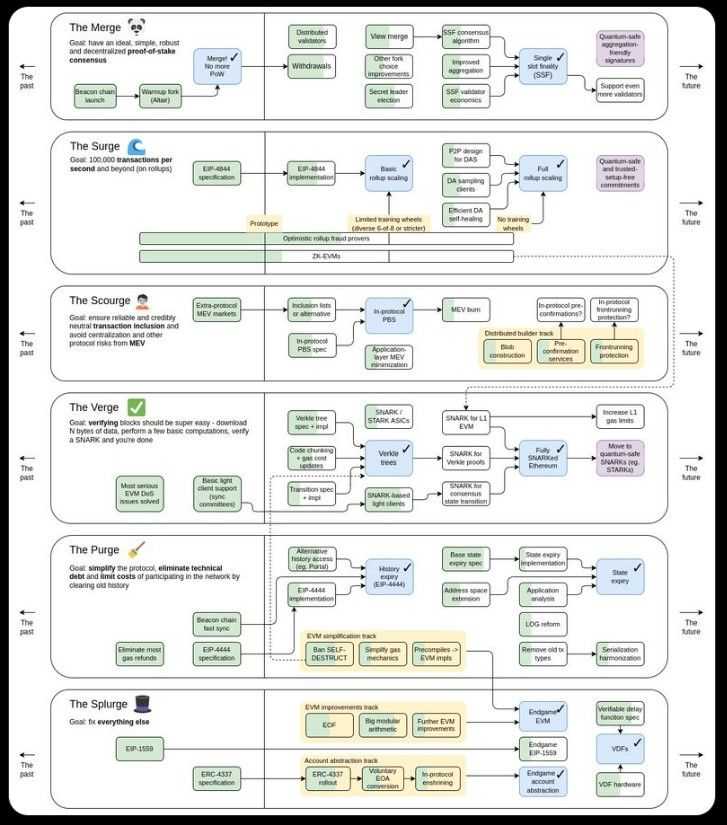
The Financial Aspect: Market Cap and Investment Potential
This section delves into comparative market analysis and investment trends for these leading digital currencies. Please note the insights provided herein are for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice.
Comparative Market Analysis
- Market Capitalization: With a combined market capitalization nearing 70% of the global cryptocurrency market, Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two most valuable crypto assets, standing at $1.27 trillion and $400 billion, respectively.
- Market Metrics: As of March 2024, liquidity for both Bitcoin and Ethereum shows stagnation or reduction. Bitcoin ETFs are drawing significant amounts of BTC out of circulation, and with the upcoming halving, BTC's liquidity is expected to tighten further. Conversely, Ethereum's supply dynamics have stabilized at around 120 million Ether in circulation, influenced by ongoing token burns post-merge.
- Historic Price Trends: Bitcoin's recent surge past its previous all-time high to around $73,000 signifies a potential new phase of price discovery, contrasting with Ethereum's struggle to revisit its peak.
- Influencing Factors: The near-term outlook for Bitcoin and Ethereum is shaped by several factors: the anticipated BTC halving, trends in ETF inflows, retail investor interest, Ethereum's Danksharding upgrade, ongoing ETH burns, and the regulatory landscape, particularly regarding ETH ETFs in the USA.
Investment Trends
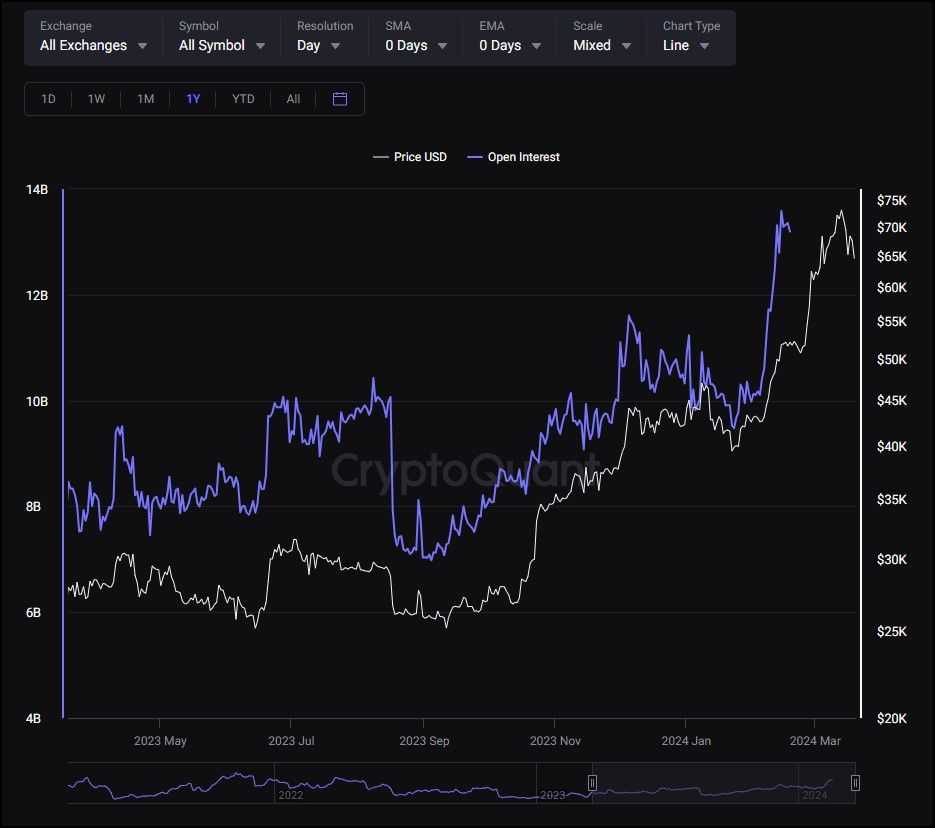
- Open Interest: The rise in open interest for BTC and ETH from January to March 2024 indicates a bullish sentiment, suggesting that the market may anticipate continued upward price movements.
- Investment Dynamics: Institutional investors have been the primary drivers of the recent BTC and ETH rallies, reflecting a cautious stance among retail investors compared to previous market cycles.
- Public Sentiment: The sentiment towards Bitcoin and Ethereum is currently mixed, with long-term holders remaining committed while new investors exhibit hesitancy. Despite this, the accessibility and integration of cryptocurrencies into traditional financial products are at an all-time high, signalling growing mainstream acceptance.
In summary, the financial landscape of Bitcoin and Ethereum is woven with trends in market capitalization, investment behaviours, and external economic factors. As these cryptocurrencies continue to evolve and intersect with broader financial markets, their trajectories will likely be influenced by a mix of technological advancements, regulatory decisions, and shifts in investor sentiment. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the intricate world of crypto investing.
Investment Strategies for Bitcoin and Ethereum
Here are a few strategies you can utilize if you're looking to invest in Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Bitcoin ETFs and ETH Futures
Investing in Bitcoin ETFs is one of the most straightforward and accessible strategies. It offers a practical way to gain exposure to Bitcoin's price movements without dealing with the complexities of direct cryptocurrency ownership. ETFs minimize counterparty risks associated with custodial services. Similarly, ETH futures provide a passive avenue for investors to speculate on Ethereum's future price without holding the actual asset.
Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
DCA is an ideal strategy for semi-passive investors. It involves regularly buying a fixed dollar amount of Bitcoin or Ethereum, regardless of the asset's price, reducing the impact of volatility and potentially lowering the average cost over time. This approach is beneficial for those looking to invest without trying to time the market.
Buying On-Chain
Purchasing Bitcoin or Ethereum directly on the blockchain adds a layer of complexity but eliminates counterparty risk, offering full control over one's digital assets. This strategy requires a deeper understanding of wallets, transactions, and network fees but provides a more hands-on investment experience.
DeFi Participation
Participating in the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem offers various strategies like yield farming, liquid staking, and more for those looking to take a more active and risk-inclined approach. Investing in DeFi involves engaging with smart contracts to earn interest or rewards, often yielding higher returns than traditional investment avenues. However, this approach demands technical knowledge and a high tolerance for risk, as the DeFi space is known for its volatility and potential for loss.
Each of these strategies caters to different levels of involvement and risk tolerance, allowing investors to choose the approach that best aligns with their investment goals and expertise in the cryptocurrency domain.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Closing Thoughts
Throughout our exploration of Bitcoin and Ethereum, we've delved into various facets that define and differentiate these blockchain titans, each illuminating a unique aspect of the crypto landscape.
In our technical comparison, we observed the foundational differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum, from their consensus mechanisms to block size and smart contract capabilities. Bitcoin remains the epitome of a digital store of value, while Ethereum has carved out its niche as a platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts, demonstrating the diverse potential within blockchain technology.
Our journey through BTC and ETH in the real world highlighted their growing adoption and integration into everyday transactions and financial systems, showcasing their practical value beyond speculative assets. The environmental impact discussion underscored Bitcoin's energy-intensive nature contrasted with Ethereum's significant strides towards sustainability post-merge, reminding us of the ecological considerations in blockchain technology.
The exploration of smart contracts and decentralized applications further differentiated Ethereum's versatile ecosystem from Bitcoin's focused design, highlighting the innovative applications and the vibrant communities they support. The legal and regulatory environment section revealed both assets' complex landscape, emphasizing the importance of clarity and compliance in their broader acceptance.
Our examination of the community and developer ecosystem showcased both networks' robust and dynamic nature, with passionate contributors driving innovation and growth. The roadmap analysis offered a glimpse into the future, outlining both blockchains' strategic directions and anticipated developments.
We dissected market trends and investment potential in the financial aspect segment, providing a nuanced understanding of their economic standings. Lastly, our dive into investment strategies showcased the spectrum of approaches available to investors, from passive to actively engaged, reflecting the diverse opportunities within the crypto domain.
As we encapsulate these insights, it's clear that Bitcoin and Ethereum are not just competitors but are complementary forces shaping the blockchain arena. Their evolution, challenges, and triumphs illuminate the broader narrative of cryptocurrency: a testament to human ingenuity and a hint at the transformative potential of decentralized technology. As investors, developers, or simply curious observers, our understanding of these pioneering platforms enriches our grasp of the digital future unfolding before us.


















![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - OM(G) , My Biggest Bag Was A Scam????](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/99de9393-38a8-4e51-a7ab-a2b2c28785bd/1)





























