Freddie Mercury
Freddie Mercury
Mercury was born Farrokh Bulsara in Stone Town in the British protectorate of Zanzibar (now part of Tanzania) on 5 September 1946. His parents, Bomi (1908–2003) and Jer Bulsara (1922–2016), were from the Parsi community of western India. The Bulsaras had origins in the city of Bulsar (now Valsad) in Gujarat. He had a younger sister, Kashmira (b. 1952).
The family had moved to Zanzibar so that Bomi could continue his job as a cashier at the British Colonial Office. As Parsis, the Bulsaras practised Zoroastrianism. Mercury was born with four extra incisors, to which he attributed his enhanced vocal range. As Zanzibar was a British protectorate until 1963, Mercury was born a British subject, and on 2 June 1969 was registered a citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies after the family had emigrated to England.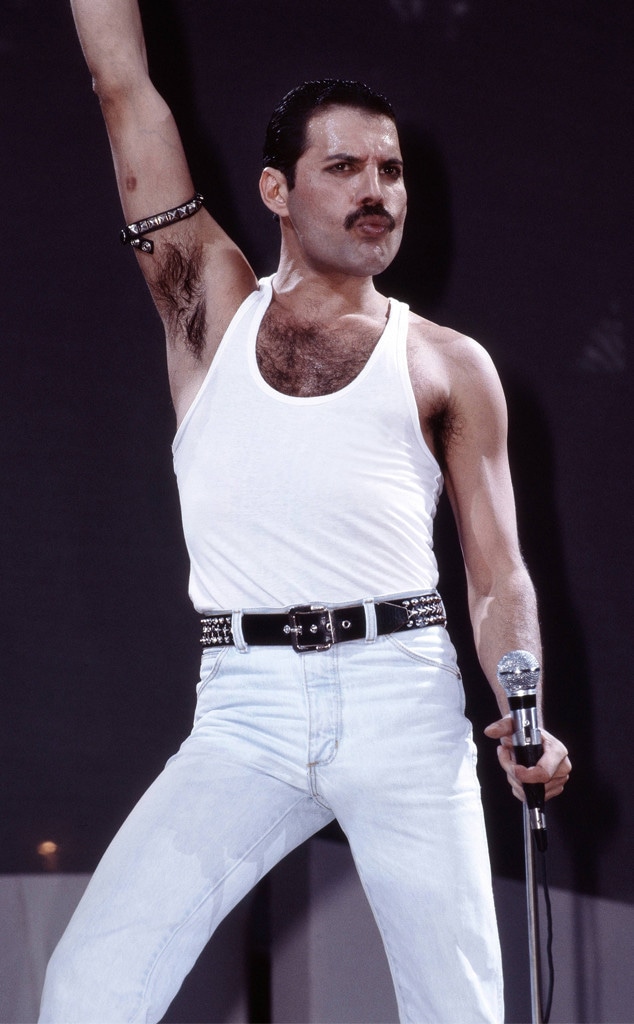
Mercury spent most of his childhood in India where he began taking piano lessons at the age of seven while living with relatives. In 1954, at the age of eight, Mercury was sent to study at St. Peter's School, a British-style boarding school for boys, in Panchgani near Bombay. Inheriting his father's interest in philately, between 9 and 12 years old Mercury collected stamps, many of which were from the British Commonwealth. One of the rare personal possessions of Mercury in museum ownership, his stamp album is displayed in the collection of the Postal Museum in London. At the age of 12, he formed a school band, the Hectics, and covered rock and roll artists such as Cliff Richard and Little Richard. One of Mercury's former bandmates from the Hectics has said "the only music he listened to, and played, was Western pop music". A friend recalls that he had "an uncanny ability to listen to the radio and replay what he heard on piano". It was also at St. Peter's where he began to call himself "Freddie". In February 1963, he moved back to Zanzibar where he joined his parents at their flat.
In the spring of 1964, Mercury and his family fled to England from Zanzibar to escape the violence of the revolution against the Sultan of Zanzibar and his mainly Arab government, in which thousands of ethnic Arabs and Indians were killed. They moved to 19 Hamilton Close, Feltham, Middlesex, a town 13 miles (21 km) west of central London. The Bulsaras briefly relocated to 122 Hamilton Road, before settling into a small house at 22 Gladstone Avenue in late October. After first studying art at Isleworth Polytechnic in West London, Mercury studied graphic art and design at Ealing Art College, graduating with a diploma in 1969. He later used these skills to design heraldic arms for his band Queen.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(687x0:689x2):format(webp)/gettyimages-823663584_preview-58150fced44d40418bf7bfed4dad78f6.jpg)
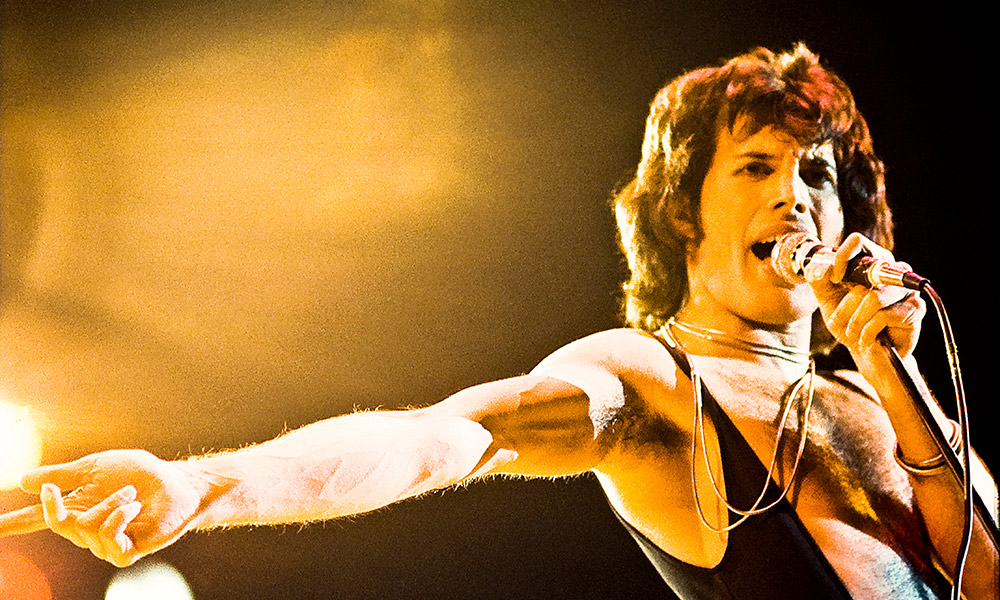
Following graduation, Mercury joined a series of bands and sold second-hand Edwardian clothes and scarves in Kensington Market in London with Roger Taylor. Taylor recalls, "Back then, I didn't really know him as a singer—he was just my mate. My crazy mate! If there was fun to be had, Freddie and I were usually involved." He also held a job as a baggage handler at Heathrow Airport. Other friends from the time remember him as a quiet and shy young man with a great interest in music. In 1969, he joined Liverpool-based band Ibex, later renamed Wreckage, which played "very Hendrix-style, heavy blues". He briefly lived in a flat above the Dovedale Towers, a pub on Penny Lane in Liverpool's Mossley Hill district. When this band failed to take off, he joined an Oxford-based band, Sour Milk Sea, but by early 1970 this group had broken up as well.
In April 1970, Mercury teamed up with guitarist Brian May and drummer Roger Taylor, to become lead singer of their band Smile. They were joined by bassist John Deacon in 1971. Despite the reservations of the other members and Trident Studios, the band's initial management, Mercury chose the name "Queen" for the new band. He later said, "It's very regal obviously, and it sounds splendid. It's a strong name, very universal and immediate. I was certainly aware of the gay connotations, but that was just one facet of it." At about the same time, he legally changed his surname, Bulsara, to Mercury. It was inspired by the line "Mother Mercury, look what they've done to me" from his song "My Fairy King".
Shortly before the release of Queen's self-titled first album, Mercury designed the band's logo, known as the "Queen crest". The logo combines the zodiac signs of the four band members: two lions for Deacon and Taylor (sign Leo), a crab for May (Cancer), and two fairies for Mercury (Virgo). The lions embrace a stylised letter Q, the crab rests atop the letter with flames rising directly above it, and the fairies are each sheltering below a lion. A crown is shown inside the Q, and the whole logo is over-shadowed by an enormous phoenix. The Queen crest bears a passing resemblance to the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, particularly with the lion supporters.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2)/freddie-mercury-handwritten-lyrics-060123-tout-b116cce4a4344a18be7ca8858ff83e39.jpg)
Although Mercury's speaking voice naturally fell in the baritone range, he delivered most songs in the tenor range. His known vocal range extended from bass low F (F2) to soprano high F (F6). He could belt up to tenor high F (F5). Biographer David Bret described his voice as "escalating within a few bars from a deep, throaty rock-growl to tender, vibrant tenor, then on to a high-pitched, perfect coloratura, pure and crystalline in the upper reaches". Spanish soprano Montserrat Caballé, with whom Mercury recorded an album, expressed her opinion that "the difference between Freddie and almost all the other rock stars was that he was selling the voice". She adds:
His technique was astonishing. No problem of tempo, he sang with an incisive sense of rhythm, his vocal placement was very good and he was able to glide effortlessly from a register to another. He also had a great musicality. His phrasing was subtle, delicate and sweet or energetic and slamming. He was able to find the right colouring or expressive nuance for each word.
The Who lead singer Roger Daltrey described Mercury as "the best virtuoso rock 'n' roll singer of all time. He could sing anything in any style. He could change his style from line to line and, God, that's an art. And he was brilliant at it." Discussing what type of person he wanted to play the lead role in his musical Jesus Christ Superstar, Andrew Lloyd Webber said: "He has to be of enormous charisma, but he also has to be a genuine, genuine rock tenor. That's what it is. Really think Freddie Mercury, I mean that's the kind of range we're talking about."
A research team undertook a study in 2016 to understand the appeal behind Mercury's voice. Led by Professor Christian Herbst, the team identified his notably faster vibrato and use of subharmonics as unique characteristics of Mercury's voice, particularly in comparison to opera singers. The research team studied vocal samples from 23 commercially available Queen recordings, his solo work, and a series of interviews of the late artist. They also used an endoscopic video camera to study a rock singer brought in to imitate Mercury's singing voice.
Mercury wrote 10 of the 17 songs on Queen's Greatest Hits album: "Bohemian Rhapsody", "Seven Seas of Rhye", "Killer Queen", "Somebody to Love", "Good Old-Fashioned Lover Boy", "We Are the Champions", "Bicycle Race", "Don't Stop Me Now", "Crazy Little Thing Called Love", and "Play the Game". In 2003 Mercury was posthumously inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame with the rest of Queen, and in 2005 all four band members were awarded an Ivor Novello Award for Outstanding Song Collection from the British Academy of Songwriters, Composers, and Authors.
The most notable aspect of his songwriting involved the wide range of genres that he used, which included, among other styles, rockabilly, progressive rock, heavy metal, gospel, and disco. As he explained in a 1986 interview, "I hate doing the same thing again and again and again. I like to see what's happening now in music, film and theatre and incorporate all of those things." Compared to many popular songwriters, Mercury also tended to write musically complex material. For example, "Bohemian Rhapsody" is non-cyclical in structure and comprises dozens of chords. He also wrote six songs from Queen II which deal with multiple key changes and complex material. "Crazy Little Thing Called Love", on the other hand, contains only a few chords. Although Mercury often wrote very intricate harmonies, he said that he could barely read music. He composed most of his songs on the piano and used a wide variety of key signatures.

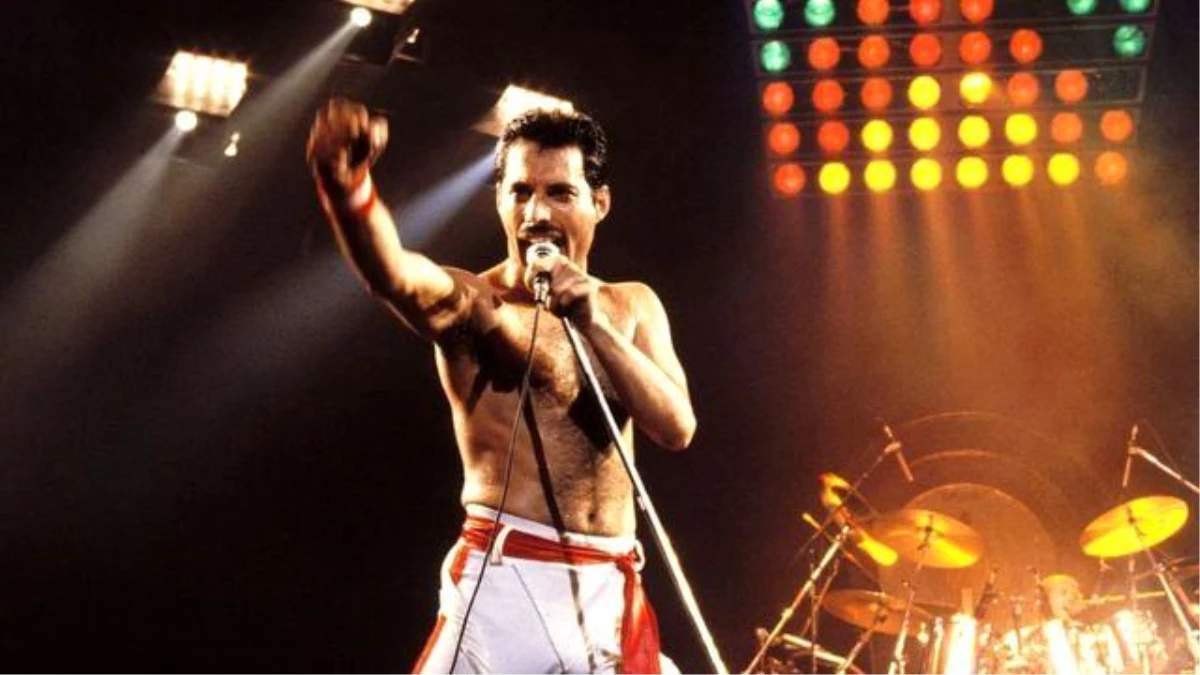
Mercury was noted for his live performances, which were often delivered to stadium audiences around the world. He displayed a highly theatrical style that often evoked a great deal of participation from the crowd. A writer for The Spectator described him as "a performer out to tease, shock and ultimately charm his audience with various extravagant versions of himself." David Bowie, who performed at the Freddie Mercury Tribute Concert and recorded the song "Under Pressure" with Queen, praised Mercury's performance style, saying: "Of all the more theatrical rock performers, Freddie took it further than the rest ... he took it over the edge. And of course, I always admired a man who wears tights. I only saw him in concert once and as they say, he was definitely a man who could hold an audience in the palm of his hand." Queen guitarist Brian May wrote that Mercury could make "the last person at the back of the furthest stand in a stadium feel that he was connected". Mercury's main prop on stage was a broken microphone stand; after accidentally snapping it off the heavy base during an early performance, he realised it could be used in endless ways.

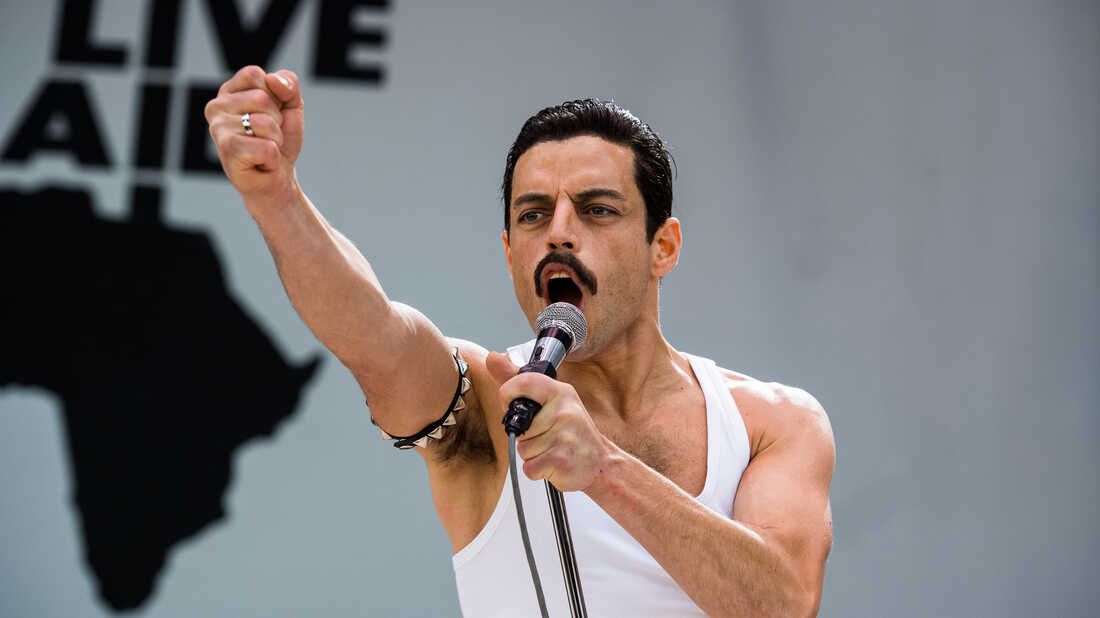
One of Mercury's most notable performances with Queen took place at Live Aid in 1985. Queen's performance at the event has since been voted by a group of music executives as the greatest live performance in the history of rock music. The results were aired on a television program called "The World's Greatest Gigs". Mercury's powerful, sustained note during the a cappella section came to be known as "The Note Heard Round the World". In reviewing Live Aid in 2005, one critic wrote, "Those who compile lists of Great Rock Frontmen and award the top spots to Mick Jagger, Robert Plant, etc. all are guilty of a terrible oversight. Freddie, as evidenced by his Dionysian Live Aid performance, was easily the most godlike of them all." Photographer Denis O'Regan, who captured a definitive pose of Mercury on stage—arched back, knee bent and facing toward the sky—during his final tour with Queen in 1986, commented "Freddie was a once-in-a-lifetime showman". Queen roadie Peter Hince states, "It wasn't just about his voice but the way he commanded the stage. For him it was all about interacting with the audience and knowing how to get them on his side. And he gave everything in every show."

Throughout his career, Mercury performed an estimated 700 concerts in countries around the world with Queen. A notable aspect of Queen concerts was the large scale involved. He once explained, "We're the Cecil B. DeMille of rock and roll, always wanting to do things bigger and better." The band was the first ever to play in South American stadiums, breaking worldwide records for concert attendance in the Morumbi Stadium in São Paulo in 1981. In 1986, Queen also played behind the Iron Curtain when they performed to a crowd of 80,000 in Budapest, in what was one of the biggest rock concerts ever held in Eastern Europe. Mercury's final live performance with Queen took place on 9 August 1986 at Knebworth Park in England and drew an attendance estimated as high as 200,000. A week prior to Knebworth, May recalled Mercury saying "I'm not going to be doing this forever. This is probably the last time." With the British national anthem "God Save the Queen" playing at the end of the concert, Mercury's final act on stage saw him draped in a robe, holding a golden crown aloft, bidding farewell to the crowd.
As a young boy in India, Mercury received formal piano training up to the age of nine. Later on, while living in London, he learned guitar. Much of the music he liked was guitar-oriented: his favourite artists at the time were the Who, the Beatles, Jimi Hendrix, David Bowie, and Led Zeppelin. He was often self-deprecating about his skills on both instruments. Brian May said that Mercury "had a wonderful touch on the piano. He could play what came from inside him like nobody else – incredible rhythm, incredible passion and feeling." Keyboardist Rick Wakeman praised Mercury's playing style, saying he "discovered [the piano] for himself" and successfully composed a number of Queen songs on the instrument. From the early 1980s Mercury began extensively using guest keyboardists. Most notably, he enlisted Fred Mandel (a Canadian musician who also worked for Pink Floyd, Elton John, and Supertramp) for his first solo project. From 1982 Mercury collaborated with Morgan Fisher (who performed with Queen in concert during the Hot Space leg), and from 1985 onward Mercury collaborated with Mike Moran (in the studio) and Spike Edney (in concert).
Mercury played the piano in many of Queen's most popular songs, including "Killer Queen", "Bohemian Rhapsody", "Good Old-Fashioned Lover Boy", "We Are the Champions", "Somebody to Love", and "Don't Stop Me Now". He used concert grand pianos (such as a Bechstein) and, occasionally, other keyboard instruments such as the harpsichord. From 1980 onward, he also made frequent use of synthesisers in the studio. Brian May said that Mercury used the piano less over time because he wanted to walk around on stage and entertain the audience. Although he wrote many lines for the guitar, Mercury possessed only rudimentary skills on the instrument. Songs like "Ogre Battle" and "Crazy Little Thing Called Love" were composed on the guitar; the latter featured Mercury playing rhythm guitar on stage and in the studio.
As well as his work with Queen, Mercury put out two solo albums and several singles. Although his solo work was not as commercially successful as most Queen albums, the two off-Queen albums and several of the singles debuted in the top 10 of the UK Music Charts. His first solo effort goes back to 1972 under the pseudonym Larry Lurex, when Trident Studios' house engineer Robin Geoffrey Cable was working in a musical project, at the time when Queen were recording their debut album; Cable enlisted Mercury to perform lead vocals on the songs "I Can Hear Music" and "Goin' Back", both were released together as a single in 1973. Eleven years later, Mercury contributed to the soundtrack for the restoration of the 1927 Fritz Lang film Metropolis. The song "Love Kills" was written for the film by Giorgio Moroder in collaboration with Mercury, and produced by Moroder and Mack; in 1984 it debuted at the number 10 position in the UK Singles Chart.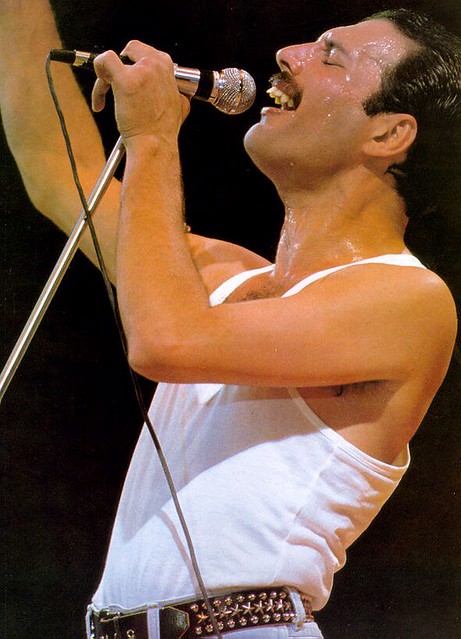
Mercury's two full albums outside the band were Mr. Bad Guy (1985) and Barcelona (1988). His first album, Mr. Bad Guy, debuted in the top ten of the UK Album Charts. In 1993, a remix of "Living on My Own", a single from the album, posthumously reached number one on the UK Singles Charts. The song also garnered Mercury a posthumous Ivor Novello Award from the British Academy of Songwriters, Composers and Authors. AllMusic critic Eduardo Rivadavia describes Mr. Bad Guy as "outstanding from start to finish" and expressed his view that Mercury "did a commendable job of stretching into uncharted territory".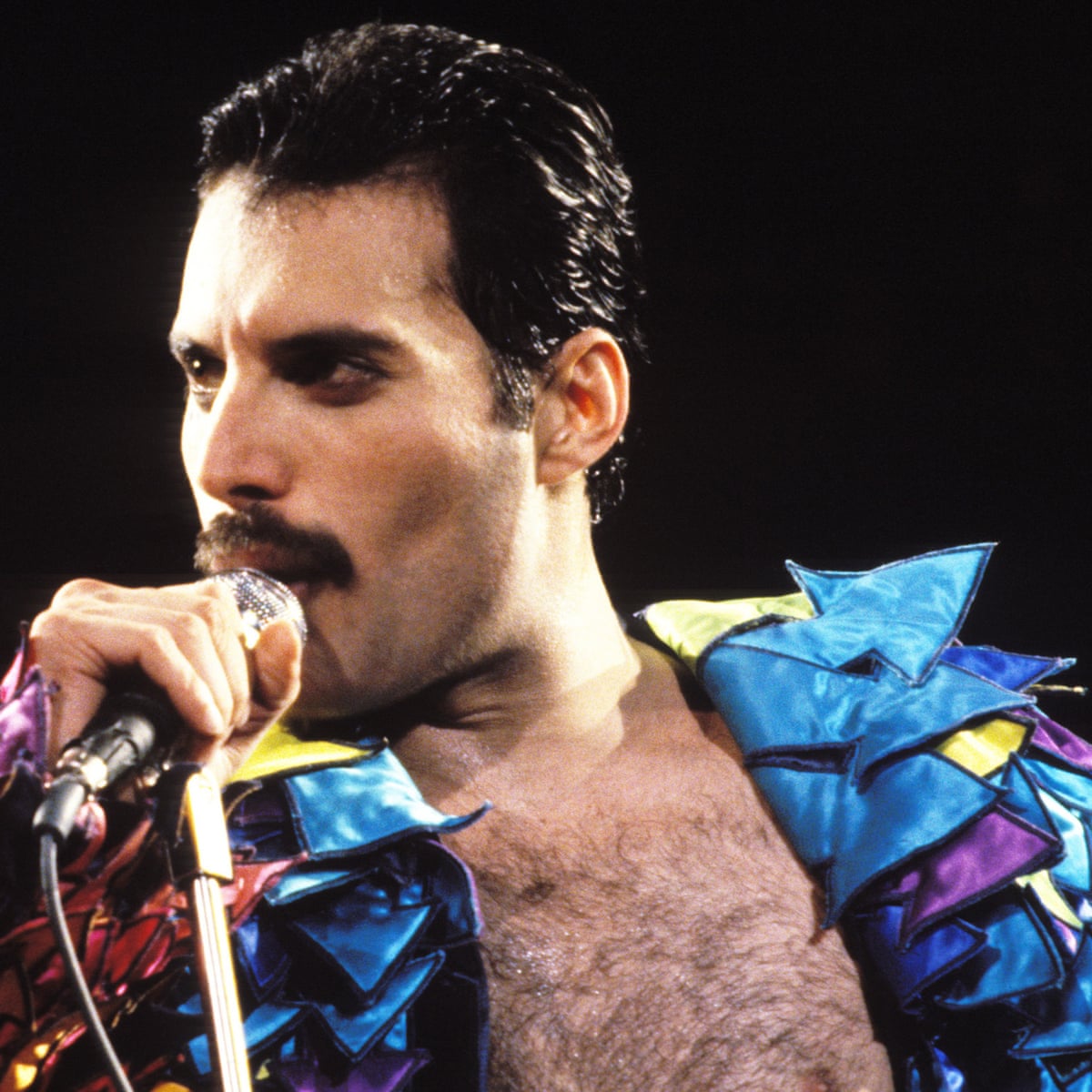
His second album, Barcelona, recorded with Spanish soprano vocalist Montserrat Caballé, combines elements of popular music and opera. Many critics were uncertain what to make of the album; one referred to it as "the most bizarre CD of the year". The album was a commercial success, and the album's title track debuted at No. 8 in the UK and was also a hit in Spain. The title track received massive airplay as the official anthem of the 1992 Summer Olympics (held in Barcelona one year after Mercury's death). Caballé sang it live at the opening of the Olympics with Mercury's part played on a screen, and again before the start of the 1999 UEFA Champions League Final between Manchester United and Bayern Munich in Barcelona.
In addition to the two solo albums, Mercury released several singles, including his own version of the hit "The Great Pretender" by the Platters, which debuted at No. 5 in the UK in 1987. In September 2006 a compilation album featuring Mercury's solo work was released in the UK in honour of what would have been his 60th birthday. The album debuted in the UK top 10. In 2012, Freddie Mercury: The Great Pretender, a documentary film directed by Rhys Thomas on Mercury's attempts to forge a solo career, premiered on BBC One.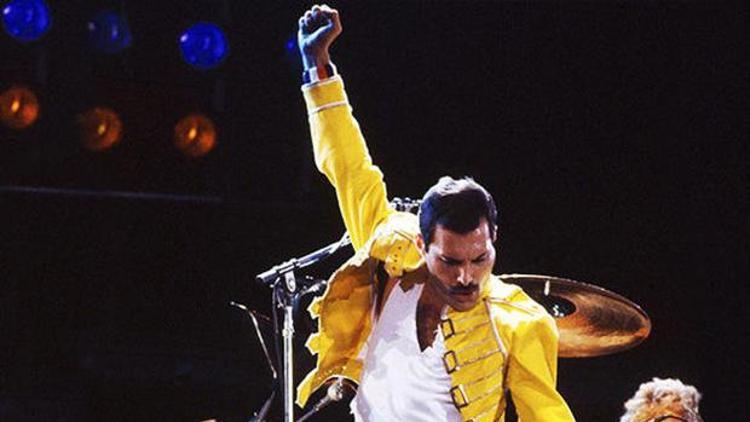
In 1986 Mercury recorded two songs for Dave Clark's West End sci-fi musical Time. Mercury performed the title song and Clark played it to Laurence Olivier who starred as the hologram Akash in a pre-filmed segment for the musical in what was one of his last roles, with Clark recalling: "Laurence Olivier was a huge god of an actor. He narrated the album [Time], and, when Freddie came on, singing "Time", Olivier said, 'Now, my dear boy, there's an actor.'" Clark relayed the reaction of Olivier to Mercury: "I told Freddie and he was over the moon. I arranged for a dinner party at my place, Olivier came along and they got on like a house on fire."/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/eb/7f/eb7f6961-6a11-486d-8508-f4a233de8037/2e6b78b2-c1bb-4826-8ee8-77b383d58bc5.jpg)
Between 1981 and 1983 Mercury recorded several tracks with Michael Jackson, including a demo of "State of Shock", "Victory", and "There Must Be More to Life Than This". None of these collaborations were officially released at the time, although bootleg recordings exist. Jackson went on to record the single "State of Shock" with Mick Jagger for the Jacksons' album Victory. Mercury included the solo version of "There Must Be More to Life Than This" on his Mr. Bad Guy album. "There Must Be More to Life Than This" was eventually reworked by Queen and released on their compilation album Queen Forever in 2014. Mercury and Roger Taylor sang on the title track for Billy Squier's 1982 studio release, Emotions in Motion and later contributed to two tracks on Squier's 1986 release, Enough Is Enough, providing vocals on "Love is the Hero" and musical arrangements on "Lady With a Tenor Sax". In 2020, Mercury's music video for "Love Me Like There's No Tomorrow" was nominated for Best Animation at the Berlin Music Video Awards. Woodlock studio is behind the animation.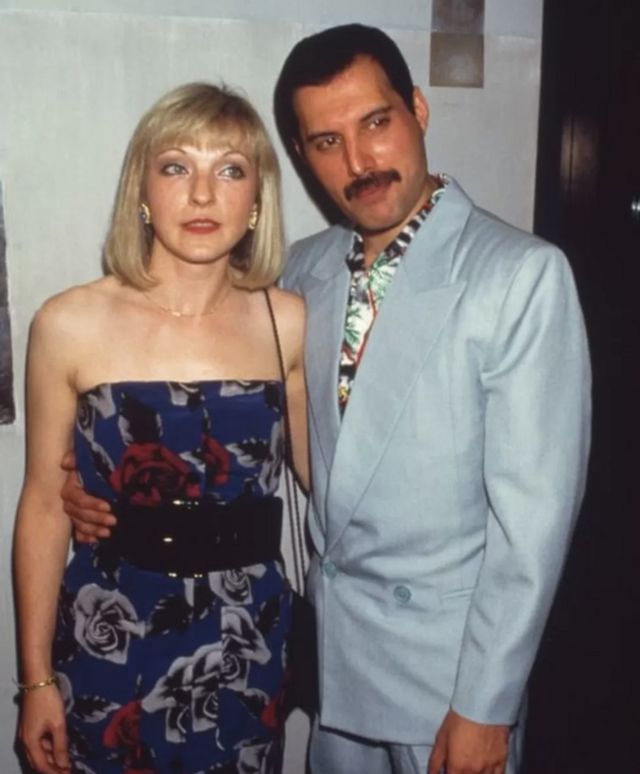
Mercury exhibited HIV/AIDS symptoms as early as 1982. Authors Matt Richards and Mark Langthorne have stated in their biographical book about Mercury, Somebody to Love: The Life, Death, and Legacy of Freddie Mercury, that Mercury secretly visited a doctor in New York City to get a white lesion on his tongue checked (which might have been hairy leukoplakia, one of the first signs of an infection) a few weeks before Queen's final American appearance with Mercury on Saturday Night Live on 25 September 1982. They also stated that he had associated with someone who was recently infected with HIV on the same day of their final US appearance, when he began to exhibit more symptoms.
In October 1986, two months after Mercury's final live performance with Queen at Knebworth House on the Magic Tour, the British newspapers the News of the World and The Sun reported that Mercury had his blood tested for HIV/AIDS at a Harley Street clinic, but he was quoted as saying he was "perfectly fit and healthy". According to his partner, Jim Hutton, Mercury was diagnosed with AIDS in late April 1987. Around that time, Mercury said in an interview that he had tested negative for HIV.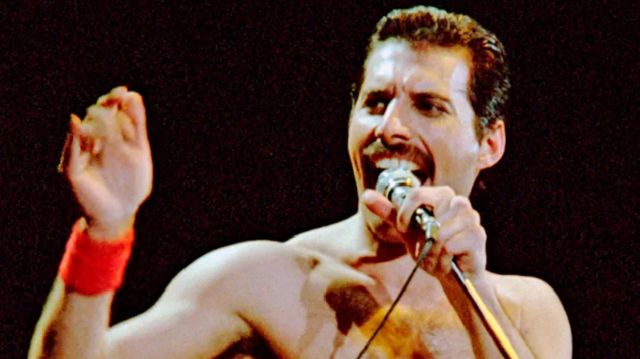
The British press pursued rumours about Mercury's health over the next few years, fuelled by his increasingly gaunt appearance, Queen's absence from touring, and reports from his former lovers to tabloid journalists. By 1990, rumours about Mercury's health were rife. At the 1990 Brit Awards held at the Dominion Theatre, London, on 18 February, Mercury made his final appearance on stage, when he joined the rest of Queen to collect the Brit Award for Outstanding Contribution to British Music.
Mercury and his inner circle of colleagues and friends continually denied the stories. It has been suggested that Mercury could have helped AIDS awareness by speaking earlier about his illness. Mercury kept his condition private to protect those closest to him; May later confirmed that Mercury had informed the band of his illness much earlier. Filmed in May 1991, the music video for "These Are the Days of Our Lives" features a very thin Mercury in his final scenes in front of the camera. Director of the video Rudi Dolezal comments, "AIDS was never a topic. We never discussed it. He didn't want to talk about it. Most of the people didn't even 100 percent know if he had it, apart from the band and a few people in the inner circle. He always said, 'I don't want to put any burden on other people by telling them my tragedy.'" The rest of the band were ready to record when Mercury felt able to come into the studio, for an hour or two at a time. May said of Mercury: "He just kept saying. 'Write me more. Write me stuff. I want to just sing this and do it and when I am gone you can finish it off.' He had no fear, really." Justin Shirley-Smith, the assistant engineer for those last sessions, said: "This is hard to explain to people, but it wasn't sad, it was very happy. He [Freddie] was one of the funniest people I ever encountered. I was laughing most of the time, with him. Freddie was saying [of his illness] 'I'm not going to think about it, I'm going to do this.'"
After the conclusion of his work with Queen in June 1991, Mercury retired to his home in Kensington, West London. His former partner, Mary Austin, was a particular comfort in his final years, and in the last few weeks made regular visits to look after him. Near the end of his life, Mercury began to lose his sight, and declined so that he was unable to leave his bed. Mercury chose to hasten his death by refusing medication and took only painkillers. On 22 November 1991, Mercury called Queen's manager Jim Beach to his Kensington home to prepare a public statement, which was released the following day: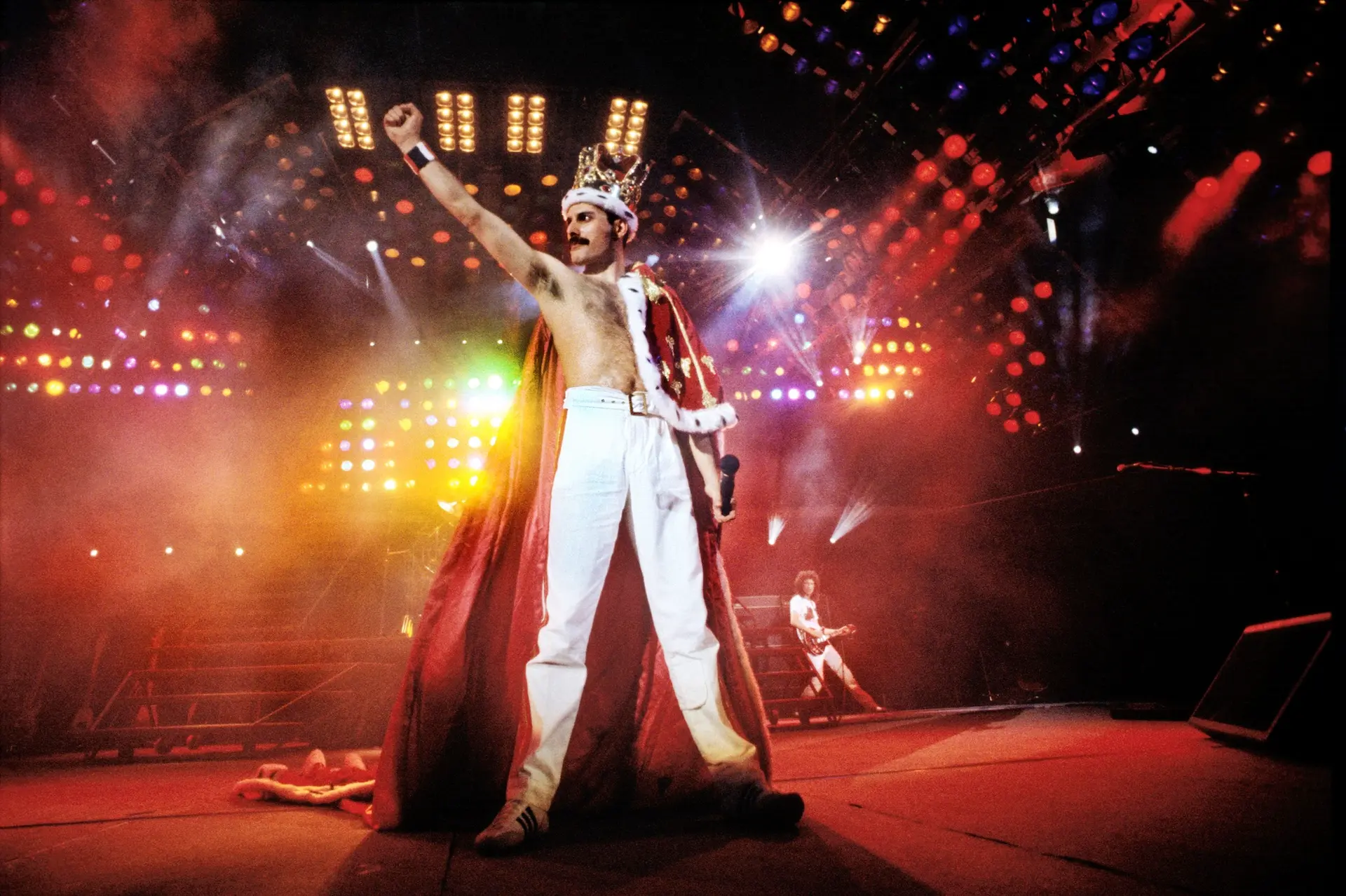
Following the enormous conjecture in the press over the last two weeks, I wish to confirm that I have been tested HIV positive and have AIDS. I felt it correct to keep this information private to date to protect the privacy of those around me. However, the time has come now for my friends and fans around the world to know the truth and I hope that everyone will join with me, my doctors and all those worldwide in the fight against this terrible disease. My privacy has always been very special to me and I am famous for my lack of interviews. Please understand this policy will continue.

References
- Runtagh, Jordan (23 November 2016). "Freddie Mercury: 10 Things You Didn't Know Queen Singer Did". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on 23 August 2018. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- "Freddie Mercury: Asteroid named after late Queen star to mark 70th birthday". BBC News. 5 September 2016.
- "Freddie Mercury, British singer and songwriter". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 11 June 2015.
- Linda B (5 October 2000), Certificate of Birth, Chorley: Mr Mercury, archived from the original (JPEG) on 28 February 2008
- "Freddie Mercury (real name Farrokh Bulsara) Biography". Inout Star. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- May, Brian (18 November 2016). "Freddie's Mum – R.I.P." brianmay.com. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- Simpson, George (15 June 2022). "Freddie Mercury's sister shuts down myth on Queen singer's death". Daily Express.




















































