Statistics for Machine Learning (Part 1)Part 1: What is Statistics
Definition
Statistics is a science that enables us to draw conclusions about various phenomena on the basis of real data collected on a sample basis. Statistics is a very broad branch of mathematics that deals with everything related to data, from the collection and organization of data to its analysis, interpretation, and presentation. Statistics is used for decision-making by understanding the data [4]. Mathematicians use statistics to collect, analyze, interpret, and visualize empirical data. With the ever-increasing amount of data, statistics has become an indispensable tool in every field where one has to work with data. When the amount of data we are dealing with is fairly small, then it might be possible to talk about all the data items individually. However, when we are dealing with large quantities of data, which is almost always the case in real-world situations, we need to have some characteristic values that can represent the data.
Types of Statistics
- Descriptive Statistics
- Inferential statistics
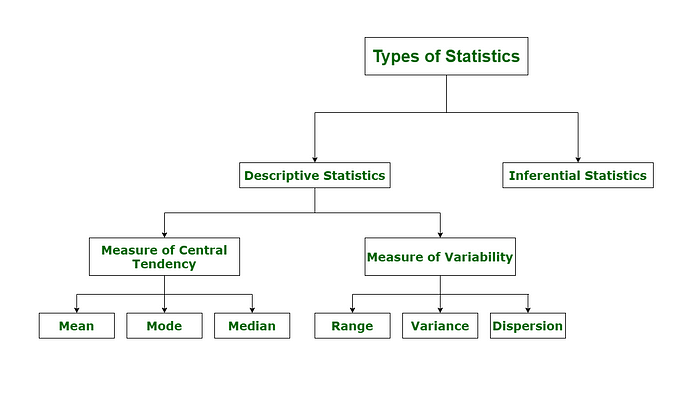
1- Descriptive Statistics
Def 1: Understand the sample. Descriptive statistics involves summarizing and organizing the data so they can be easily understood. Descriptive statistics is a subset of statistics that deals with data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It allows you to summarise and describe the key characteristics of a data set, such as its central tendency, variability, and shape. Descriptive statistics are frequently used as the first step in data analysis, providing a preliminary understanding of the data before more complex statistical techniques are applied [6]. Descriptive statistics, unlike inferential statistics, seeks to describe the data but does not attempt to make inferences from the sample to the whole population. This generally means that descriptive statistics, unlike inferential statistics, is not developed on the basis of probability theory [1]. The purpose of descriptive statistics is to describe sample and population characteristics (what has happened). As you know, in descriptive statistics, we generally deal with data available in a sample, not in a population.[1]. collecting, analyzing, presenting, and interpreting or summarizing the data [2].In descriptive statistics, no prediction will be there to understand the data of current samples (Mean, Median, Mode, IQR, Range) [4].
Descriptive statistics can be used to gain insights into data, identify outliers and anomalies, detect trends and patterns, and make data-informed decisions. It helps in the identification of key features and variables that can then be used for modeling and prediction [6].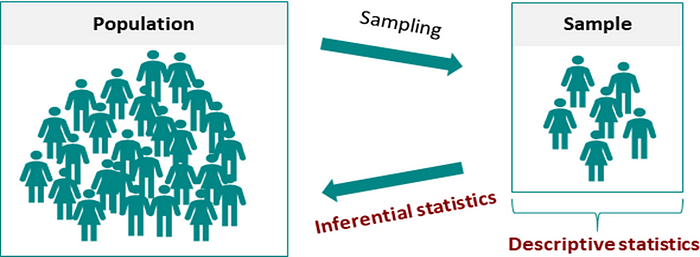
2- Inferential Statistics
Statistical inferences are based on those properties to test hypotheses, reach conclusions, and predict (what can be expected).[3].Inferential Statistics is the process of deducing or concluding from the data. With inferential statistics, we deduce a conclusion about the larger population by executing different tests and deductions from the smaller sample [5]. There are several approaches in inferential statistics which are suitable for data science. Let us look at some of these techniques [5].
- Central Limit Theorem
- Hypothesis Testing
- Qualitative Data Analysis
If you want to learn more about these topics: Python, Machine Learning Data Science, Statistic For Machine learning, Linear Algbra for Machine learning Computer Vision,
Then Login and Enroll in Coursesteach to get fantastic content in the data field.
Remember, learning is a continuous process. So keep learning and keep creating and sharing with others!💻✌️
If you’re looking for a following services, then contact me at:
Skype: themushtaq48, email:mushtaqmsit@gmail.com
👉Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning tutoring
👉 Research Paper supervision
👉 Machine learning and Deep learning projects
👉 Machine learning and Deep learning Content writing
References
1- Understanding Descriptive Statistics
2-Statistics For Data Science — Part 1
3- For Machine Learning, a Complete Guide for Applied Statistics
4- STATISTICS FOR DATA SCIENCE
5-Statistics for Data Science
6-The Ultimate Guide to Statistics: Part 1 — Descriptive Statistics










































