Impact of Internet Growth on the Online Stock Trading in India
Abstract
Nearly two billion people are connected to the Internet. During the last twenty years, the technology revolution has had an intense and irreversible impact on the world and Indian stock market has also witnessed these changes. From its formal inception in the 19th century, the Indian capital market has come a long way and can be said to be in a maturity stage, backed by a developed legal system. The internet has made financial products and services available to more customers and eliminated geographical barriers. Earlier investors were solely dependent on their brokers but nowadays they are participating more in buying and selling of shares with the help of internet. E-trading has saved time, energy and money as it helps to access the market from any where at any time. The primary objective of this research paper is to analyze the impact of internet growth on the stock market transactions. The paper also discusses the current state of internet trading in India and particularly the scope of online trading market available in India.
Keywords
Indian Stock Market, Internet, Online Stock Trading
INTRODUCTION
India was introduced to the Internet in the early 90's and the use started to increase rapidly. India stands 5th in the list of countries by number of internet users. The Stock markets introduced Internet trading (online-trading) in February 2002 which has brought a tremendous change in trading. The National Stock Exchange started the first form of online trading wherein user/investors can buy/sell stocks in a day without much paper work. Earlier it used to take around 60 days to buy/sell stocks in stock markets and the investor also had to go though loads of paper work. But thanks to Internet the wait has curbed and in the last ten years, Indian capital markets have recorded 1488% of growth in exchange turnover.
ONLINE STOCK TRADING IN INDIA
Online stock trading in India has gained ground in the last two years. It’s interesting to note that it was a beer making company, "WIT Beer” that for first time, way back in 1969, had introduced the idea of online stock trading. There are several leading companies involved in online stock trading in India. ICICIDirect, Sharekhan, AnandRathi ,Geojit securities, Indiabulls, Religare, Kotak Securities, Motilal Oswal Securities, Reliancemoney, India Infoline.com Securities limited , and IDBI Paisabuilder are the major players in online Indian stock trading.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Brad M. Barber and Terrance Odean (2002) analyzed 1,607 investors who switched from phone based to online trading during the 1990s. Those who switched to online trading perform well prior to going online, beating the market by more than 2% annually. After going online, they trade more actively, more speculatively, and less profitably than before—lagging the market by more than 3% annually.Reductions in market frictions (lower trading costs, improved execution speed, and greater ease of access) do not explain these findings. Overconfidence—augmented by self attribution bias and the illusions of knowledge and control—can explain the increase in trading and reduction in performance of online investors. They found that investors who choose to make investments online are better performers than those who do not go online before the switch but worse performers after the shift. The idea is that overconfidence induces them to switch but then excessive trading after the switch dissipates their profits.Haroun Alryalat, Yogesh Kumar Dwivedi, Jasna Kuljis, and Ray J. Paul (2006) analyzed the effect of online and traditional trading on effective market performance on the NASDAQ. The purpose of this paper was to present a critical analysis on the competition between online (ECN) and traditional (Market Maker (MM)) trading on the NASDAQ stock exchange. Online stock trading mechanisms at the exchanges are often a hybrid of dealer and auction markets. Different aspects of trading execution, which is the most commonly used market centre at present, were analyzed. This leads to a discussion on: (1) the path that executes order is organized and (2) its impact on the effective market performance, trading cost and investor behaviour.Nidhi Walia and Ravinder Kumar (2007) wrote in their research paper, which was published in Indian journal of marketing, that there is no denying the fact that internet trading offered investors convenience of trading along with reduced cost. But Indian investors have not yet fully realized the importance of using technology for stock trading. The major findings of the study are the Indian investors are more conservative, they do not change brokers for trading, whereas net traders are more comfortable with online trading for its transparency and complete control of the terminal.In the Indian context, online trading can be rightly called as a recent phenomenon, and even till day online trading is not much popular among investors for which a list of factors can be blamed. This fact is clearer from the information available that where numbers of stock exchanges in India have grown from 7 exchanges in 1946 to total 23 stock exchanges till 2011, only two stock exchanges are providing online share trading. Over the past two years, the value of all trades executed through internet on NSE has grown from less than Rs. 100 Cr. to over Rs. 700 Cr. in June 2005.Online trading is gaining momentum with trading volume growing by 150 % per annum.
FACTS AND FIGURES OF INDIAN STOCK MARKET
Trading Volume
In the year 2009-10, the trading volumes increased by 50.36 % to 4,138,023 crore (US $ 916,709 million) from 2,752,023 crore (US $ 540,142 million) during 2008-09. The average daily trading volume increased from 11,325 crore (US $ 2,223 million) during 2008-09 to 16,959 crore (US $ 3,757 million) during 2009-10. The remarkable aspect was that the trading volumes in the year 2009-10 showed a growth of 16.53 % over the trading volumes witnessed in 2007-08.
Market Capitalization
The total market capitalization of securities available for trading on the CM segment increased from 363,350 crore (US $ 115,606 million) as at end March 1995 to 6,009,173 crore (US $ 1,331,230 million) as at end March 2010. The Market capitalization witnessed an increase of 107.49 % during 2009-10 as compared to the market capitalization of 2,896,194 crore (US $ 568,439 million) in 2008-09. As compared with 2007-08, the market capitalization in 2009-10 increased by 23.69 %. The market capitalization ratio of NSE was 97.49% as of March 31, 2010. The company with the highest market capitalization as of March 2010 was Reliance Industries Limited followed by Oil and Natural Gas Corporation of India Limited and NTPC Ltd.
On-line IPOs
The on-line trading system of NSE is used by companies to make IPOs through book building. It is a fully automated screen based bidding system that allows trading members to enter bids on behalf of their clients. All bids received by the system are numbered, time stamped, and stored in the book till the last day of the book building process and the offer price is determined after the bid closing date. While ensuring efficient price discovery, this system reduces time taken for completion of the issue process. 342 companies have used the on-line IPO system of NSE by the end of March 2010.
Internet Trading
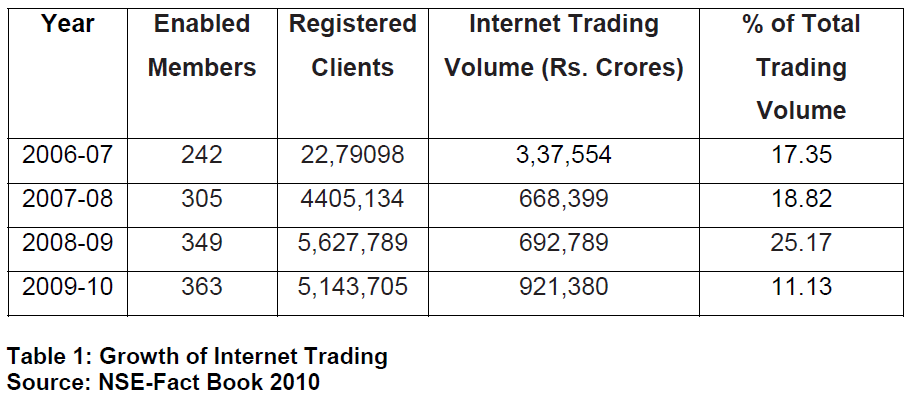
At the end of March 2010, a total number of 363 members were permitted to allow investor’s web based access to NSE’s trading system. The members of the exchange in turn had registered 5,143,705 clients for web based access as on March 31, 2010. During the year 2009-10, 11.13 % of the trading value in the Capital Market segment (692,789 - US $ 135,974 million) was routed and executed through the internet. The table below shows the growth of internet trading from the fiscal years 2006-07 till 2009- 10. Chart-1 shows the internet trading volumes in the CM segment of NSE in comparison with the total traded volumes at NSE.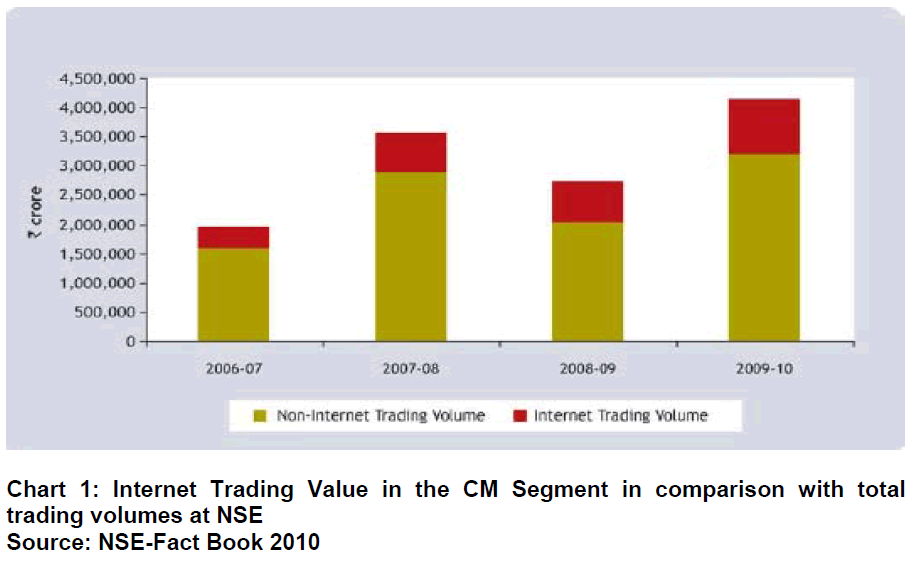
 INTERNET AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
INTERNET AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
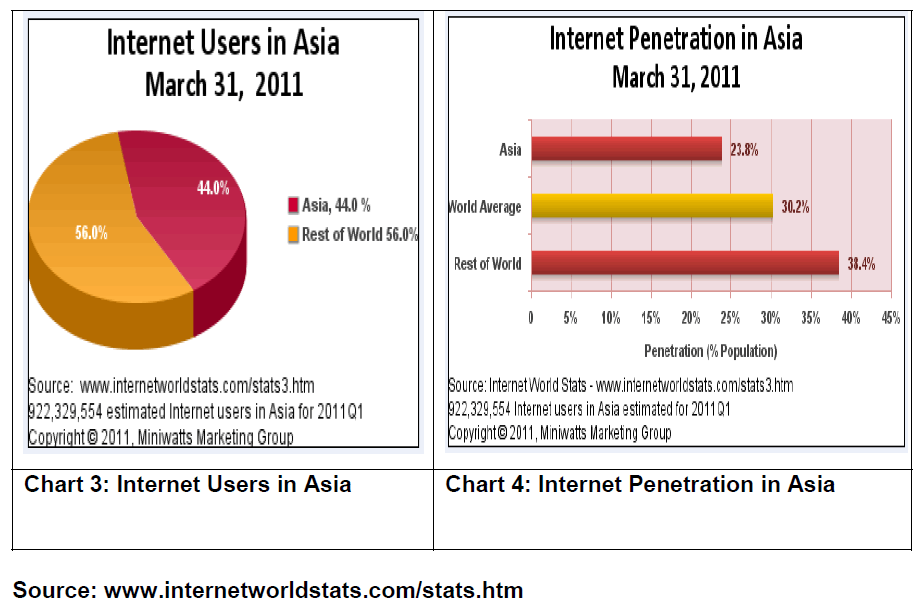
According to a McKinsey report titled ‘Internet matters: The Net’s sweeping impact on growth, jobs, and prosperity’, released at the e-G8 Forum held in Paris on May 24-25, 2011, internet contributed 5 per cent to the total gross domestic product (GDP) growth of India in the past five years compared with the average 3 per cent for BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India and China) economies. As per the report, companies are able to keep costs down, target customers better and bring goods and services to markets around the world much more easily.Individuals are able to compare prices, search hard-to-find items or information, communicate and learn in new, improved ways. Governments can serve citizens much more quickly and at a much lower cost through e-governance. According to the report there are 2 billion internet users worldwide and as a sector, internet related consumption and expenditure is now bigger than agriculture or energy.The report further said that internet has a sweeping impact on growth, prosperity of a country and has created 2.4 jobs for every job that it has destroyed. “The Internet is a contributor to net job creation. While jobs have been destroyed by the emergence of internet, many more have been created during the same period, including jobs directly linked to the internet, such as software engineers and online marketers as well as more traditional jobs, logistics to deliver online purchases," the report added.Moving towards an Internet-based economy can help fill the gaps that lead to poor performance in a traditional economy. Initiatives in the agriculture sector, such as ‘mKrishi’ in Madhya Pradesh, allow farmers to benefit from timely expert advice. The ‘aAqua’ project in Maharashtra uses the Internet to connect with farmers to address a range of concerns related to production, pricing, input and output supply.The Internet is also promoting government services in a big way. Examples such as Aarogyasri in Andhra Pradesh are enabling end-to-end cashless services to citizens, and filling health sector gaps in doctors or basic infrastructure.Broadband-supported, community-driven initiatives such as Barefoot College in Rajasthan, Chanderiyaan in Madhya Pradesh and AirJaldi in Himachal Pradesh are having accelerated effects on citizens. HarVa is a greenfield project that serves as an outstanding example to demonstrate the causal impact of the Internet on income.The Internet is now widely considered a fundamental infrastructure in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries in much the same way as electricity, water and transportation. India, as an OECD member, must recognize access to the Internet as a basic right.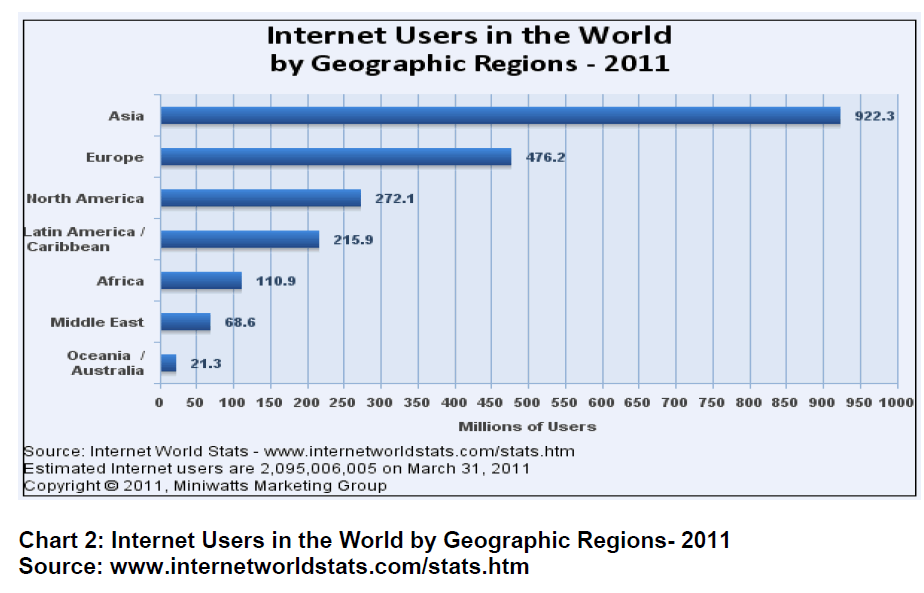
 IMPACT OF INTERNET ON THE GROWTH OF FINANCIAL MARKET
IMPACT OF INTERNET ON THE GROWTH OF FINANCIAL MARKET
E-Commerce Market to Be Rs. 46,520 Crores In 2011
The internet commerce industry in India has seen a manifold increase in the last couple of years with the total market size increasing from INR 19, 688 crores by the end of 2009 to an estimated INR 31, 598 crores in 2010. The net commerce market size is expected to grow by 47% and touch INR 46,520 crores by end of 2011. This was highlighted by a report on the E-commerce released by the Internet and mobile Association of India (IAMAI).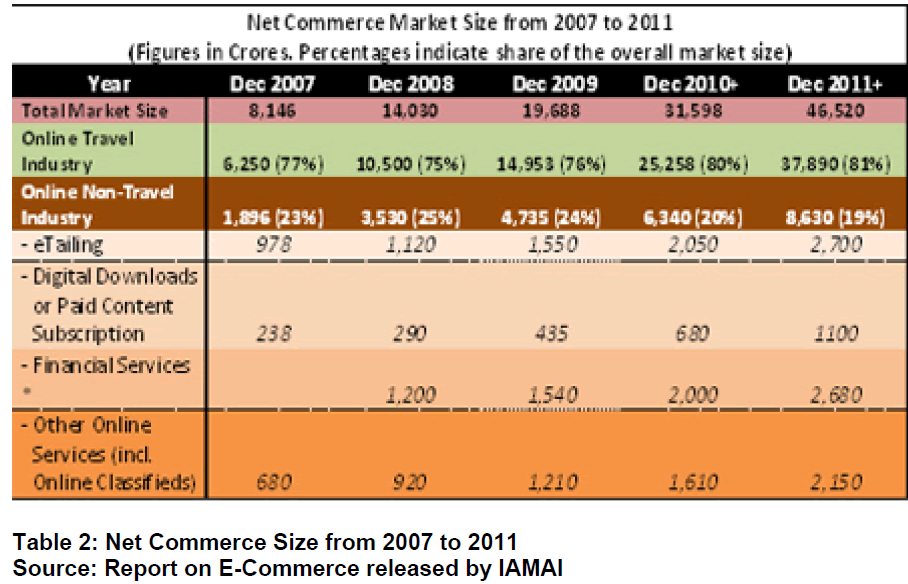 The report also highlights that other areas like digital downloads and e-tailing are showing promise and growing rapidly. These sectors are predicted to grow by 62% and touch INR 1100 crores and INR 2700 crores respectively by December 2011.Another area that has shown significant growth is the financial services market that has grown from INR 1540 crores to an estimated INR 2000 crores by end of December 2010. This sector is expected to grow by 34% and touch INR 2680 crores by end of December 2011.
The report also highlights that other areas like digital downloads and e-tailing are showing promise and growing rapidly. These sectors are predicted to grow by 62% and touch INR 1100 crores and INR 2700 crores respectively by December 2011.Another area that has shown significant growth is the financial services market that has grown from INR 1540 crores to an estimated INR 2000 crores by end of December 2010. This sector is expected to grow by 34% and touch INR 2680 crores by end of December 2011.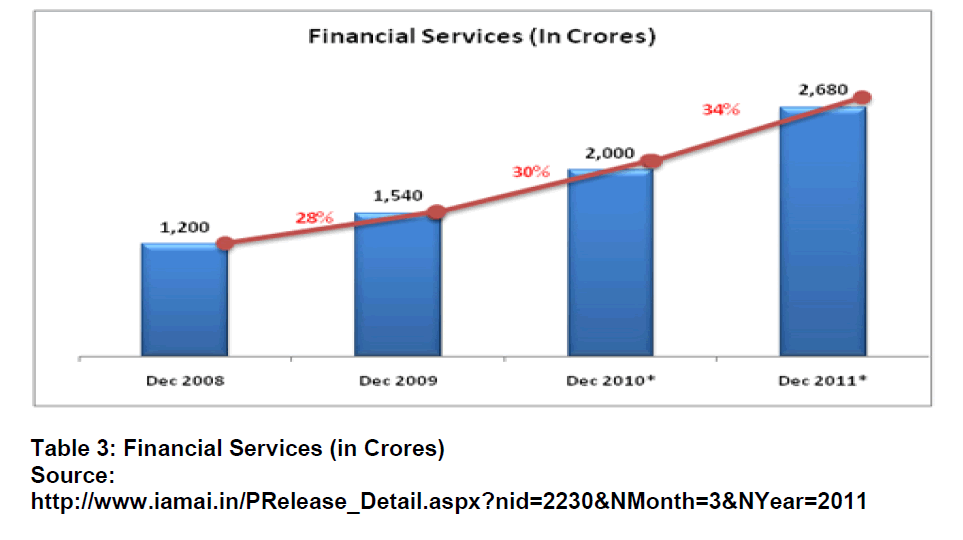




























![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - I Think I Have Crypto PTSD](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/819e7cdb-b6d8-4508-8a8d-7f1106719ecd/1)


