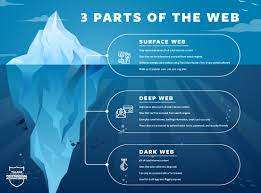
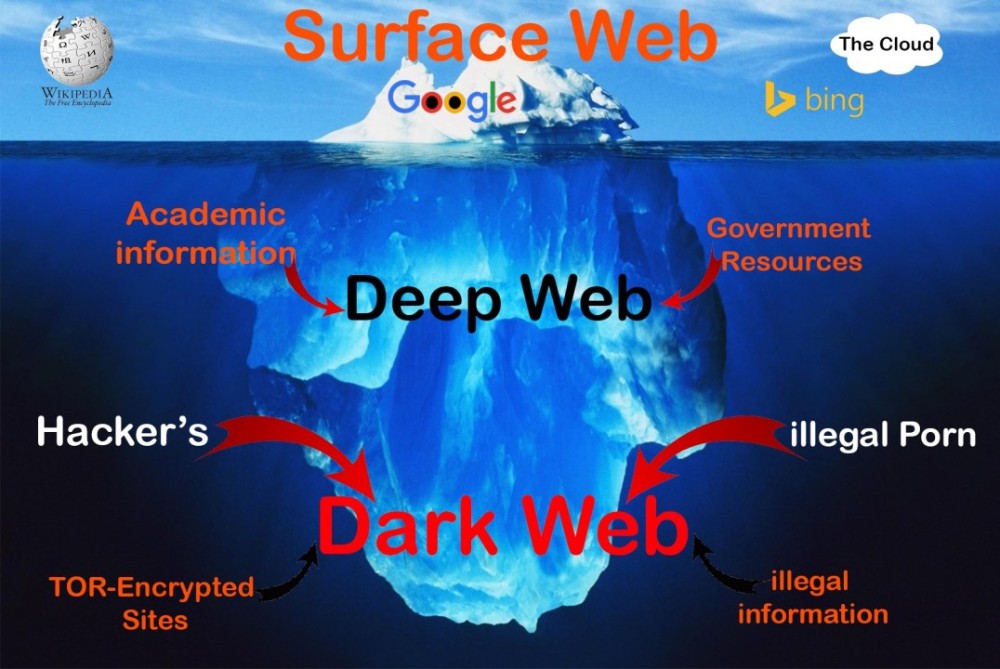
What is the Dark Web
The History of the Dark Web: Unveiling the Shadows of the Internet
The emergence of the Dark Web has added an enigmatic layer to the vast landscape of the internet. As a realm hidden from conventional search engines, the Dark Web has a complex history marked by technological innovation, anonymity, and the evolution of illicit activities. This article delves into the historical timeline of the Dark Web, exploring its origins, key developments, and the transformative events that have shaped its present state.
- Genesis of the Dark Web:
- The roots of the Dark Web can be traced back to the 1970s and 1980s when the concept of anonymous communication networks began to take shape. The Cypherpunk movement played a pivotal role during this period, advocating for privacy and secure communication. Early experiments with encryption laid the groundwork for the future development of the Dark Web.
- The Birth of Tor:
- The Dark Web as we know it today largely relies on Tor (The Onion Router), a project developed by the U.S. Navy in the 1990s for secure communication. Tor's unique architecture, routing traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers, provided a robust platform for anonymous internet browsing. It was later released to the public, becoming a crucial tool for both privacy advocates and those with more nefarious intentions.
- Silk Road and the Rise of Cryptocurrency:
- One of the watershed moments in the Dark Web's history was the launch of Silk Road in 2011. This underground marketplace, accessible only through Tor, facilitated the trade of illegal goods and services using Bitcoin, marking the beginning of the Dark Web's association with cryptocurrency. The subsequent takedown of Silk Road by law enforcement underscored the challenges of regulating this hidden realm.
- Evolution of Dark Web Marketplaces:
- Following Silk Road's demise, numerous other Dark Web marketplaces emerged, adopting enhanced security measures and a decentralized approach. These platforms diversified their offerings beyond narcotics to include cybercrime tools, stolen data, and even hacking-for-hire services. The constant cat-and-mouse game between authorities and Dark Web operators became a defining characteristic of this underground economy.
- Anonymous Activism and Whistleblowing:
- While the Dark Web gained notoriety for illegal activities, it also became a sanctuary for activists and whistleblowers seeking to communicate without fear of reprisal. Platforms like WikiLeaks leveraged the Dark Web to share sensitive information, emphasizing the dual nature of this hidden space as a refuge for both the righteous and the criminal.
- Challenges and Controversies:
- The Dark Web has faced ongoing challenges, including increased scrutiny from law enforcement, cybersecurity threats, and ethical debates surrounding online privacy. As technology evolves, new layers of complexity are added to the Dark Web's landscape, prompting a continuous reassessment of regulatory approaches.
- The Present and Future Landscape:
- Today, the Dark Web remains a dynamic and evolving space. Authorities continue to grapple with the illicit activities conducted on the Dark Web, while privacy advocates argue for the importance of anonymous communication. The future trajectory of the Dark Web is uncertain, with emerging technologies and societal shifts likely to influence its direction.
The history of the Dark Web is a tapestry woven with threads of technological innovation, anonymity, and the ever-present tension between privacy and security. Understanding its origins and evolution is essential for navigating the complexities of the digital age, as society continues to grapple with the implications of this hidden corner of the internet.
The Underworld of the Dark Web: Unveiling Illegal Activities in the Shadows
The Dark Web, often shrouded in mystery, serves as a breeding ground for various illegal activities, ranging from cybercrime to illicit trade. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the spectrum of illegal activities that find refuge in the hidden corners of the internet. From illegal marketplaces to cyber-attacks for hire, the Dark Web has become a haven for those seeking to operate outside the boundaries of conventional legality.
- Illicit Marketplaces:
- One of the most infamous aspects of the Dark Web is its role as a platform for illegal marketplaces. These marketplaces operate similarly to legitimate e-commerce sites but specialize in the trade of illegal goods and services. From drugs and weapons to stolen data and hacking tools, the range of offerings on these platforms is extensive. The closure of prominent marketplaces by law enforcement has, however, done little to stifle the persistence of these underground economies.
- Drug Trade:
- The Dark Web has become a virtual haven for drug trafficking, providing a platform for buyers and sellers to conduct transactions anonymously. Cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, have become the preferred method of payment, offering a level of anonymity that traditional currencies cannot provide. The international nature of these transactions makes it challenging for law enforcement to curb the drug trade effectively.
- Cybercrime as a Service:
- The Dark Web has given rise to a disturbing trend known as "Cybercrime as a Service." Criminals can now hire hackers and purchase ready-made malware to execute cyber-attacks. This commodification of cybercrime lowers the entry barrier for aspiring criminals and contributes to the proliferation of online threats such as ransomware, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and identity theft.
- Stolen Data Markets:
- Hacked databases, personal information, and login credentials are frequently traded commodities on the Dark Web. These stolen datasets are often used for identity theft, financial fraud, or sold to other cybercriminals. The abundance of such information poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations, highlighting the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
- Weapons Trade:
- The Dark Web provides a clandestine platform for the illegal trade of firearms and other weapons. Buyers and sellers can connect without the traditional risks associated with physical black markets. The anonymity offered by the Dark Web amplifies the challenges faced by law enforcement agencies attempting to regulate the illegal arms trade.
- Human Trafficking:
- Tragically, the Dark Web is not immune to the horrors of human trafficking. Illegal forums and websites facilitate the trafficking of individuals, often exploiting their vulnerabilities. Law enforcement agencies worldwide are engaged in an ongoing battle to identify and dismantle these networks, but the hidden nature of such activities poses a significant challenge.
- Challenges for Law Enforcement:
- Policing the Dark Web presents numerous challenges for law enforcement, including jurisdictional issues, encryption technologies, and the constant evolution of tactics employed by criminals. The cat-and-mouse game between authorities and those engaged in illegal activities on the Dark Web continues to unfold.
The Dark Web's role in facilitating illegal activities underscores the need for a comprehensive and collaborative approach to cybersecurity and law enforcement. As technology advances, society must remain vigilant in addressing the challenges posed by the hidden corners of the internet. Only through a concerted effort can we hope to mitigate the impact of illegal activities flourishing in the shadows of the Dark Web.
The Technological Infrastructure of the Dark Web: Navigating the Depths of Anonymity
The Dark Web, with its cloak of anonymity and encrypted communication, relies on a sophisticated technological infrastructure that enables users to operate beyond the gaze of conventional internet surveillance. This article delves into the intricate technological underpinnings of the Dark Web, exploring the tools, protocols, and encryption mechanisms that contribute to its clandestine nature.
- The Onion Router (Tor):
- At the heart of the Dark Web's technological framework lies Tor, short for The Onion Router. Tor is an open-source software designed to facilitate anonymous communication by directing internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers. Each server in this network peels back a layer of encryption, akin to layers of an onion, hence the name. Tor provides a crucial layer of anonymity for users accessing the Dark Web.
- Encryption Protocols:
- Encryption is a cornerstone of Dark Web technology. Beyond the inherent encryption within the Tor network, end-to-end encryption is widely employed to secure communications between users. PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) and GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) encryption tools are commonly used to encrypt messages and files, ensuring that only the intended recipients can access the information.
- Cryptocurrencies:
- The financial transactions on the Dark Web are predominantly conducted using cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the most prevalent. Cryptocurrencies provide a level of financial anonymity that traditional currencies lack. The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of blockchain technology underpinning cryptocurrencies aligns with the ethos of the Dark Web, allowing users to engage in transactions without revealing their identities.
- Hidden Services and .onion Domains:
- Dark Web websites are typically accessed through .onion domains, a special top-level domain specifically designed for anonymous services within the Tor network. These hidden services allow website operators and users to conceal their identities and locations. The decentralized nature of these domains adds an extra layer of resilience against censorship and takedowns.
- Decentralized Hosting:
- Traditional websites rely on centralized hosting services, making them susceptible to takedowns. In contrast, the Dark Web embraces decentralized hosting. Peer-to-peer networks and distributed file-sharing systems allow for the hosting of content across multiple nodes, making it challenging for authorities to pinpoint and shut down specific servers.
- Blockchain and Smart Contracts:
- Beyond cryptocurrencies, the Dark Web has started to explore the potential of blockchain technology for other purposes. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, have the potential to automate and secure various transactions on the Dark Web, further enhancing its efficiency and security.
- Challenges and Evolving Technologies:
- The technological infrastructure of the Dark Web continues to evolve, presenting challenges for law enforcement and cybersecurity experts. As artificial intelligence, machine learning, and quantum computing advance, the Dark Web must adapt to maintain its level of anonymity and security, prompting a continuous cycle of technological innovation.
The technological underpinnings of the Dark Web illustrate a fascinating interplay between privacy-enhancing technologies and the quest for anonymity in the digital age. As the Dark Web continues to evolve, understanding its technological landscape becomes crucial for policymakers, cybersecurity professionals, and society at large to navigate the complex intersection of technology, privacy, and security.











































![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - Is Trump Dying? Or Only Killing The Market?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/a129e75e-4fa1-46cc-80b6-04e638877e46/1)



![[FAILED] Engage2Earn: McEwen boost for Rob Mitchell](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c798d46f-d3b8-4a66-bf48-7e1ef50b4338/1)










