Best DeFi Projects in 2024: Top DApps to Watch!
Ever since Bitcoin, born from the ashes of the 2008 financial crisis, was unveiled to the world, its role, along with that of other cryptocurrencies, has been about disrupting the traditional financial system, tracing back to feudal times when monarchs ruled the world.
From time immemorial, those who have power control the wealth distribution, and it has never been as obvious as now, when the gap between the haves and have-nots has widened tremendously. However, with the birth of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, there is now another attempt at a better way of wealth distribution where ordinary people like you and I can have a stab at getting a sliver of that pie. How this will be done will be through Decentralised Finance.
In this article, we will look at what decentralised finance is, the risks involved, the types of activities that can be undertaken, and of course, the top DeFi projects.
What is Decentralized Finance?
Finance, as we know it, is the realm where a lot of financial experts and professionals eagerly guard their domain, oftentimes with great ferocity. By intentionally keeping finance behind a wall of red tape, restrictions, jargon and technicalities, it is designed to incentivise ordinary people to put trust in their expertise and centralized systems. This has not always been to their clients' benefit and plenty of intermediaries, both companies and individuals, have taken advantage of this situation, sometimes to the extreme, as seen with the subprime mortgage crisis that almost toppled Wall Street.
Decentralised Finance is pretty much the opposite. There are no gatekeepers, so anyone with an internet connection is free to participate. There is still plenty of jargon, but there are plenty of folks, like us at the Coin Bureau, who aim to educate everyone on the basics.  Most important of all, there are very few, if any, intermediaries involved. Most of the heavy lifting is done using smart contracts, which are a series of computer codes crafted with specific conditions to be fulfilled automatically.
Most important of all, there are very few, if any, intermediaries involved. Most of the heavy lifting is done using smart contracts, which are a series of computer codes crafted with specific conditions to be fulfilled automatically.
Unlike borrowing with a bank, which requires jumping through a lot of hoops in the hope of getting a loan, none of that is necessary when borrowing from a DeFi platform. As long as you have the necessary collateral, you can get a loan. However, there is no grace period when it comes to getting liquidated. Once the value of the collateral goes below the borrowed amount, the collateral is liquidated almost immediately, no questions asked as the code in the smart contract is triggered based on a predetermined set of coded instructions.
How Safe is DeFi?
When crypto's potential first started popping its head up, it was reasonable to expect that the same playbook could be applied to this new space. From Mt Gox as the first Bitcoin exchange to a plethora of other centralised exchanges that came up after, people new to crypto and familiar with the way things work are more inclined to trust these centralised finance (CeFi) entities. Some of that trust is warranted but others are misplaced as many of us have found out.
Meanwhile, DeFi also has its share of bad actors spoiling the pot for everyone. Hacks, rugpulls, scams are what occupy the forefront of people's minds. This gives those unfamiliar with the environment the impression that everything is bonkers in crypto, like the minute you put something down, it's immediately swept away by a gust of scammy wind. Is that the objective truth? I'd beg to differ. Everyone knows that bad news is always more eye-catching than good news. “If it bleeds, it leads” is something one would hear in perhaps a slightly disreputable newsroom. Who wants to hear about things working well? It's what's not working well that is newsworthy. So it is the same with DeFi. It would be reasonable to assume that DeFi sustains the most losses compared to CeFi given all the airtime each time a hack happens.
However, the actual situation paints a slightly different picture than what is usually believed. ImmuneFi, a leading bug bounty and security services platform for web3 based in Singapore, has given us some stats worth covering: 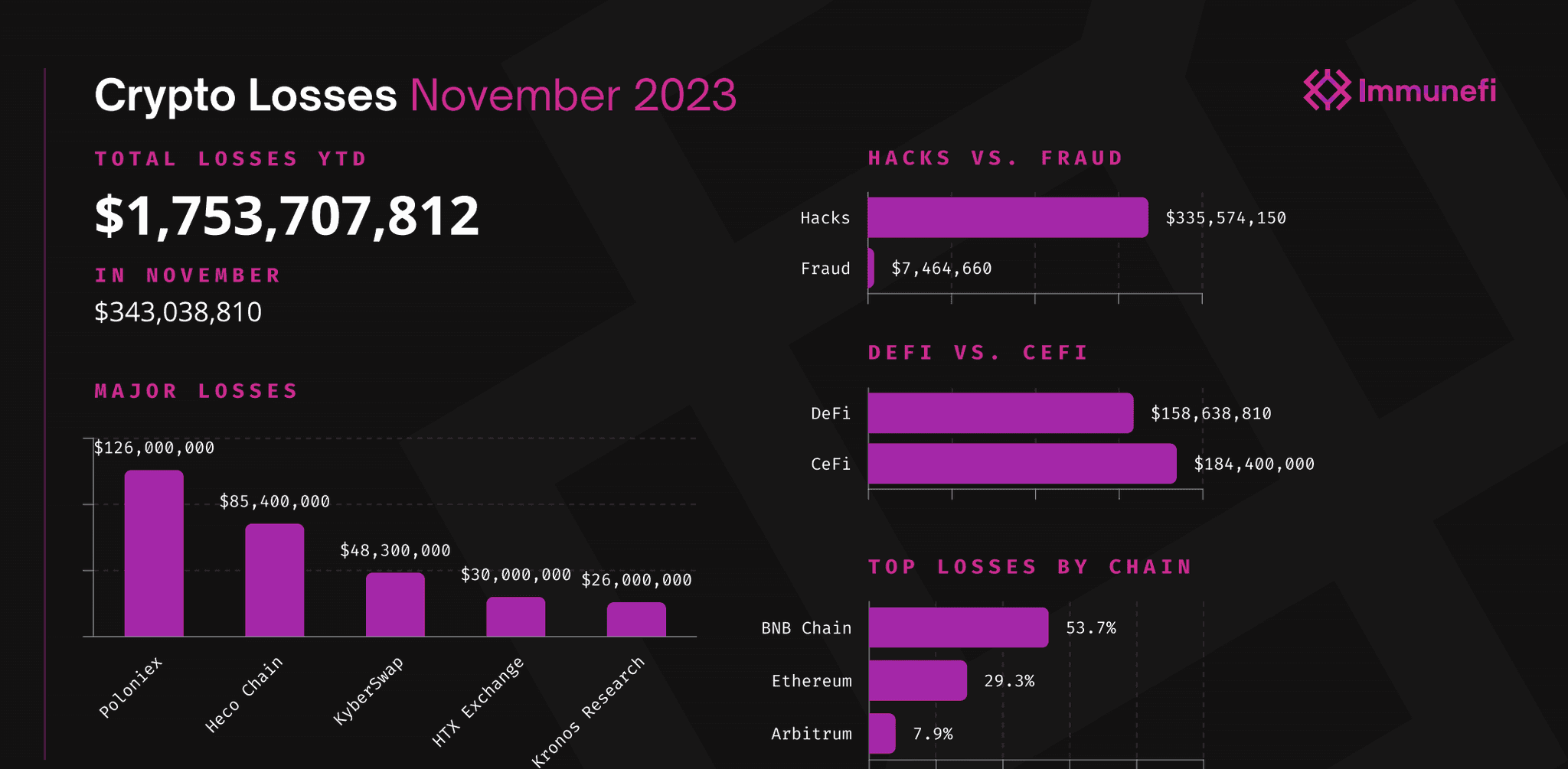 As startling as the numbers may appear, what is notable is that of the total losses in crypto in November 203, the majority of it is attributed to CeFi, not DeFi. Frauds also play a much smaller role than hacks.
As startling as the numbers may appear, what is notable is that of the total losses in crypto in November 203, the majority of it is attributed to CeFi, not DeFi. Frauds also play a much smaller role than hacks.
What makes CeFi more susceptible to hacks is its centralised nature. It's like having 5 people stand guard over 100 acres of land vs 50 people stand guard over the same land size. The 5 people may each be giants, each equivalent to 20 people, but there are still only 5. If any of them falls the risk of a breach is huge. In the latter scenario, even though the 50 people individually may not be as strong as a single giant, there are more to fight against and when one falls, the loss is minimal. It's easier to focus resources on a few points of failure than to spread out resources to attack over a larger space.
The overall numbers representing losses are certainly nothing to sniff at. The silver lining though is that DeFi isn't as bad as it has been portrayed because it is less risky than CeFi.
What Can You Do in DeFi?
DeFi is not just about borrowing and lending money on decentralised blockchain platforms. Taking a wider perspective, DeFi includes various finance-related activities. There are exchanges where one can swap one asset for another without undergoing KYC or trusting a custodial intermediary, buy insurance for the protocols that you interact with to hedge against the risk of failure, bet on predictions based on the outcome of real-world events, or just pure gambling in online casinos.
The majority of DeFi activity still revolves around lending, borrowing, yield farming, providing liquidity, and staking of tokens to earn yield. To that end, numerous platforms are offering a variety of strategies, including automated yield farming ones, to help users get the most out of their funds.
Best DeFi Projects
At a glance, here is a look at some of the leading DeFi platforms, their supported chains, TVL and category: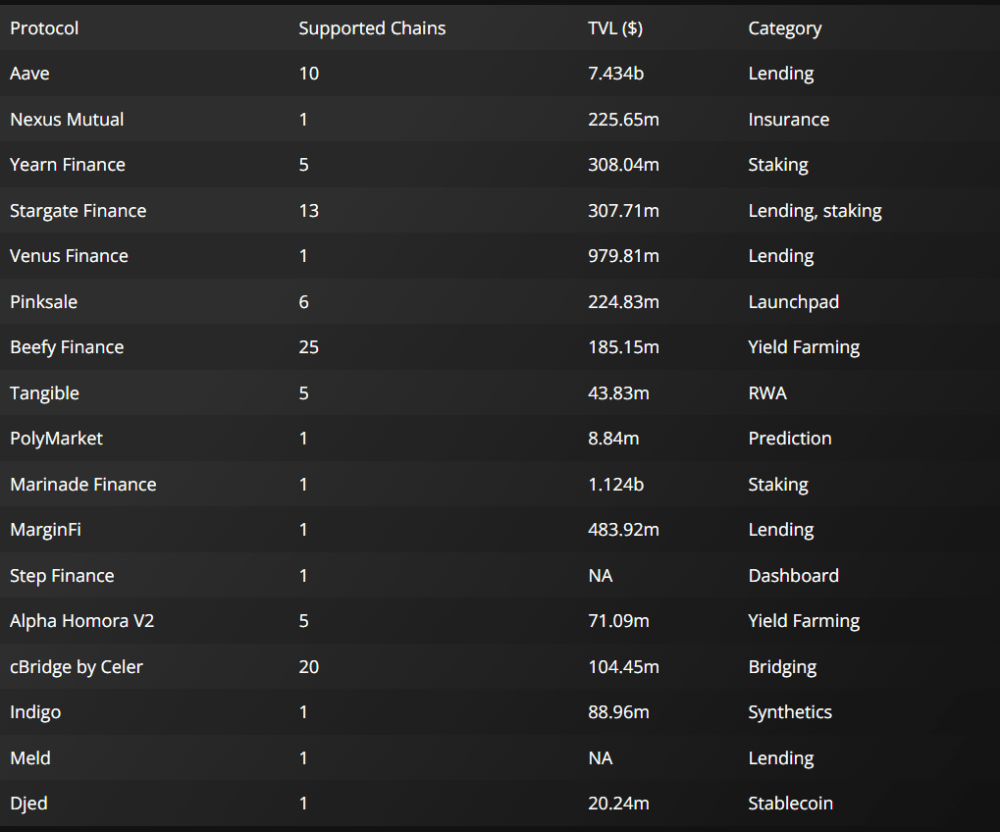
Ethereum
Aave
Aave is one of the earliest DeFi projects on Ethereum back in 2020 when DeFi was just coming into being. The open-source, non-custodial protocol allows lenders to earn interest through deposits and borrowers to borrow assets. As one of the first movers in the space, it is now firmly in position as the third-largest dApp in Ethereum by TVL. 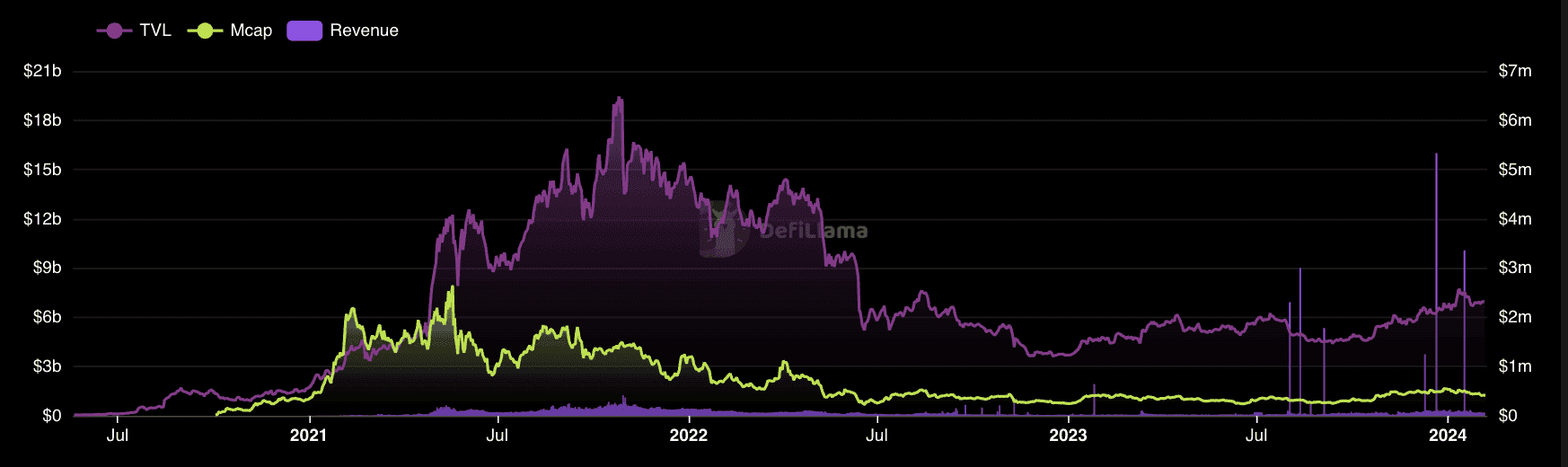 Currently, at $7 billion in TVL, Aave has branched out to other L2s on Ethereum including Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon. You can also find Aave in Avalanche, a non-Ethereum blockchain. More than $10 billion has made its way to Aave across 8 networks and 15 markets.
Currently, at $7 billion in TVL, Aave has branched out to other L2s on Ethereum including Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon. You can also find Aave in Avalanche, a non-Ethereum blockchain. More than $10 billion has made its way to Aave across 8 networks and 15 markets.
The protocol has a kitty fund of more than $300 million that acts as a backstop in case of protocol insolvency. This gives lenders peace of mind when interacting on their platform. The smart contracts have been vetted by 6 top-notch security firms as an example of their commitment to security.
Nexus Mutual
Crypto investing is a risky business which most traditional insurance companies would not dare to cover. Fear not, for Nexus Mutual is here.
This is a decentralised insurance protocol that allows users to insure against smart contract failure. Two types of products are available:
- Protocol cover: This insurance guards against risks faced by the protocol such as exploits, liquidation failure, oracle failure, hacks, and governance attacks.
- ETH Slashing cover: This insurance is for ETH stakers who incur losses due to penalties in the Ethereum consensus process.
Users need to be members before they can use the services offered. Coverage funds come from staking pools managed by members with risk and pricing expertise who earn a fee for their services.
Even with a ton of competitors nipping at its heels, Nexus is still the premier crypto insurance protocol that other similar projects measure against. Not satisfied with resting on its laurels, Nexus is also planning to launch two new types of products, one related to real-world risks and another is a directors-and-officers cover.
Yearn Finance
Yearn Finance is where DeFi investors go to earn yield without staring at the screen every day. The protocol uses automation that maximizes profits gained from yield farming. It's like robo-investing for crypto.
The vaults in Yearn Finance are sources of capital that automatically generate yield for investors. Some of them have a special boost of more rewards than others.  Each vault utilises multiple investing strategies. The overall robustness of the vault is represented by a risk score. Each strategy is asses based on 8 factors: Team Knowledge, Protocol Safety, Audit, Code Review, Complexity, Longevity, TVL Impact, and Testing Score.
Each vault utilises multiple investing strategies. The overall robustness of the vault is represented by a risk score. Each strategy is asses based on 8 factors: Team Knowledge, Protocol Safety, Audit, Code Review, Complexity, Longevity, TVL Impact, and Testing Score.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Stargate Finance (STG)
Stargate Finance is a cross-chain liquidity protocol that allows native assets to easily be swapped amongst all the chains it supports with instant guaranteed finality. Most bridging solutions face a common risk which is a lack of sufficient liquidity. Too many requests might easily drain a pool because these pools are standalone pools for each token within each chain. Not only that, users might also face high fees and long bridging time. Given that the proportion of hacks occurs on bridges, the long settlement time is also an added risk.
Stargate's Delta Algorithm lets all chains supported by Stargate maintain individual liquidity pools “soft-partitioned” into multiple sub-pools. Then it programmatically controls the unified liquidity pools so that they are not drained before the swaps are carried out. If there isn't enough liquidity to support the transaction, it simply won't go through. Stargate also utilises rebalancing fees to encourage users to replenish assets low in balance and discourage users from depleting certain assets. This helps to maintain a certain level of liquidity in pools.
Out of the $308.48 million of TVL locked in STG, $55.07 million of it is in the Binance Smart Chain, which is the second-highest TVL contributor. 
Venus Finance
Venus Finance is a decentralised borrowing and lending platform on the Binance Smart Chain. You can see it is Binance's version of Compound and MakerDAO as the protocol itself is a fork from those two projects. The Money Market Protocol is where users do the borrowing and lending, with interest accrued every block.
The version 4 upgrade introduced isolated liquidity pools so that each of them has custom risk management configurations. The price oracle used also got an upgrade as it can fetch prices from multiple feeds and validate through decentralised sources. Another key component is stablecoin minting, which is known as VAI, the protocol's stablecoin pegged at a 1:1 ratio against the US dollar. Users can stake VAI or XVS, the protocol's governance token in Vaults to earn passive income while helping to secure the platform's security.
It's worthwhile to note that the protocol experienced a bad debt loss back in May 2021 of $77 million following a significant liquidation event. Since then, numerous proposals have been made and upgrades added to ensure similar events such as these don't happen in the future. 
Pinksale
Ever wondered how you can launch a custom token on the blockchain and have it be available to trade without any technical know-how? If the answer is yes, then Pinksale is worth checking out. This protocol, which launched on the BSC blockchain, is a one-stop-shop for anyone looking to launch their token and have it listed on the BSC DEXes such as PinkSwap and PancakeSwap for trading. In addition, users can also create their project launchpad, airdrops, and staking programs on the platform.
Other services offered by PinkSale include bridging capabilities, anti-bot program connected to the token's contract address, and multi-sending functionality to batch-send your new tokens to multiple addresses at once. With a slew of other supporting services available, Pinksale has almost all the ingredients you need to successfully launch your token not just on the BSC chain, but also Fantom, AVAX, Polygon, and ETH.
Polygon
Beefy Finance (BIFI)
Beefy Finance is an automated yield-farming optimizer. What this means is that Beefy maximizes the user's rewards from various liquidity pools automatically with investment strategies enforced by smart contracts. This allows users to earn yield through auto-compounding to maximize earning potential. Users have a few ways of earning yield: staking their BIFI tokens, staking their crypto assets, or depositing their Liquidity Pool tokens (LPs) from external DEXes into vaults.
The main product for Beefy is the Vaults, which are non-custodial, thus ensuring users have complete control of their assets during the staking process. Each vault has an investment strategy designed to compound all rewards earned by reinvesting them to supercharge your gains. There are three kinds of vaults available:
- Single asset vaults
- Stablecoin vaults
- Liquidity Pools
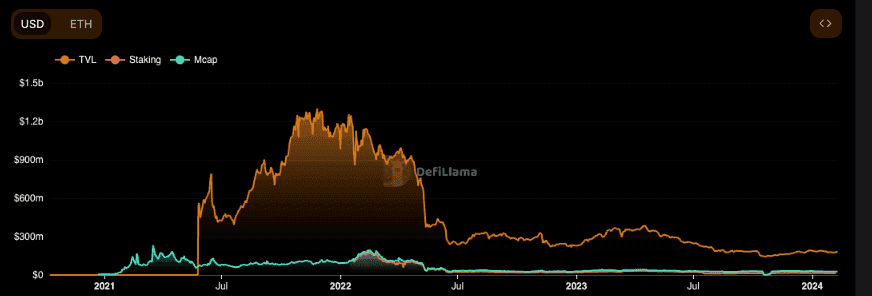 Even though Beefy got started on the Binance Smart Chain, their share on Polygon and Polygon zkEVM totals $21.72 million, far superseding its TVL on BSC, which is $16.91 million according to DeFi Llama. In addition, the protocol is supported in over 20 blockchain networks for a combined TVL of $185.2 million.
Even though Beefy got started on the Binance Smart Chain, their share on Polygon and Polygon zkEVM totals $21.72 million, far superseding its TVL on BSC, which is $16.91 million according to DeFi Llama. In addition, the protocol is supported in over 20 blockchain networks for a combined TVL of $185.2 million.
Tangible
Tangible is an exciting entry into the world of Real-World Asset (RWAs) tokenisation. A Tangible Non-Fungible Token (TNFT) is created from the tokenized asset that can be used as collateral in other DeFi projects. The NFTs can then be used to redeem the physical asset at any time. It is also the creator of Real USD, the first stablecoin backed by tokenised, yield-producing real estate. With Real USD, users can access tokenised and fractionalised RWAs in their NFT marketplace. Currently, there are 4 main types of assets available for purchase: gold bars, wines, real estate, and watches. Pricing is denoted in DAI.
Aside from buying a whole asset, users can also buy a fraction of an asset, usually involving real estate. This allows greater access to a wider pool of users who may not have the funds for an entire property but can still get a foot on the property ladder by owning a small piece. The TNFT is also easily transferred through the marketplace. It is up to the seller to determine the minimum fraction for the property and also the price of the entire available percentage.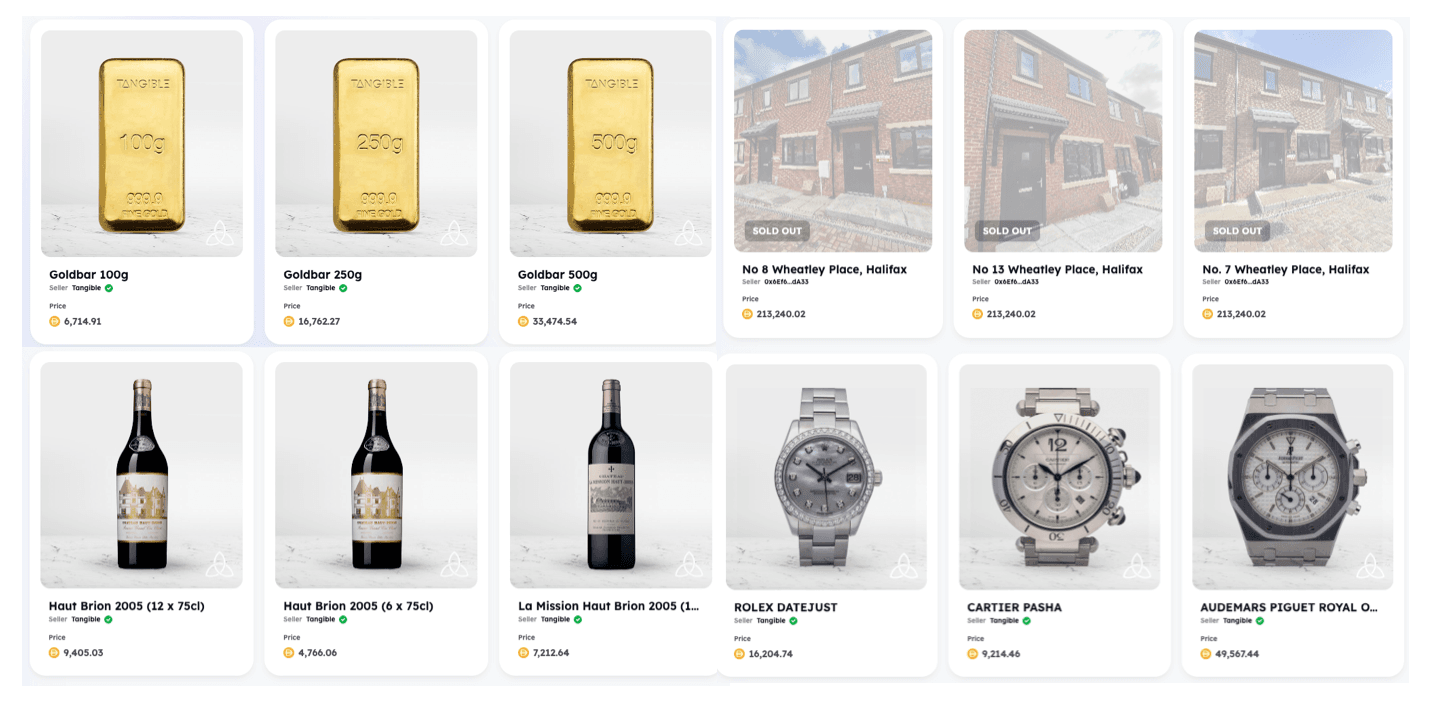
PolyMarket
Betting on predictions of real-world outcomes has always been something that has been around as long as gambling has existed in human society. PolyMarket puts a DeFi spin to it by allowing betters to buy “outcome shares” using USDC. The pricing reflects the aggregated probability of the expected outcome. If it's a Yes/No result, and the shares are only worth a few cents, the likelihood of it being a Yes is very low.
These shares can be traded at any point in time before the results are in and Polymarket doesn't charge a fee for the trades. Once the results are unveiled, they will end up costing either $1 or $0. Those who picked the right outcome get to cash out their shares at $1.00. Gas fees are calculated in MATIC so participants ought to hold both USDC and MATIC.
Note that due to a CFTC fine of $1.4 million, the platform has been closed to US residents.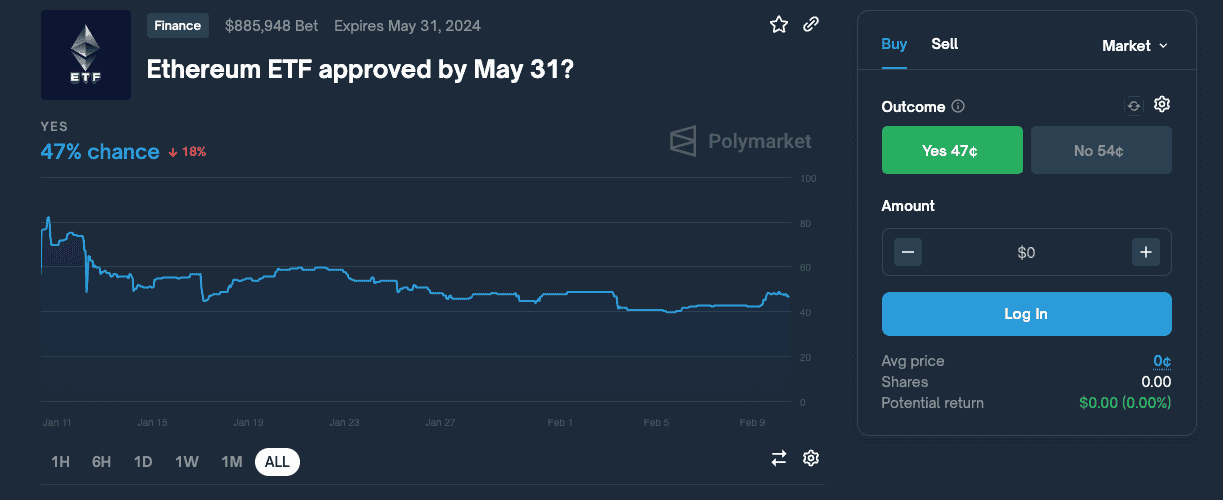
Solana
Marinade Finance (MNDE)
Marinade Finance is the top staking platform for SOL tokens in the Solana ecosystem. The platform offers two types of strategies for staking: Marinade Native earns users up to 8.37% APY for staking SOL tokens via automatic staking delegation across hundreds of validators. Note that the SOL tokens are locked into the protocol during the staking period. Liquid Staking lets users earn up to 7.89% APY and gives you a liquid staking token (mSOL) that can then be used across more than 20+ DeFi integrations. As long as you have access to the mSOL tokens, you can always use them to redeem your staked SOL. Users can also look up the validators on the platform to gauge which ones they specifically want to stake with. Alternatively, they can leave it up to the platform's algorithm to decide. 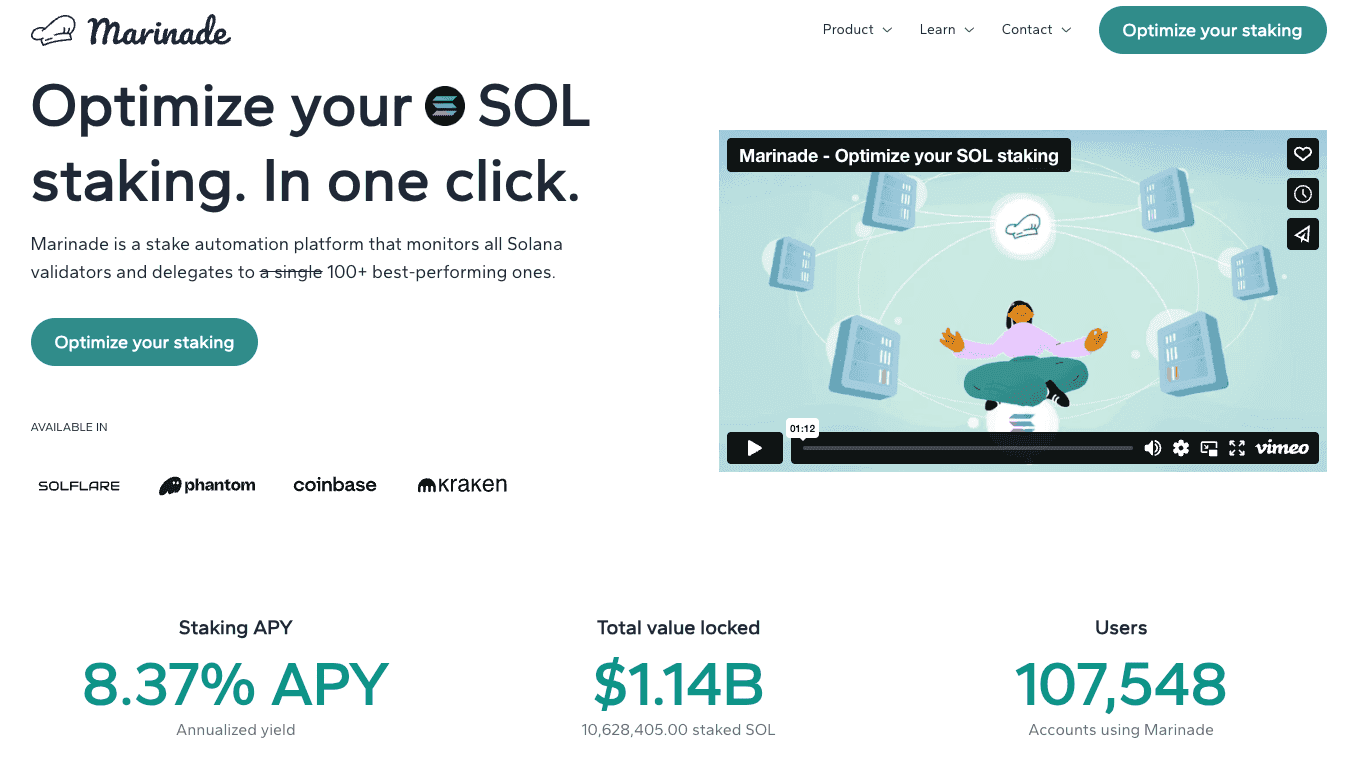 The platform is governed by the Marinade DAO using the MNDE token. This can be earned through staking SOL on the platform. The proposals and actual governing occur on the Realms platform where claimed MNDE tokens are locked in 30 days.
The platform is governed by the Marinade DAO using the MNDE token. This can be earned through staking SOL on the platform. The proposals and actual governing occur on the Realms platform where claimed MNDE tokens are locked in 30 days.
MarginFi
MarginFi is a lending and borrowing protocol on Solana where lenders earn yield and borrowers obtain loans through over-collateralization. Interest is paid to the loan specific to the asset and is of the variable sort. One way to gauge the borrower's ability to repay loans is through a metric known as Account Health, represented by a percentage. The lower it is, the less likely the borrower can repay the loan. Once it hits 0% or lower, the borrower is at risk of liquidation, which is both automatic and permissionless. MarginFi offers Lite mode and Pro mode for those who want to get started.
Lenders deposit their tokens into the liquidity pools which are then lent out to borrowers. In addition to the interest earned, lenders also receive margin points. This is part of a loyalty point campaign to incentivise usage. Users can also earn points through borrowing assets or referrals. Lenders earn 1 point per dollar per day but borrowers can get 4 points per day for the same amount. 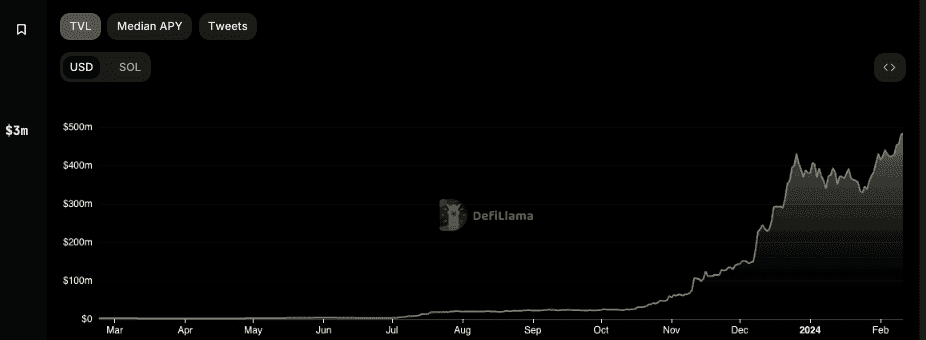
Step Finance
If you've ever had the experience of interacting with too many DeFi products and want just one place to see everything that's happening, Step Finance is the answer, at least for the DeFi products in the Solana ecosystem. This platform is a portfolio visualisation that displays all the liquidity pools, farming positions, tokens, and any DeFi activity related to the wallet that is connected with it. The dashboard is easy to understand combined with various useful metrics and visualizations. Not only do users get an overall view of their activity in Solana, but they can also execute swaps and enter into various yield farming positions and automated vaults within the Step platform.
In addition, they've added a Transaction History section that provides more details than what the transaction history in the wallet offers so that you can do a more detailed investigation of each transaction. The dashboard comes with the ability to view or hide all balances on the portfolio. You can also view any NFTs in the wallet via their NFT Gallery. Staking options are also available for both STEP and SOL tokens.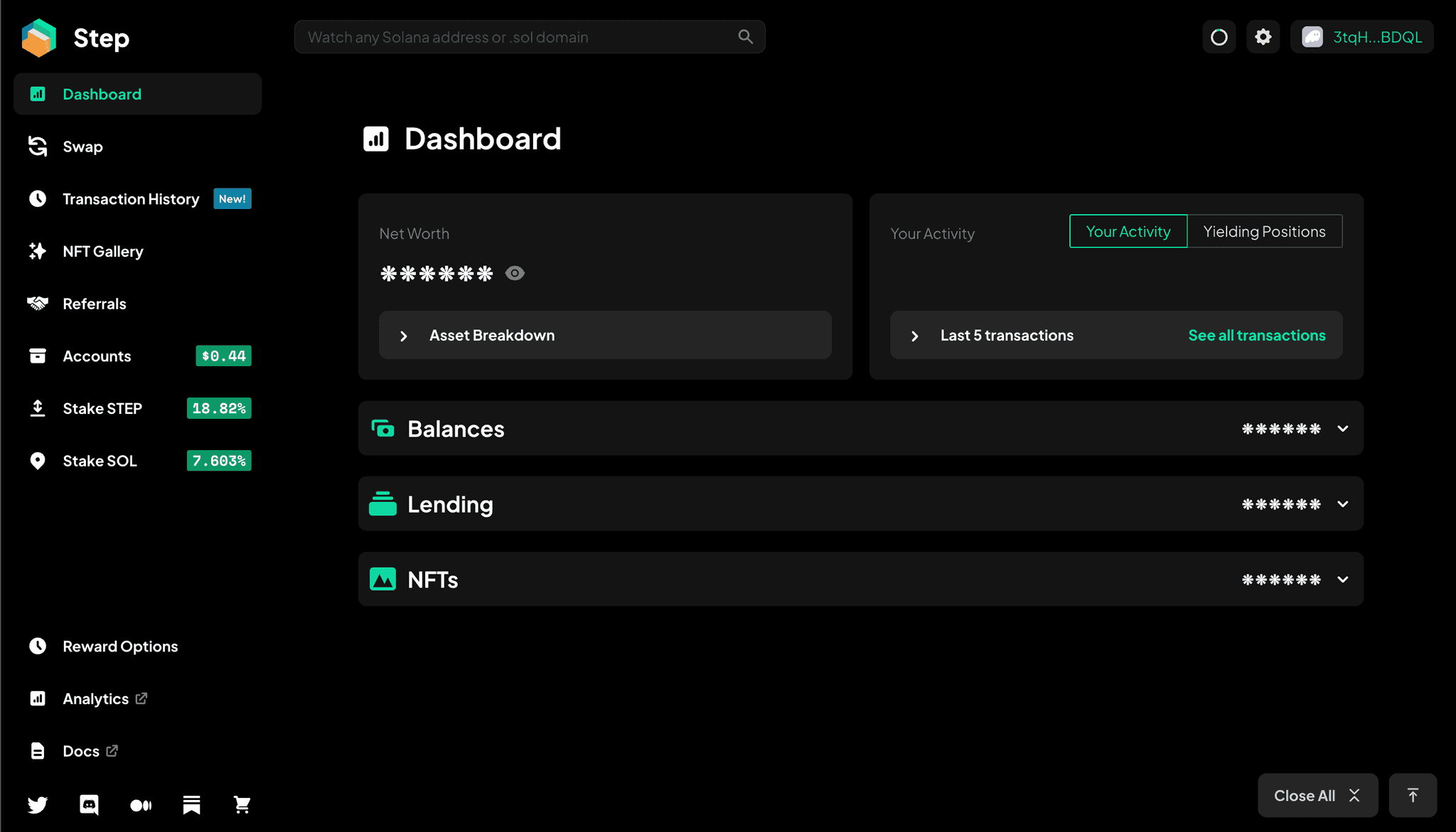
Avalanche
Alpha Homora V2
Alpha Homoroa V2 is a multi-chain lending platform and is DeFi's first leveraged yield farming protocol. Let's see what's the difference. Normal yield farming is where lenders deposit their funds into a DEX like Trader Joe's and earn trading fees. Lenders also get LP tokens which are then further staked to get more APR. In leveraged yield farming, lenders both lend and borrow funds to obtain 3x APR by yield farming with the combined value. This leads to a much higher APR. 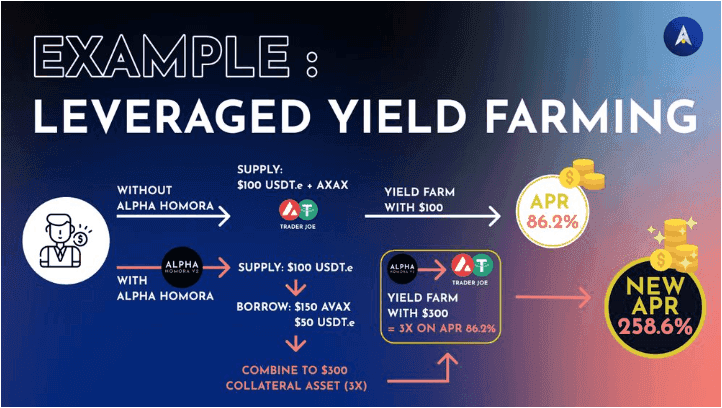
Celer Network
Celer Network is a Layer 2 scaling platform that allows for off-chain transactions. The platform provides developers with a means to build fast, cheap, and easy-to-use blockchain applications. In addition, it offers products to solve challenges within the crypto world. One of the products is cBridge, a bridging solution for asset transference for 40+ blockchains and layer-2 rollups. The bridge has facilitated more than $14 billion cross-chain asset transfer volume for over 540k unique users. This is a non-custodial bridge, meaning users have full control of their funds.
The other product is Layer2.Finance that allows for instant transactions without having to wait for confirmations on the main blockchain.
Cardano
Indigo (INDY)
Indigo is a platform that offers synthetic assets known as iAssets in a decentralized manner. Synthetic assets mean a virtual version of an asset. Examples can be a virtual version of an Apple share or Bitcoin. You don't need to possess the actual share or Bitcoin with you but you can still benefit from the price movement of the asset. iAssets are minted with smart contracts and are used to create new markets on various Automated Market Makers (AMM) and be the liquidity for yield farming. The synthetic assets can also be used to participate in other DeFi protocols, such as SundaeSwap, COTI, and Minswap, as collateral or liquidity.
The protocol has an Autonomous Oracle with the key functionality of updating the prices of the real-world assets so that the synthetic ones are at par with their real-life counterparts. With the various partnerships in place, Indigo aims to be the main platform for those entering the DeFi world of Cardano.
MELD (MELD)
MELD is one of the earliest DeFi projects on Cardano when it was first launched, aided by an aggressive marketing campaign. The campaign results were satisfactory as the platform gained more than 600 million ADA in its staking pools within the first few months. What makes Meld unique is that it allows you to borrow fiat (USD and EUR) against your crypto assets and earn a yield on the deposits. Most DeFi platforms do not play well with TradFi but Meld is breaking down that barrier with MELD Neobank.
Note that fiat-users are subject to a KYC process but this is not necessary for crypto users.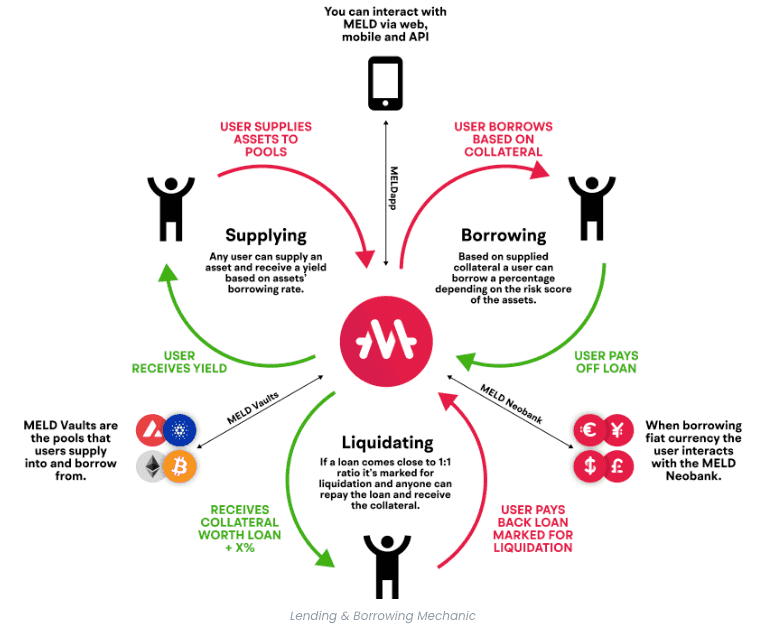 The protocol is supported on 5 other blockchains aside from Cardano (Ethereum, Bitcoin, Avalanche, Polygon, and Binance Smart Chain), making it easy to transfer assets from one blockchain to another as the bridging part is already taken care of in the MELDapp. One of the keys to Meld's success is MELD Vaults. These are community-backed staking pools, each pool for one asset. One can borrow and lend while generating returns from the pool. You can learn more in our in-depth MELD Review.
The protocol is supported on 5 other blockchains aside from Cardano (Ethereum, Bitcoin, Avalanche, Polygon, and Binance Smart Chain), making it easy to transfer assets from one blockchain to another as the bridging part is already taken care of in the MELDapp. One of the keys to Meld's success is MELD Vaults. These are community-backed staking pools, each pool for one asset. One can borrow and lend while generating returns from the pool. You can learn more in our in-depth MELD Review.
Djed (DJED)
Djed is an algorithmic stablecoin offered on the Cardano blockchain. Unlike how UST works on Terra, Djed also has a collateral component with ADA and a reserve coin called SHEN behind it. The algorithm is to monitor the difference between DJED and the USD it is pegged against. How Djed prevents what happens with UST is with SHEN. This token's function is to safeguard Djed from falling lower than 1USD by having a minimum number of tokens in place. If it looks like Djed is going to exceed its peg, then there is also a maximum amount of SHEN in circulation to prevent this from happening.
The whitepaper states that Djed “behaves like an autonomous bank that buys and sells stablecoins for a price in a range that is pegged to a target price”. It is also “the first stablecoin protocol where stability claims are precisely and mathematically stated and proven.”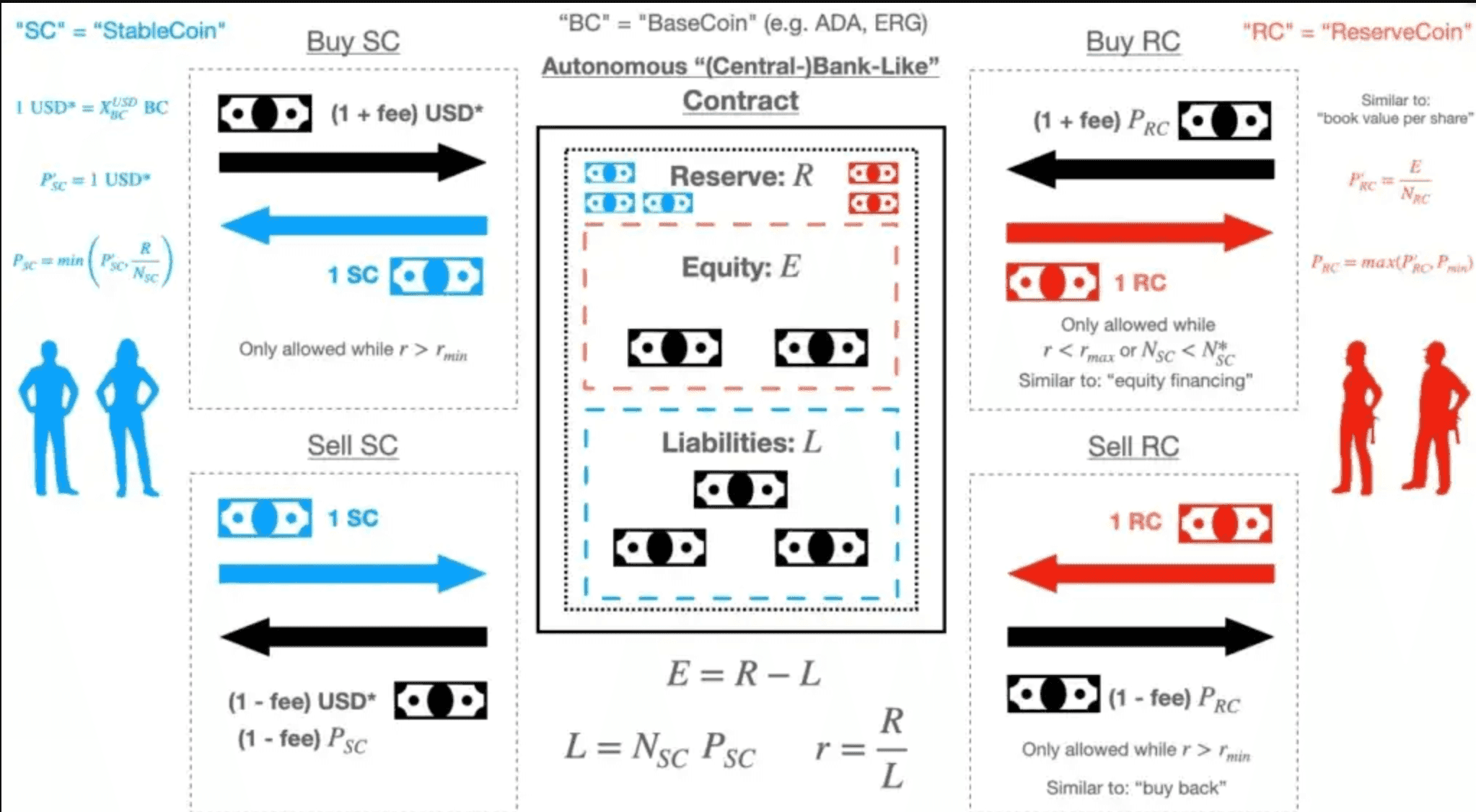 Djed can be used on other protocols as collateral or to provide liquidity. Empowa, another project on Cardano that allows local African housing developers to provide lease-to-own options for eco homes, accepts the stablecoin.
Djed can be used on other protocols as collateral or to provide liquidity. Empowa, another project on Cardano that allows local African housing developers to provide lease-to-own options for eco homes, accepts the stablecoin.
DeFi vs CeFi
DeFi and CeFi are two distinct approaches to crypto, with vocal proponents in both camps. Let's take a brief look to understand them better.
One can consider CeFi as an extension of TradFi in the crypto space. Many of the models that make up TradFi can be found in CeFi. This includes a single company with opaque record-keeping that is only available to permissioned parties, such as regulators, investors and internal staff. As a company, profits and the bottom line are very much a key component of the business. Just like conventional companies, they have a payroll and staff costs associated with running the business.
Trust in CeFi is often attained through regulation, compliance, reputation, track record, and multi-layer security. Centralised exchanges, which fall under CeFi, allow for fiat-to-crypto conversions and digital asset banking-style products, thus providing a valuable service in getting people onboard the crypto train. Therefore, it also deals with banks and other intermediaries so that they can offer services to the public.
Another service that CeFi offers is custodial services, which sits well with those who are more comfortable with someone holding their funds for them. Unlike banks that are usually insured in some form by the government for a certain amount, CeFi companies are not on the same level of accountability so the risk of them going rogue is a double-whammy. This is because not only are funds absconded, it's the severance of trust between the client and the entity that is fatal. However, in some cases, like Celsius, FTX and Mt Gox, there are legal avenues for customers to seek some form of compensation, long though it may take.  DeFi protocols rely heavily on smart contracts to execute all functionality on the platform. These smart contracts are automatic, immutable, transparent and auditable by security firms specialising in smart contract creation. This removes all the intermediaries usually involved in CeFi, thus lowering the cost of providing similar types of services to the user. All the transactions occur on-chain, meaning they are available for consumption in a public ledger that can be accessed by anyone.
DeFi protocols rely heavily on smart contracts to execute all functionality on the platform. These smart contracts are automatic, immutable, transparent and auditable by security firms specialising in smart contract creation. This removes all the intermediaries usually involved in CeFi, thus lowering the cost of providing similar types of services to the user. All the transactions occur on-chain, meaning they are available for consumption in a public ledger that can be accessed by anyone.
For those who want the responsibility of holding their own funds, DeFi is their preferred choice because these are non-custodial platforms. Users also do not need to provide any kind of personal identification or fill in any application form to access the services offered on DeFi. All one needs is a wallet to interact with the platform. These wallets are usually free or can easily be obtained without revealing any personal information.
DeFi typically has no management team to speak of. What they have is a governance model known as a DAO. This is a community-led initiative where the ones who are incentivised for the project to grow are usually the very users of the platform. Users holding governance tokens can propose proposals that are voted on by other token holders. Successful proposals are then implemented by the team, which is a more democratic process than centralised entities.
Due to the decentralised nature of DeFi protocols, there is no single governing agency that can hold the protocol accountable for any malicious behaviour occurring on its platform. A good example is Tornado Cash, a mixing service that allows the origins of funds to be obfuscated so that the funds cannot be traced back to a single source. Even though some of the users using the mixing service are up to no good, the operations are handled by smart contracts, which are lines of computer code. There is some debate as to whether the creators of the protocol should be held responsible, as the creators of Tornado Cash have been the targets of legal action. I am of the personal opinion that it's like asking the person who invented money to be responsible for money laundering activities.
Why Consider DeFi?
If you live in a country where the financial infrastructure is well set up, you might not have any particular incentive to incorporate DeFi into your realm of financial activity, simply because you have no need for it. You have creditworthiness that you've established with a single bank where you get your mortgage from.
If you have no problem obtaining loans through regular money-lending entities, you have no need to use DeFi to get a loan. If you're happy earning a small interest from your bank even though the mortgage interest you pay far outweighs the interest you're getting, you don't need to lend your money on DeFi protocols to earn a bigger interest but shoulder some risk at the same time.
However, if you are someone who has difficulty getting a loan after getting turned down for one reason or another even though you do have some collateral you can use to guarantee the loan, you might want to give DeFi borrowing a try. If you are interested in getting a higher rate of interest, you might be incentivised to do some research on which DeFi protocols can offer a good return that outperforms banking returns.
If you want to get on the property ladder but don't have enough for a down payment, you might be tempted to give fractional NFTs of real-world assets a try because at least, you can tell your friends that you are collecting rent from 1/16th of a property in New York. This can go towards growing your capital so that you can eventually buy a place of your own one day.





































