The Evolution of Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Journey Through Its Storied History
Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency that has reshaped the landscape of finance, emerged from the shadows of the 2008 financial crisis. Created by the mysterious and pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced a decentralized and borderless form of digital currency, challenging traditional financial systems. This article aims to provide a thorough exploration of Bitcoin's history, from its conceptualization to its current status as a global financial phenomenon.
I. Genesis of Bitcoin:
A. Satoshi Nakamoto's White Paper (2008):
The origin of Bitcoin can be traced back to a white paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," published by an unknown entity named Satoshi Nakamoto in October 2008. The paper outlined the conceptual framework for a decentralized digital currency that would operate on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks.
B. Mining the First Block (2009):
In January 2009, Nakamoto mined the first-ever block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the "genesis block" or "block 0." Embedded within this block was a reference to a headline from The Times newspaper, underscoring the intention of Bitcoin's creation as a response to the financial crisis.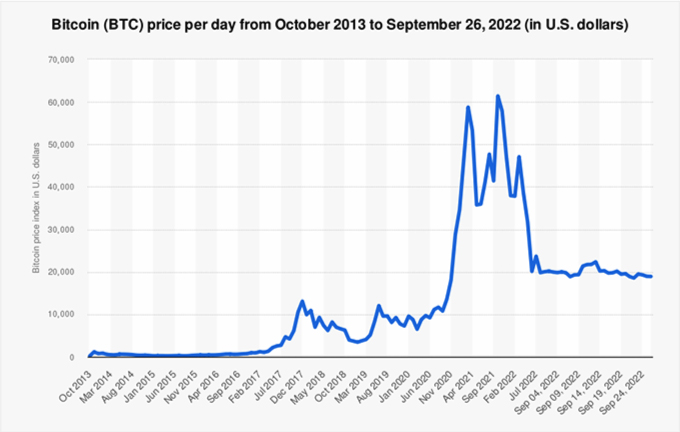
II. Early Days and Adoption:
A. Mining and the Halving:
In the early days, mining Bitcoin was relatively easy, and enthusiasts could mine substantial quantities using standard computers. The first recorded commercial transaction with Bitcoin occurred in May 2010 when Laszlo Hanyecz famously paid 10,000 BTC for two pizzas. As time progressed, Bitcoin's code introduced a mechanism known as "halving," reducing the reward for miners and increasing scarcity.
B. Silk Road and Regulatory Scrutiny:
Bitcoin's association with the Silk Road, an online marketplace for illegal goods, brought it into the spotlight in 2013. The subsequent government crackdown on the Silk Road highlighted the challenges and regulatory scrutiny faced by Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
III. Maturation and Mainstream Recognition:
A. Rise of Altcoins:
Bitcoin paved the way for the emergence of alternative cryptocurrencies, commonly referred to as altcoins. Litecoin, introduced in 2011, was one of the first notable altcoins, followed by a plethora of others aiming to improve upon Bitcoin's limitations.
B. Institutional Interest and Price Volatility:
Bitcoin's price experienced significant volatility during its early years, with remarkable price surges and corrections. The cryptocurrency captured the attention of institutional investors, leading to the creation of regulated cryptocurrency exchanges and the development of financial instruments like futures contracts.
IV. Bitcoin Scaling Debate:
A. Block Size Limit:
As Bitcoin gained popularity, a debate emerged within the community regarding the block size limit – the maximum size of each block in the blockchain. This debate, which lasted for several years, ultimately led to the creation of Bitcoin Cash, a fork of the original Bitcoin blockchain.
B. Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Lightning Network:
To address scalability issues, the Bitcoin community implemented Segregated Witness in 2017. This upgrade aimed to increase the transaction throughput by separating witness data from transaction data. Additionally, the Lightning Network, a second-layer scaling solution, gained traction as a way to facilitate faster and cheaper transactions.
V. Institutional Adoption and Regulatory Developments:
A. Bitcoin ETFs and Wall Street:
The approval of Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in various jurisdictions marked a significant step toward mainstream adoption. Institutional players, including major financial institutions and corporations, began expressing interest in Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class.
B. Regulatory Landscape:
The regulatory environment surrounding Bitcoin has evolved, with governments worldwide adopting diverse approaches. Some countries embraced and regulated Bitcoin, while others imposed restrictions or outright bans. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve as policymakers grapple with the implications of decentralized digital currencies.
VI. Current Landscape and Future Outlook:
A. Market Capitalization and Price Dynamics:
Bitcoin's market capitalization has grown exponentially, making it a significant player in the global financial markets. Price movements, influenced by factors such as macroeconomic trends, regulatory developments, and technological advancements, continue to shape the cryptocurrency's trajectory.
B. Technological Developments:
Ongoing technological developments, such as the integration of the Taproot upgrade in 2021, demonstrate the commitment of the Bitcoin development community to enhance the protocol's functionality and security.
C. Challenges and Opportunities:
Bitcoin faces challenges related to scalability, environmental concerns associated with mining, and the ongoing debate surrounding its role as a store of value or medium of exchange. However, it also presents opportunities for financial inclusion, innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi), and a reimagining of traditional financial systems.
In conclusion, the history of Bitcoin is an epic journey that transcends the realms of technology, finance, and societal paradigms. From its mysterious inception in the aftermath of the financial crisis to its present-day status as a global financial phenomenon, Bitcoin has evolved, adapted, and persevered. Its story encompasses technological breakthroughs, regulatory challenges, and the relentless pursuit of a decentralized and inclusive financial future.
As Bitcoin continues to mature, its impact on the world unfolds as a captivating narrative, full of challenges and possibilities. The cryptocurrency remains a symbol of financial sovereignty, challenging established norms and inspiring a new era of decentralized innovation. The Bitcoin saga, far from reaching its conclusion, is an ever-unfolding epic, promising a future where the principles of decentralization and inclusivity may redefine the foundations of the global financial landscape.









![[LIVE] Engage2Earn: McEwen boost for Rob Mitchell](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/c798d46f-d3b8-4a66-bf48-7e1ef50b4338/1)




![[ℕ𝕖𝕧𝕖𝕣] 𝕊𝕖𝕝𝕝 𝕐𝕠𝕦𝕣 𝔹𝕚𝕥𝕔𝕠𝕚𝕟 - Is Trump Dying? Or Only Killing The Market?](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/a129e75e-4fa1-46cc-80b6-04e638877e46/1)







