Evolving Elections in Nigeria: From Challenges to Digital Solutions for Free and Fair Elections.
Introduction:

The Unique Legacy of the June 12, 1993 Election:
The June 12, 1993 election stands out as a defining moment in Nigeria's electoral history. Led by Humphrey Nwosu, the Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC) introduced innovative voting methods, including the Option A4 voting system and the Open ballot system. 
The Story of MKO Abiola:

Transition to Closed Ballot System:
Following the turmoil of the June 12, 1993 election, Nigeria transitioned to a closed ballot system, aimed at addressing the shortcomings of previous methods. While this approach improved secrecy and reduced instances of voter intimidation, it still faced challenges such as ballot box snatching, result manipulation, and logistical issues.
Present-Day Method with BVAS:
In recent years, Nigeria has embraced technology in its electoral process, employing Biometric Voter Authentication Systems (BVAS) to verify voters' identities and prevent multiple voting. While BVAS has helped enhance the credibility and integrity of elections, it is not without its challenges, including technical glitches and security concerns.
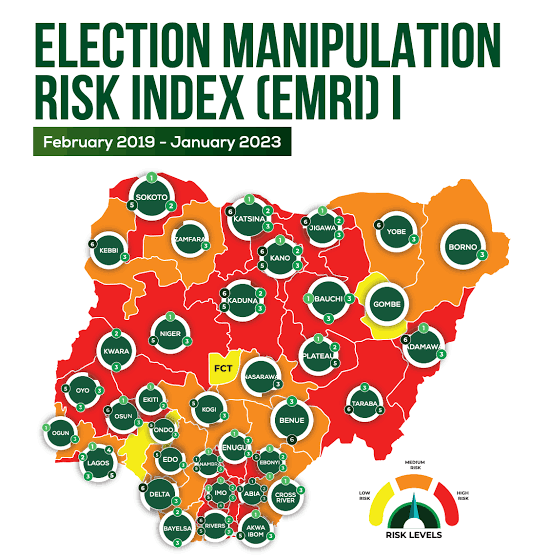
Challenges Associated with Traditional Methods:
The traditional methods of conducting elections in Nigeria have been marred by several issues, including but not limited to:
Voter Intimidation:
Instances of voter intimidation, coercion, and violence have been rampant, particularly in regions with political tensions.
Ballot Stuffing:
The manual nature of paper ballots has made them susceptible to manipulation, with reports of ballot stuffing and tampering.
Logistical Challenges:
Ensuring the timely distribution of election materials and the efficient management of polling stations has been a significant logistical hurdle.
Result Manipulation:
The manual counting and collation of votes have led to allegations of result manipulation and electoral fraud.
Proposing Digital Online Voting:
Digital online voting presents a viable solution to address the shortcomings of traditional election methods. By leveraging secure digital platforms and robust encryption technologies, online voting offers several advantages, including:
Enhanced Security:
Advanced encryption techniques and multi-factor authentication can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of votes, minimizing the risk of tampering and fraud.
Increased Accessibility:
Online voting can improve voter accessibility, allowing citizens to cast their ballots from the comfort of their homes or through designated voting centers, thereby reducing barriers to participation.
Real-time Results:
Digital online voting enables the instantaneous tabulation and publication of election results, eliminating the need for manual counting and reducing the likelihood of result manipulation.
Cost Savings:
By streamlining the electoral process and reducing the need for physical infrastructure, online voting can result in significant cost savings for electoral authorities.
Proposed Solution: Digital Online Voting
Digital online voting presents a promising solution to Nigeria's electoral challenges. By leveraging secure digital platforms and encryption technologies, online voting can enhance security, accessibility, transparency, and efficiency in the electoral process.
Countries like Estonia, Switzerland, and Canada have successfully implemented online voting, showcasing its feasibility and benefits.
Digital online voting offers a promising solution for Nigeria's electoral challenges, ensuring accessibility and participation across various demographics, including those in remote and extreme locations. Here's how digital online voting can be implemented to cater to the needs of different voter groups:
- Home Voting via Secure Online Platforms: Implement a secure online voting platform accessible through personal computers, tablets, or smartphones. Voters can log in using secure authentication methods such as biometric verification or two-factor authentication. They can then cast their votes from the comfort of their homes using their unique credentials.
- Established Online Voting Locations: Set up designated online voting centers in urban and rural areas with reliable internet access. These centers can be equipped with computers and internet connectivity, allowing voters without personal devices or internet access at home to cast their votes securely.
- Mobile Voting Apps: Develop mobile voting applications that are compatible with smartphones. These apps can be downloaded from official sources, and voters can use them to securely cast their votes from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Offline Voting Options: Implement offline voting options for voters in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. This can involve the use of electronic voting machines equipped with offline capabilities, where votes are stored securely and transmitted to central servers once an internet connection is available.
- Proxy Voting for Remote Areas: Introduce proxy voting options for voters in extremely remote locations who may face challenges accessing online voting platforms. Designated proxies, such as community leaders or election officials, can cast votes on behalf of eligible voters following a stringent verification process.
Examples from Other Countries: Several countries have successfully implemented digital online voting methods, catering to diverse populations and ensuring accessibility:
- Estonia: Estonia is a pioneer in digital online voting, offering secure online voting options since 2005. Estonian citizens can vote online using their national ID cards and secure authentication methods. The system has been praised for its reliability, security, and convenience.
- Switzerland: Switzerland has piloted online voting initiatives in select regions, allowing voters to cast their ballots securely through designated online platforms. The Swiss approach emphasizes transparency, integrity, and accessibility, ensuring that online voting complements traditional voting methods.
- Canada: Canada has explored online voting options in federal and municipal elections, offering voters the flexibility to cast their ballots remotely. Canadian online voting systems prioritize security and privacy, with robust authentication measures and encryption protocols in place to safeguard voter information.
By drawing on the experiences of these countries and leveraging advancements in technology, Nigeria can implement digital online voting solutions that cater to the needs of its diverse population, including those in remote and extreme locations. Through secure, accessible, and user-friendly online voting platforms, Nigeria can enhance electoral participation and ensure the integrity of its democratic process.
Conclusion:
The evolution of elections in Nigeria reflects the country's journey toward democracy and electoral integrity. From the innovative methods of the June 12, 1993 election to the present-day use of BVAS, each step has brought both challenges and progress. As Nigeria looks to the future, digital online voting offers an opportunity to further enhance electoral transparency, participation, and credibility, ensuring that the voices of the citizens are heard and respected.
References:
- "June 12: The Struggle for Power in Nigeria" by Adedeji Doherty.
- "MKO Abiola: The Biography of a Business Legend" by Dele Momodu.
- "Digital Democracy: The Impact of Technology on Elections" by Emily Rose.
- "Electronic Voting in Nigeria: Lessons from the US Experience" by Okey Nwankwo.
- "The Challenges of Electronic Voting Machines and the Prospects for Nigeria's Electoral System" by Chinedu Nwadike.
- "Digital Online Voting: A Comparative Analysis of International Practices" by Emily Rose.